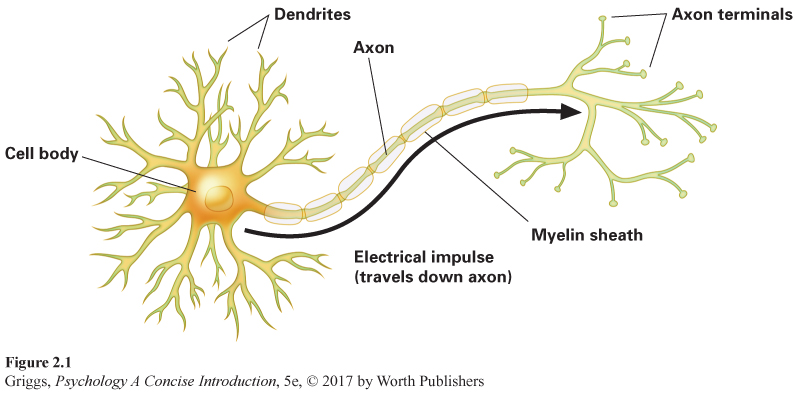
Figure 2.1 | The Structure of a Neuron | The three main parts of a neuron are the dendrites, cell body, and axon. The dendrites receive information from other neurons and pass it along to the cell body. The cell body decides whether the information should be passed on to other neurons. If it decides it should, then it does so by means of an electrical impulse that travels down the axon— the longer, thin fiber coming out of the cell body. The pictured neuron has a myelinated axon. Please note that there are periodic gaps where there is no myelin. The impulse jumps from one gap to the next down the axon. When the impulse reaches the axon terminals, it triggers chemical communication with other neurons.
[Leave] [Close]