The Changing American Population
As the technological revolution transformed the U.S. economy and society, an influx of immigrants began to alter the composition of the American population. Since passage of the Immigration Act of 1965, which repealed discriminatory national origins quotas established in 1924, the country had experienced a wave of immigration comparable to that at the turn of the twentieth century. As the population of the United States grew from 202 million to 300 million between 1970 and 2006, immigrants accounted for some 28 million of the increase. They came to the United States for much the same reasons as those arriving earlier: to seek economic opportunity and to find political and religious freedom.
Most newcomers in the 1980s and 1990s arrived from Latin America and South and East Asia. Relatively few Europeans (approximately 2 million) moved to the United States, though their numbers increased after the collapse of the Soviet empire in the early 1990s. Poverty and political unrest pushed migrants out of Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. At the beginning of the twenty-first century, Latinos (35 million) had surpassed African Americans (34 million) as the nation’s largest minority group. However, with the arrival of Caribbean and African immigrants, black America was also becoming more diverse.
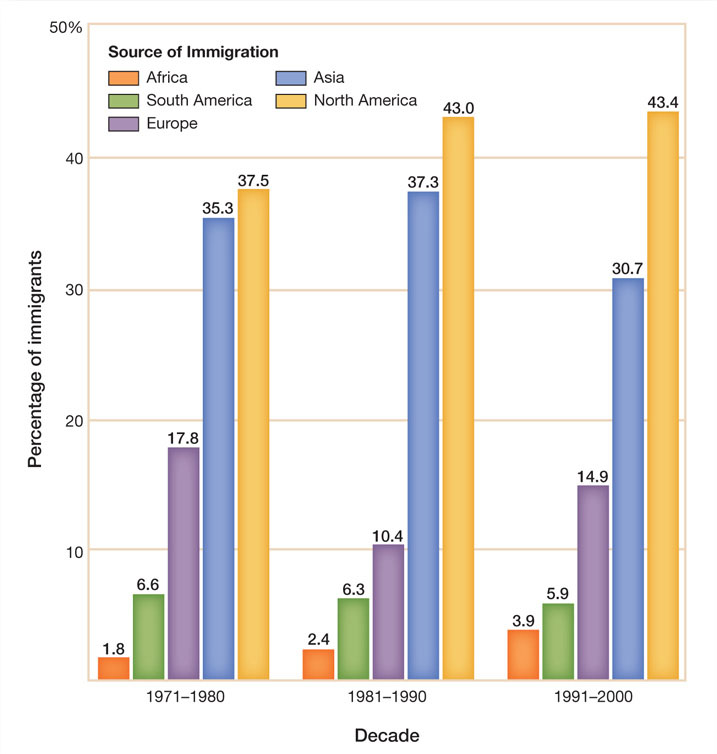
In addition to the 16 million immigrants who came from south of the U.S. border, another 9 million headed eastward from Asia, including Chinese, South Korean, and Filipinos, together with refugees from Vietnam and Cambodia. By 2010 an estimated 3.18 million Indians from South Asia lived in the United States, most arriving after the 1960s. Indian Americans became the third-largest Asian American group behind Chinese and Filipinos. Another 1 to 2 million people came from predominantly Islamic nations such as Pakistan, Lebanon, Iraq, and Iran (Figure 29.1).
Like their predecessors, new immigrants formed ethnic and religious enclaves. California displayed this fresh face of immigration most vividly. Latinos and Asians had long settled there, and by 2001, 27 percent of the state’s population was foreign-born. The majority of Californians consisted of Latinos, Asian Americans, and African Americans, with whites in the minority. In addition to California, immigrants also flocked to the Southwest and to northeastern and midwestern cities like New York City, Jersey City, Chicago, and Detroit. However, now they also fanned out across the Southeast, adding to the growing populations of Atlanta, Raleigh-Durham, Charlotte, Columbia, and Memphis and providing these cities with an unprecedented ethnic mixture. Like immigrants before them, they created their own businesses, spoke their own languages, and retained their own religious and cultural practices.
Explore
See Document 29.1 for one immigrant’s experience in low-wage factory work.
Immigrants also encountered hostility from many native-born Americans. Some workers felt threatened by newcomers who took jobs, both commercial and agricultural, at lower wages. Middle-class taxpayers complained that the flood of impoverished immigrants placed the burden on them to fund the social services—schools, welfare, public health—that the newcomers required. Some children and grandchildren of earlier immigrants had now assimilated into American culture and resented foreigners who pushed for bilingual education and signs and instructions in their native languages. Immigration critics also complained about the influx of illegal residents among the immigrant population.
California led the way in reacting to the effects of immigration. In 1986 Californians approved Proposition 63, which declared English to be the state’s official language. Thirty states passed similar laws. In 1994 California voters approved Proposition 187, which prohibited illegal residents from attending public schools and using any social services except emergency health facilities. This proposition never took effect because federal courts ruled it unconstitutional. Also, some conservative Republicans like President Ronald Reagan, former governor of California, along with agribusiness and other corporate interests that relied on cheap immigrant labor, opposed such severe measures.
REVIEW & RELATE
How did computers change life in the United States at the turn of the millennium?
How has globalization affected business consolidation and immigration in recent decades?
Exploring American HistoriesPrinted Page 968
Exploring American Histories Value EditionPrinted Page 716
Chapter Timeline