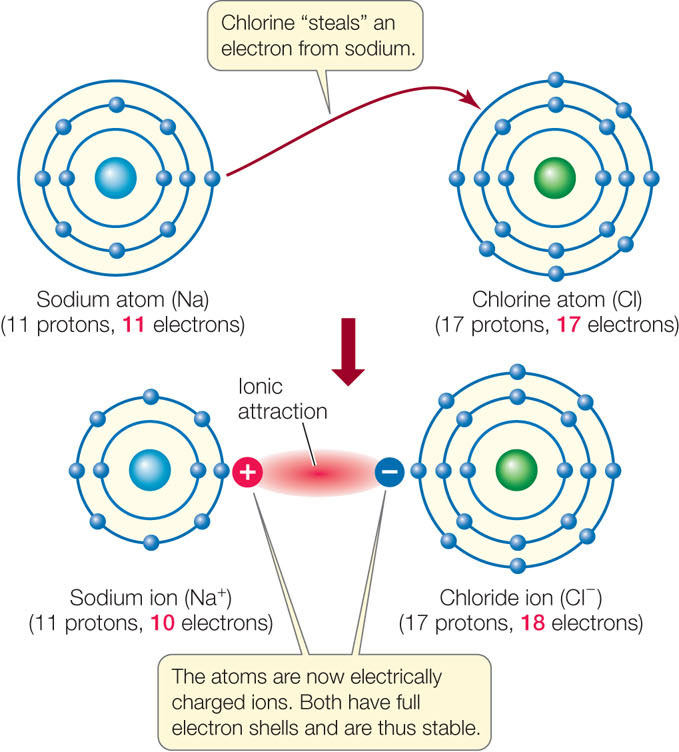
Figure 2.6: Ionic Attraction between Sodium and Chlorine When a sodium atom reacts with a chlorine atom, the chlorine fills its outermost shell by “stealing” an electron from the sodium. In so doing, the chlorine atom becomes a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl−). With one less electron, the sodium atom becomes a positively charged sodium ion (Na+).