CHAPTER SUMMARY
17.1 THE X AND Y CHROMOSOMES OF SOME ANIMALS, INCLUDING HUMANS, DETERMINE SEX AND ARE INHERITED DIFFERENTLY FROM THE AUTOSOMES.
- In humans and other mammals, XX individuals are female and XY individuals are male.
- The human X and Y chromosomes are different lengths and contain different genes, except for small regions of homology that allow the two chromosomes to pair in meiosis.
- Segregation of the X and Y chromosomes during male meiosis results in half of the sperm receiving an X chromosome and half a Y chromosome so that random union of gametes predicts a 1:1 female:male sex ratio at the time of fertilization.
17.2 X-LINKED GENES, WHICH SHOW A CRISSCROSS INHERITANCE PATTERN, PROVIDED THE FIRST EVIDENCE THAT GENES ARE PRESENT IN CHROMOSOMES.
- Morgan studied a mutation in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster that resulted in fruit flies with white eyes rather than normal red eyes. In this species, as in mammals, females are XX and males are XY.
- In a cross of a normal red-eyed female with a mutant white-eyed male, all of the male and female progeny had red eyes. When brothers and sisters of this cross were mated with each other, all of the females had red eyes, but males were red-eyed and white-eyed in a 1:1 ratio.
- This pattern of inheritance is observed because the gene Morgan studied, called white, is located in the X chromosome. The nonmutant w+ allele is dominant to the mutant w– allele, and the gene is present only in the X chromosome and not in the Y chromosome.
- X-linked genes show a crisscross inheritance pattern, in which the X chromosome with the mutant gene that is present in males in one generation is present in females in the next generation.
- Bridges observed rare fruit flies that did not follow the usual pattern for X-linked inheritance and inferred that these exceptional fruit flies resulted from nondisjunction, or failure of homologous chromosomes to segregate, in male or female meiosis. His observations provided evidence that genes are carried in chromosomes.
- In humans, X-linked inheritance shows a pattern in which affected individuals are almost always males, affected males have unaffected sons, and a female whose father is affected can have affected sons.
17.3 GENETIC LINKAGE OCCURS WHEN TWO GENES ARE SUFFICIENTLY CLOSE TOGETHER IN THE SAME CHROMOSOME THAT THE COMBINATION OF ALLELES PRESENT IN THE CHROMOSOME TENDS TO REMAIN TOGETHER IN INHERITANCE.
- Genes that are close together in the same chromosome are linked and do not undergo independent assortment.
- Recombinant chromosomes result from crossing over between genes on the same chromosome and show a nonparental combination of alleles.
- Nonrecombinant chromosomes have the same configuration of alleles as one of the parental chromosomes.
- In genetic mapping, the observed proportion of recombinant chromosomes is the frequency of recombination and can be used as a measure of distance along a chromosome. A recombination frequency of 1% is one map unit.
- Gene linkage and mapping are used to identify the locations of disease genes in the human genome.
17.4 MOST Y-LINKED GENES ARE PASSED FROM FATHER TO SON.
- In humans and other mammals, the Y chromosome contains a gene called SRY that results in male development.
- In Y-linked inheritance, only males are affected and all sons of an affected male are affected. Females are never affected and do not transmit the trait.
- Most Y-linked genes show complete linkage, which allows their evolutionary history to be traced.
17.5 MITOCHONDRIA AND CHLOROPLAST DNA FOLLOW THEIR OWN INHERITANCE PATTERN.
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own genomes, which reflect their evolutionary history as free-living prokaryotes.
- Mitochondria in humans and other mammals show maternal inheritance, in which individuals inherit their mitochondrial DNA from their mother.
- Because mitochondrial DNA does not undergo recombination and is maternally inherited, it can be used to trace human ancestry and migration.
Self-Assessment Question 1
Explain how the human X and Y chromosomes can pair during meiosis even though they are of different lengths and most of their genes are different.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
The X and Y chromosomes can pair during meiosis through regions of homology located near the tips of the chromosomal arms.
Self-Assessment Question 2
Describe the biological basis for the 1:1 ratio of males and females at conception in mammals.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Meiosis in the mammalian egg cell results in X-bearing eggs only. In contrast, meiosis in the sperm cell results in a 1:1 ratio of X-bearing and Y-bearing cells. Random fertilization of the egg results in a 1:1 ratio of female to male offspring.
Self-Assessment Question 3
For a recessive X-linked mutation, such as color blindness, draw and explain its pattern of inheritance through a set of crosses.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
See diagram.
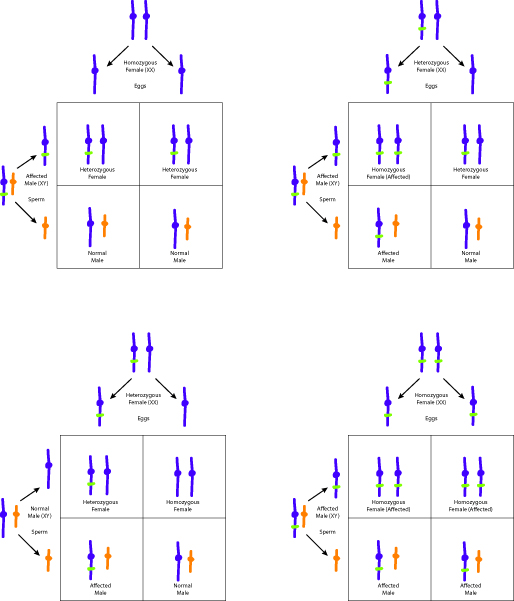
In the first cross, a homozygous normal female is crossed with an affected male; their resulting progeny are all of normal phenotype. In the second cross, a heterozygous female is crossed with an affected male; their resulting progeny are half affected phenotype and half normal phenotype. In the third cross, a heterozygous female is crossed with a normal male; their resulting progeny are ¾ normal phenotype and ¼ affected phenotype. In the fourth cross, a homozygous affected female is crossed with an affected male; their resulting progeny would be all affected.
Self-Assessment Question 4
Explain why linked genes do not exhibit independent assortment.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Linked genes do not exhibit independent assortment because they are located sufficiently close together on the same chromosome.
Self-Assessment Question 5
Describe how recombination frequency can be used to build a genetic map.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
The closer, or more tightly linked, that two genes are to each other, the smaller the frequency of recombination because it is less likely that a crossover event would take place in the interval between them. The further two genes are from each other the greater the frequency of recombination because there would be a greater chance that a crossover event would happen in the interval between the genes. The frequency of recombination can be used as a measure of distance between the genes.
Self-Assessment Question 6
Describe the pattern of inheritance expected from a Y-linked gene in a human pedigree.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
For a Y-linked gene, only males are affected with the trait. Females never inherit or transmit the trait, and all sons of affected males are affected. This is due to the fact that males get their Y chromosome from their father only.
Self-Assessment Question 7
Describe the pattern of inheritance expected from a gene present in mitochondrial DNA in a human pedigree.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
A gene present in mitochondrial DNA is transmitted from the egg cell (mother) to the offspring. Both males and females can show the trait, all offspring from an affected female show the trait and males never transmit the trait to their offspring.
Self-Assessment Question 8
Explain how Y-chromosome and mitochondrial DNA data can be used to trace ancestry.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Y-linked genes show complete linkage, and mitochondrial DNA does not undergo recombination and is maternally inherited. For these reasons, Y-linked and mitochondrial DNA are good traits to use when tracing ancestry.