Chapter 1.
Introduction
The Wittig reaction is one of the most widely used methods for forming carbon-carbon double bonds, because it is easy to carry out and often gives high yields of pure product. It is named after its discoverer, German chemist Georg Wittig.1 The reaction involves the addition of a phosphorus ylide to an aldehyde or ketone to form a double bond with the elimination of phosphine oxide.
1. Wittig, G. Pure & Appl. Chem.1964, 9, 245–254
Reaction

Lab Objective
To perform the Wittig reaction with a commercially available ylide (carbethoxymethylene)triphenylphosphorane and one of the three aldehydes (2-, 3-, or 4-chlorobenzaldehyde) below. The Wittig product should be characterized using Infrared spectroscopy, m.p. (if the product is a solid), and Thin Layer Chromatography.
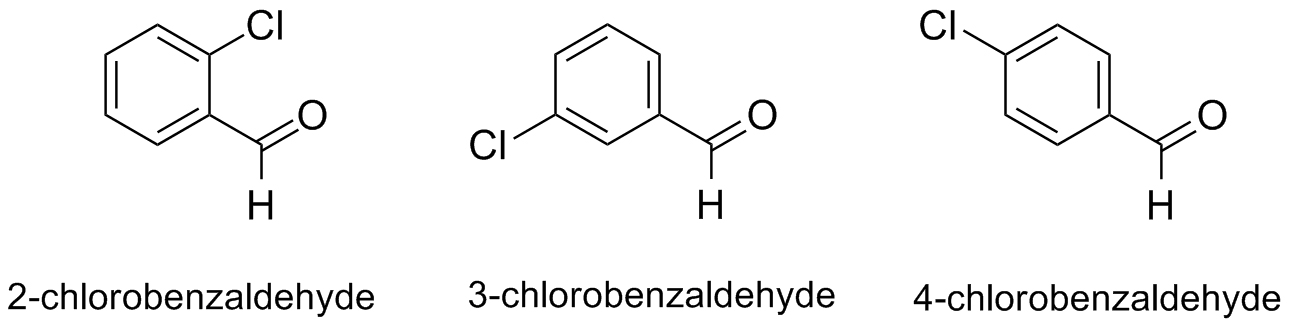
Procedure
Dissolve chlorobenzaldehyde (150 mg) in dichloromethane (8 mL) in a dram vial equipped with a stir vane. Add 1.5 mol equivalents of the ylide (mol. wt. 348.38 g/mol) portion-wise while stirring. Stir at room temperature for two hours while monitoring the reaction by TLC. When the reaction is complete evaporate the dichloromethane solvent with a stream of N2 gas and dissolve the reaction mixture in 25% diethyl ether in hexanes (3–5 mL). Note the formation of a white precipitate, which is triphenylphosphine oxide. Transfer the solution to a clean vial and evaporate the majority of the solvent. Purify the crude product using a microscale wet column. Group members will work together to modify the purification procedure as necessary based on the alternative solvent selected and to identify appropriate solvents for use in TLC and purification by microscale wet column chromatography.
Reagents
| Compound | CAS Number | mol. wt. (g mol-1) | Concentration or Density | m.p. or b.p. (°C) | SAFETY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-chlorobenzaldehyde | 89-98-5 | 140.57 | 1.248 g/mL | 209–215 (bp) | corrosive |
| 3-chlorobenzaldehyde | 587-04-2 | 140.57 | 1.241 g/mL | 213–214 (bp) | toxic |
| 4-chlorobenzaldehyde | 104-88-1 | 140.57 | -- | 213–214 (bp) | toxic |
| dichloromethane | 75-09-2 | 84.93 | 1.325 g/mL | 39.8–40 (bp) | health hazard |
| (carbethoxymethylene) triphenylphosphorane | 1099-45-2 | 348.37 | -- | 128–130 (mp) | -- |