15.8 Biomedical Therapies
KEY THEME
The biomedical therapies are medical treatments for the symptoms of psychological disorders and include medication and electroconvulsive therapy.
KEY QUESTIONS
What medications are used to treat the symptoms of schizophrenia, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder, and how do they achieve their effects?
What is electroconvulsive therapy, and what are its advantages and disadvantages?
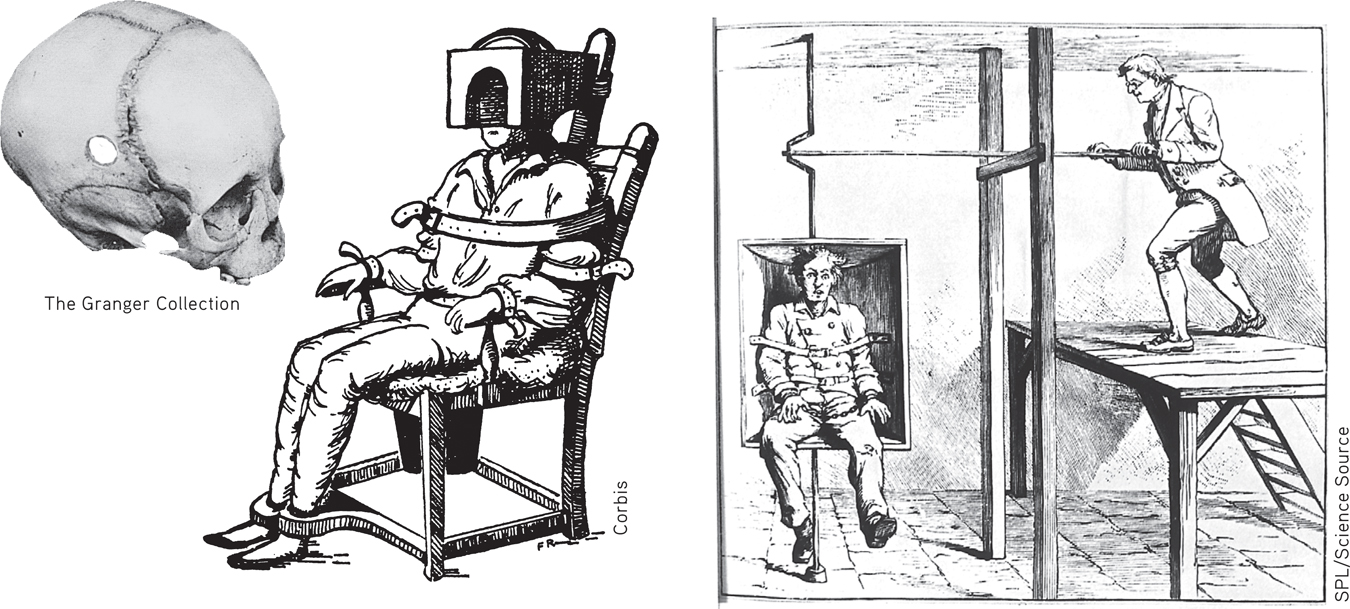
Medical treatments for psychological disorders actually predate modern psychotherapy by hundreds of years. In past centuries, patients were whirled, soothed, drenched, restrained, and isolated—all in an attempt to alleviate symptoms of psychological disorders. Today, such “treatments” seem cruel, inhumane, and useless. Keep in mind, however, that these early treatments were based on the limited medical knowledge of the time. As you’ll see in this section, some of the early efforts to treat psychological disorders did eventually evolve into treatments that are widely used today.
For the most part, it was not until the twentieth century that effective biomedical therapies were developed to treat the symptoms of mental disorders. Today, the most common biomedical therapy is the use of psychotropic medications—prescription drugs that alter mental functions and alleviate psychological symptoms. You can see how medications affect neurotransmitter functioning in the synapses between neurons in FIGURE 2.7 on page 52. Although often used alone, psychotropic medications are increasingly combined with psychotherapy (Kaut & Dickinson, 2007; Sudak, 2011).
psychotropic medications
(sy-ko-TRO-pick) Drugs that alter mental functions, alleviate psychological symptoms, and are used to treat psychological or mental disorders.
Antipsychotic Medications
For more than 2,000 years, traditional practitioners of medicine in India used an herb derived from the snakeroot plant to diminish the psychotic symptoms commonly associated with schizophrenia: hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thought processes (Bhatara & others, 1997). The same plant was used in traditional Japanese medicine to treat anxiety and restlessness (Jilek, 1993). In the 1930s, Indian physicians discovered that the herb was also helpful in the treatment of high blood pressure. They developed a synthetic version of the herb’s active ingredient, called reserpine.

Reserpine first came to the attention of American researchers as a potential treatment for high blood pressure. But it wasn’t until the early 1950s that American researchers became aware of research in India demonstrating the effectiveness of reserpine in treating schizophrenia (Frankenburg, 1994).
It was also during the 1950s that French scientists began investigating the psychoactive properties of another drug, called chlorpromazine. Like reserpine, chlorpromazine diminished the psychotic symptoms commonly seen in schizophrenia. Hence, reserpine and chlorpromazine were dubbed antipsychotic medications. Because chlorpromazine had fewer side effects than reserpine, it nudged out reserpine as the preferred medication for treating schizophrenia-related symptoms. Since then, chlorpromazine has been better known by its trade name, Thorazine, and is still used to treat psychotic symptoms. The antipsychotic drugs are also referred to as neuroleptic medications, or simply neuroleptics.
antipsychotic medications
(an-tee-sy-KAHT-ick or an-ty-sy-KAHT-ick) Prescription drugs that are used to reduce psychotic symptoms; frequently used in the treatment of schizophrenia; also called neuroleptics.
How do these drugs diminish psychotic symptoms? Reserpine and chlorpromazine act differently on the brain, but both drugs reduce levels of the neurotransmitter called dopamine. Since the development of these early drugs, more than 30 other antipsychotic medications have been developed (see TABLE 15.7). These antipsychotic medications also act on dopamine receptors in the brain (Abi-Dargham, 2004; Laruelle & others, 2003; Richtand & others, 2007).
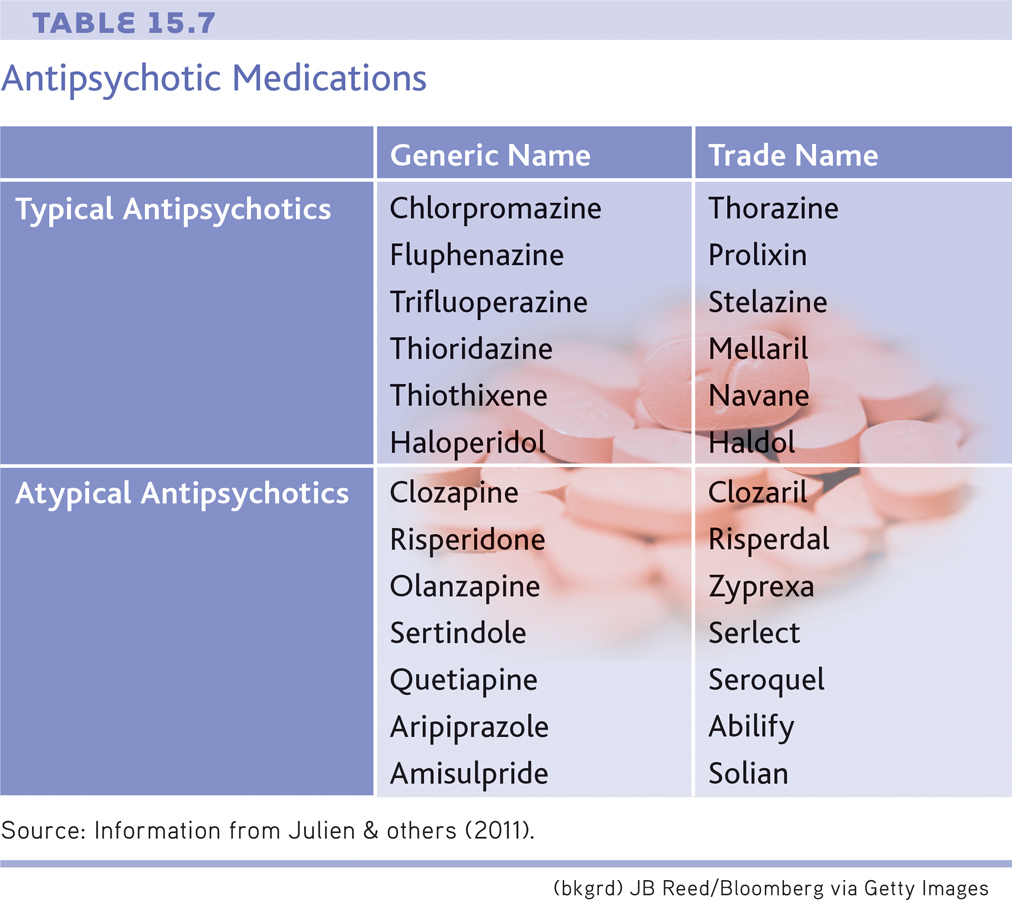
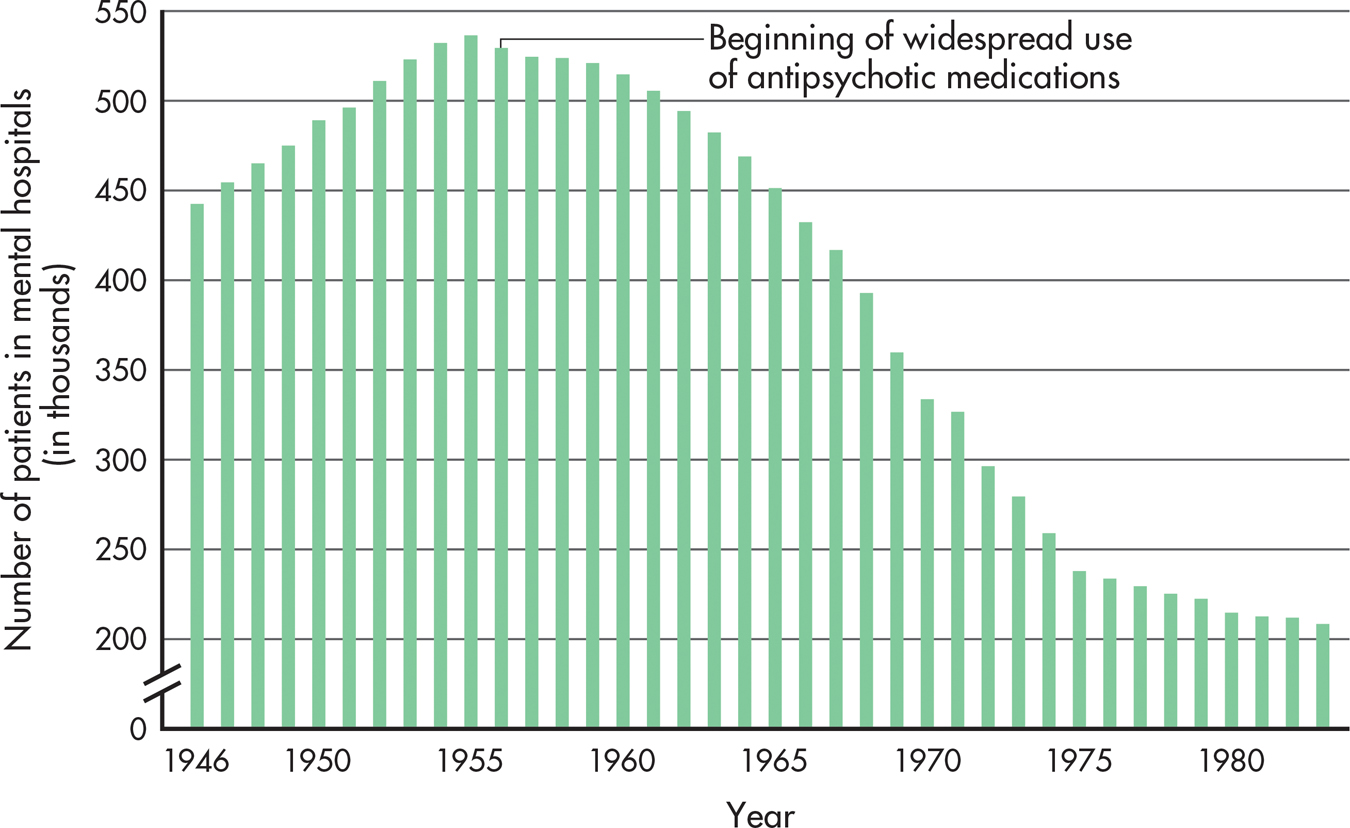
The first antipsychotics effectively reduced the positive symptoms of schizophrenia—hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking (see Chapter 14). This therapeutic effect had a revolutionary impact on the number of people hospitalized for schizophrenia. Until the 1950s, patients with schizophrenia were thought to be incurable. These chronic patients formed the bulk of the population in the “back wards” of psychiatric hospitals. With the introduction of the antipsychotic medications, however, the number of patients in mental hospitals decreased dramatically (see FIGURE 15.5).
Question 15.16
VSLyd7O6G9CVEmEGrkA8WpfQTZX/AhvZDm2H5vVjqme7aGoBGwEMMd8rIrWLcQ3lohDTfGTDcRjbmTa1ZB9tPEyU+cXDSHsBHyoXyTlsVLzrzdiLefKtfvx8pS7PyUhPAGlNT42LsXSyVHVhnV3QimaqCFGR08VfxX2pa3x+g2D7Wxb6rWiY+BB7ZfCaGbwBv6Vb18yFHdzhpVEm75WWVYtiD1RJQ6k792j9EUiU9TkuD6ZOCeaOpvO8SpS4KGdnrA6GWjVbKtWlCoI0F+OCm55r3mzT2aEsJKuJqXRd4eUESalSq9cTwQ==DRAWBACKS OF ANTIPSYCHOTIC MEDICATIONS
Even though the early antipsychotic drugs allowed thousands of patients to be discharged from hospitals, these drugs had a number of drawbacks. First, they didn’t actually cure schizophrenia. Psychotic symptoms often returned if a person stopped taking the medication.
Second, the early antipsychotic medications were not very effective in eliminating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia—social withdrawal, apathy, and lack of emotional expressiveness. In some cases, the drugs even made negative symptoms worse.
Third, the antipsychotics often produced unwanted side effects, such as dry mouth, weight gain, constipation, sleepiness, and poor concentration (Stahl, 2009).
Fourth, the fact that the early antipsychotics globally altered brain levels of dopamine turned out to be a double-edged sword. Dopamine pathways in the brain are involved not only in psychotic symptoms but also in normal motor movements. Consequently, the early antipsychotic medications could produce motor-related side effects—muscle tremors, rigid movements, a shuffling gait, and a masklike facial expression. This collection of side effects occurred so commonly that mental hospital staff members sometimes informally referred to it as the “Thorazine shuffle.”
Even more disturbing, the long-term use of antipsychotic medications causes a small percentage of people to develop a potentially irreversible motor disorder called tardive dyskinesia. Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by severe, uncontrollable facial tics and grimaces, chewing movements, and other involuntary movements of the lips, jaw, and tongue.
Closely tied to the various side effects of the first antipsychotic drugs is a fifth problem: the “revolving door” pattern of hospitalization, discharge, and rehospitalization. Schizophrenic patients, once stabilized by antipsychotic medication, were released from hospitals into the community. But because of either the medication’s unpleasant side effects or inadequate medical follow-up, or both, many patients eventually stopped taking the medication. When psychotic symptoms returned, the patients were rehospitalized.
THE ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
Beginning around 1990, a second generation of antipsychotic drugs began to be introduced. Called atypical antipsychotic medications, these drugs affect brain levels of dopamine and serotonin. The first atypical antipsychotics were clozapine and risperidone. More recent atypical antipsychotics include olanzapine, sertindole, and quetiapine.
atypical antipsychotic medications
Newer antipsychotic medications that, in contrast with the early antipsychotic drugs, block dopamine receptors in brain regions associated with psychotic symptoms rather than more globally throughout the brain, resulting in fewer side effects.
The atypical antipsychotics have several advantages over the older antipsychotic drugs (Julien & others, 2011). First, the new drugs are less likely to cause movement-related side effects. That’s because they do not block dopamine receptors in the movement areas of the brain. Instead, they more selectively target dopamine receptors in brain areas associated with psychotic symptoms. The atypical antipsychotics are also much more effective in treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia—apathy, social withdrawal, and flat emotions (Woo & others, 2009). Some patients who have not responded to the older antipsychotic drugs improve dramatically with the new medications (Turner & Stewart, 2006).
The atypical antipsychotic medications also appear to lessen the incidence of the “revolving door” pattern of hospitalization and rehospitalization. As compared to discharged patients taking the older antipsychotic medications, patients taking risperidone or olanzapine are much less likely to relapse and return to the hospital (Bhanji & others, 2004).
The atypical antipsychotic medications sparked considerable hope for better therapeutic effects, fewer adverse reactions, and greater patient compliance. Although they were less likely to cause movement-related side effects, the second-generation antipsychotics caused some of the same side effects as the first-generation antipsychotics, including weight gain and cardiac problems. The atypical antipsychotic medications are also associated with a sharply increased risk of developing diabetes, especially in patients younger than age 40 (Angell, 2011; Julien & others, 2011). Equally important, large-scale studies have demonstrated that the newer antipsychotic medications do not produce greater improvements than the older traditional antipsychotics (Crossley & others, 2010).
Antianxiety Medications
Anxiety that is intense and persistent can be disabling, interfering with a person’s ability to eat, sleep, and function. Antianxiety medications are prescribed to help people deal with the problems and symptoms associated with pathological anxiety (see TABLE 15.8).
antianxiety medications
Prescription drugs that are used to alleviate the symptoms of anxiety.
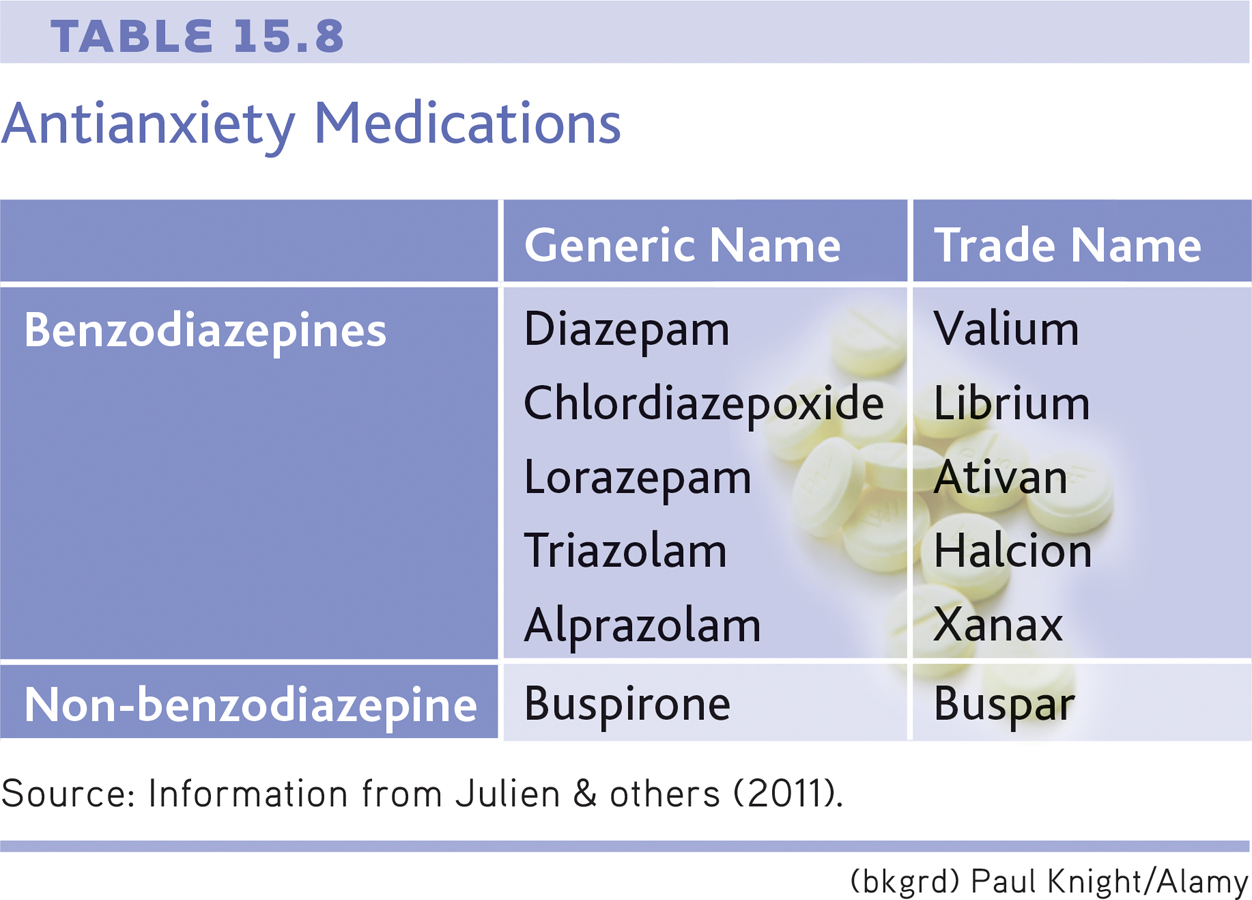
The best-known antianxiety drugs are the benzodiazepines, which include the trade-name drugs Valium and Xanax. These antianxiety medications calm jittery feelings, relax the muscles, and promote sleep. They used to go by the name “tranquilizers” because of this effect. They take effect rapidly, usually within an hour or so. In general, the benzodiazepines produce their effects by increasing the level of GABA, a neurotransmitter that inhibits the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain and slows brain activity (see Chapter 2).
Taken for a week or two, and in therapeutic doses, the benzodiazepines can effectively reduce anxiety levels. However, the benzodiazepines have several potentially dangerous side effects. First, they can reduce coordination, alertness, and reaction time. Second, their effects can be intensified when they are combined with alcohol and many other drugs, including over-the-counter antihistamines. Such a combination can produce severe drug intoxication, even death.
Third, the benzodiazepines can be physically addictive if taken in large quantities or over a long period of time. If physical dependence occurs, the person must withdraw from the drug gradually, as abrupt withdrawal can produce life-threatening symptoms. Because of their addictive potential, the benzodiazepines are less widely prescribed today.
An antianxiety drug with the trade name Buspar has fewer side effects. Buspar is not a benzodiazepine, and it does not affect the neurotransmitter GABA. In fact, exactly how Buspar works is unclear, but it is believed to affect brain dopamine and serotonin levels (Davidson & others, 2009). Regardless, Buspar relieves anxiety while allowing the individual to maintain normal alertness. It does not cause the drowsiness, sedation, and cognitive impairment that are associated with the benzodiazepines. And Buspar seems to have a very low risk of dependency and physical addiction.
However, Buspar has one major drawback: It must be taken for two to three weeks before anxiety is reduced. While this decreases Buspar’s potential for abuse, it also decreases its effectiveness for treating acute anxiety.
Another new medication that has been explored as a treatment for anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder is MDMA, short for methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Baldwin & others, 2014). MDMA is often called “ecstasy” when used as a recreational drug. There is growing evidence that a few doses of MDMA, prescribed and monitored by a physician, can improve the outcome for people undergoing behavioral therapy for these disorders (Johansen & Krebs, 2009). MDMA use can lead to dangerous or unpleasant side effects and has the potential for abuse. It is typically taken only a few times, however, diminishing the likelihood that this will occur (Meyer, 2013; Oehen & others, 2013). Despite the availability of newer treatment options for immediate, short-term relief from anxiety, the benzodiazepines are still regarded as the most effective medications currently available.
Lithium

In Chapter 14, on psychological disorders, we described bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression. The medication most commonly used to treat bipolar disorder is lithium, a naturally occurring substance. Lithium counteracts manic symptoms, and to a lesser degree depressive symptoms, in bipolar patients (Nivoli & others, 2010; Nivoli & others, 2012). Its effectiveness in treating bipolar disorder has been well established since the 1960s (Preston & others, 2008).
lithium
A naturally occurring substance that is used in the treatment of bipolar disorder.
As a treatment for bipolar disorder, lithium can prevent acute manic episodes over the course of a week or two. Once an acute manic episode is under control, the long-term use of lithium can help prevent relapses into either mania or major depressive disorder. The majority of patients with bipolar disorder respond well to lithium therapy. However, lithium doesn’t help everyone. Some people on lithium therapy experience relapses (Severus & others, 2009).
Like all other medications, lithium has potential side effects. If the lithium level is too low, manic symptoms persist. If it is too high, lithium poisoning may occur, with symptoms such as vomiting, muscle weakness, and reduced muscle coordination. Consequently, the patient’s lithium blood level must be carefully monitored.
How lithium works was once a complete mystery. Lithium’s action was especially puzzling because it prevented mood disturbances at the manic end of the emotional spectrum, and to some degree at the depressive end as well. It turns out that lithium affects levels of an excitatory neurotransmitter called glutamate, which is found in many areas of the brain. Apparently, lithium stabilizes the availability of glutamate within a narrow, normal range, preventing both abnormal highs and abnormal lows (Keck & McElroy, 2009; Malhi & others, 2013).
Bipolar disorder can also be treated with an anticonvulsant medicine called Depakote. Originally used to prevent epileptic seizures, Depakote seems to be especially helpful in treating those who rapidly cycle through bouts of bipolar disorder several times a year. It’s also useful for treating bipolar patients who do not respond to lithium (Davis & others, 2005).
Antidepressant Medications
The antidepressant medications counteract the classic symptoms of major depressive disorder—hopelessness, guilt, dejection, suicidal thoughts, difficulty concentrating, and disruptions in sleep, energy, appetite, and sexual desire. The first generation of antidepressants consists of two classes of drugs, called tricyclics and MAO inhibitors (see TABLE 15.9). Tricyclics and MAO inhibitors affect multiple neurotransmitter pathways in the brain. Evidence suggests that these medications alleviate major depressive disorder by increasing the availability of two key brain neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and serotonin. However, even though brain levels of norepinephrine and serotonin begin to rise within hours of taking a tricyclic or MAO inhibitor, it can take up to six weeks before depressive symptoms begin to lift (Thase & Denko, 2008).
antidepressant medications
Prescription drugs that are used to reduce the symptoms associated with major depressive disorder.
Antidepressant Medications
| Generic Name | Trade Name | |
|---|---|---|
| First-Generation Antidepressants | ||
| Tricyclic antidepressants | Imipramine Desipramine Amitriptyline |
Tofranil Norpramin Elavil |
| MAO inhibitors | Phenelzine Tranylcypromine |
Nardil Parnate |
| Second-Generation Antidepressants | Trazodone Bupropion |
Desyrel Wellbutrin |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | Fluoxetine Sertraline Paroxetine Fluvoxamine Citalopram Escitalopram |
Prozac Zoloft Paxil Luvox Celexa Lexapro |
| Dual-Action Antidepressants | Nefazodone Mirtazapine |
Serzone Remeron |
| Dual-Reuptake Inhibitors | Venlafaxine Duloxetine |
Effexor Cymbalta |
| Source: Information from Julien & others (2011). | ||
Tricyclics and MAO inhibitors can be effective in reducing depressive symptoms, but they can also produce numerous side effects (Holsboer, 2009). Tricyclics can cause weight gain, dizziness, dry mouth and eyes, and sedation. And, because tricyclics affect the cardiovascular system, an overdose can be fatal. As for the MAO inhibitors, they can interact with a chemical found in many foods, including cheese, smoked meats, and red wine. Eating these foods while taking an MAO inhibitor can result in dangerously high blood pressure, leading to stroke or even death.
The search for antidepressants with fewer side effects led to the development of the second generation of antidepressants. Second-generation antidepressants include trazodone and bupropion, trade name Wellbutrin. Wellbutrin, for example, is a dopamine-norepinephrine inhibitor that does not affect serotonin neurons (Julien & others, 2011). Although chemically different from the tricyclics, the second-generation antidepressants were generally no more effective than the first-generation ones, and they turned out to have many of the same side effects.
In 1987, the picture changed dramatically with the introduction of a third group of antidepressants, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, abbreviated SSRIs. Rather than acting on multiple neurotransmitter pathways, the SSRIs primarily affect the availability of a single neurotransmitter—serotonin. Compared with the earlier antidepressants, the new antidepressants act much more selectively in targeting specific serotonin pathways in the brain. The first SSRI to be released was fluoxetine, which is better known by its trade name, Prozac. Prozac was quickly followed by its chemical cousins, Zoloft and Paxil.
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Class of antidepressant medications that increase the availability of serotonin in the brain and cause fewer side effects than earlier antidepressants; they include Prozac, Paxil, and Zoloft.

Prozac was specifically designed to alleviate depressive symptoms with fewer side effects than earlier antidepressants. It achieved that goal with considerable success. Although no more effective than tricyclics or MAO inhibitors, Prozac and the other SSRI antidepressants tend to produce fewer, and milder, side effects. But no medication is risk-free. Among Prozac’s potential side effects are headaches, nervousness, difficulty sleeping, loss of appetite, and sexual dysfunction (Bresee & others, 2009).
Partly because of its relatively mild side-effects profile, Prozac quickly became very popular. By the early 1990s, an estimated 1 million prescriptions per month were being written for Prozac. By the late 1990s, Prozac had become the best-selling antidepressant in the world. Today, Prozac is available in generic form, greatly reducing its cost. In 2010, sales of antidepressants surpassed $11 billion a year in the United States alone (Hayes, 2011).
Since the original SSRIs were released, several new antidepressants have been developed, including Serzone and Remeron. These antidepressants, called dual-action antidepressants, also affect serotonin levels, but their mechanism is somewhat different from that of the SSRIs. Effexor and Cymbalta belong to another class of antidepressants, called dual-reuptake inhibitors, that affect levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine.
One promising new treatment is an experimental drug called ketamine (Larkin & Beautrais, 2011). As discussed in Chapter 4, ketamine is used in high doses as an anesthetic, and called Special K when sold as a street drug. In one study, 71% of severely depressed patients who received intravenous ketamine saw a decrease in depressive symptoms within just one day compared with 0% of those taking placebo (Zarate & others, 2006). There were some serious side effects from ketamine, such as hallucinations, but none that lasted more than two hours.
Despite its impressive effectiveness, ketamine is likely to be used only in emergency situations, in large part because its effects tend to last no more than a week. However, ketamine’s fast response time means that seriously depressed people who visit the ER might be able to forego inpatient treatment. During the time it takes for ketamine to wear off, more traditional antidepressants and psychotherapy might have time to start working. There also is evidence that the use of ketamine reduces suicide rates (DiazGranados & others, 2010).
Antidepressants are often used in the treatment of disorders other than depression, sometimes in combination with other drugs. For example, the SSRIs are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety disorders, obsessive–
With so many antidepressants available today, which should be prescribed? Many factors, including previous attempts with antidepressants, possible interactions with other medications, and personal tolerance of side effects, can influence this decision. Currently, medications are typically prescribed on a “trial-and-error” basis—people are prescribed different drugs or combinations of drugs in different dosages until they find the regimen that works for them. Thus, patients may need to try multiple medications before finding an effective treatment.
Think Like a SCIENTIST
How would a “party drug” end up being prescribed for depression? Go to LaunchPad: Resources to Think Like a Scientist about Ketamine.

Many researchers believe that genetic differences may explain why people respond so differently to antidepressants and other psychotropic medications (Crisafulli & others, 2011). The new field of pharmacogenetics is the study of how genes influence an individual’s response to drugs (Nurnberger, 2009). As this field advances, it may help overcome the trial-and-error nature of prescribing not only antidepressants, but other psychotropic medications as well.
How do antidepressants and psychotherapy compare in their effectiveness? Several large-scale studies have found that both cognitive therapy and interpersonal therapy are just as effective as antidepressant medication in producing remission from depressive symptoms (Imel & others, 2008; Thase & others, 2007). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy has also been shown to be as effective as antidepressant treatment in preventing relapse. Brain imaging studies are just beginning to show how such treatments might change brain activity—a topic that we showcase in the Focus on Neuroscience box below. Despite these findings, more people with depression are treated with antidepressants than with psychotherapy (Marcus & Olfson, 2010).
FOCUS ON NEUROSCIENCE
Psychotherapy and the Brain
As we discussed in Chapter 14, major depressive disorder is characterized by a variety of physical symptoms, including changes in brain activity (Abler & others, 2007; Kempton & others, 2011). Anti-depressants are assumed to work by changing brain chemistry and activity. Does psychotherapy have the same effect?
MYTH !rhtriangle! SCIENCE
Is it true that, for some disorders, psychotherapy and medications lead to similar changes in brain activity?
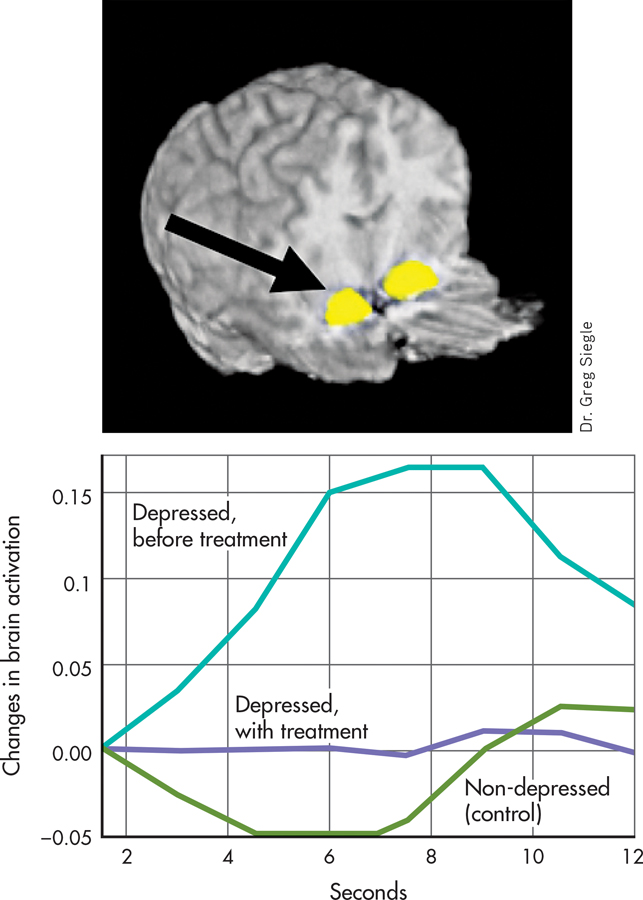
To address this question, fMRI scans were done on 27 people with major depressive disorder and compared to a matched group of 25 normal control subjects who were not depressed (Siegle & others, 2007). Compared with the nondepressed adults, the depressed individuals showed altered brain activity following an emotional task and a cognitive task. These tasks were chosen because major depressive disorder tends to affect both people’s emotional responses and their thought processes.
For the emotional task, both groups were asked to briefly view negative emotional words that they perceived to be relevant for them personally. The depressed people showed increased activity in the amygdala. The control group, made up of people who were not depressed, did not exhibit activity in the amygdala following this task. In addition, after completing a cognitive task in which they were asked to mentally sort a short list of numbers, depressed people showed less activity in the prefrontal cortex than did those in the control group.
A sample of nine of the depressed people in this study then completed fourteen weeks of cognitive therapy (DeRubeis & others, 2008). After treatment, the brain activity of the people treated for depression resembled that of the control group. The post-treatment brain scan shown here displays the activity in the amygdala in response to viewing the negative emotional word “ugly” for people in the control group or for people treated for depression. The graph highlights the differences among these two groups and a third group, people who have not yet been treated for depression. People who do not suffer from depression are indicated in green; people with depression who have not been treated are indicated in turquoise; and people with depression who have been treated with cognitive therapy are indicated in purple. There is increased brain activation only among the second group, the depressed people before treatment.
Interestingly, the changes in brain activation that result from psychotherapy are similar to changes that result from medications. For example, in a study of people with major depressive disorder, PET scans revealed that patients who took the antidepressant Paxil and patients who completed interpersonal therapy (discussed earlier in this chapter) showed a trend toward more normalized brain functioning (Brody & others, 2001). Activity declined significantly in brain regions that had shown abnormally high activity before treatment began. Similar results were found in a study comparing a different antidepressant, Effexor, and a different type of psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (Kennedy & others, 2007).
As these findings emphasize, psychotherapy—and not just antidepressant medication—affects brain chemistry and functioning. Such effects are not limited to depression. Similar changes toward a more normal pattern of brain functioning have also been found in people with panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, obsessive–
CRITICAL THINKING
Do Antidepressants Work Better Than Placebos?
Are antidepressants just fancy placebos? Consider this statement by psychologist Irving Kirsch on a 2012 episode of the TV news show 60 Minutes: “The difference between the effect of the placebo and the effect of an antidepressant is minimal for most people.” Interviewer Lesley Stahl was astounded: “So, you’re saying if they took a sugar pill, they’d have the same effect?”
Kirsch’s surprising statement is based on meta-analyses (Fournier & others, 2010; Kirsch & others, 2008). As discussed in Chapter 1, a meta-analysis combines the results of many studies into a single analysis. The meta-analyses to which Kirsch referred included all studies, published and unpublished, that had been submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration during the process of approval for new antidepressants. It is important that they included unpublished studies because unpublished studies are more likely than published studies to have found no difference between the placebo and the antidepressant. This is because journal editors tend to prefer publishing articles that found some difference rather than articles that found no difference (Turner, 2013).
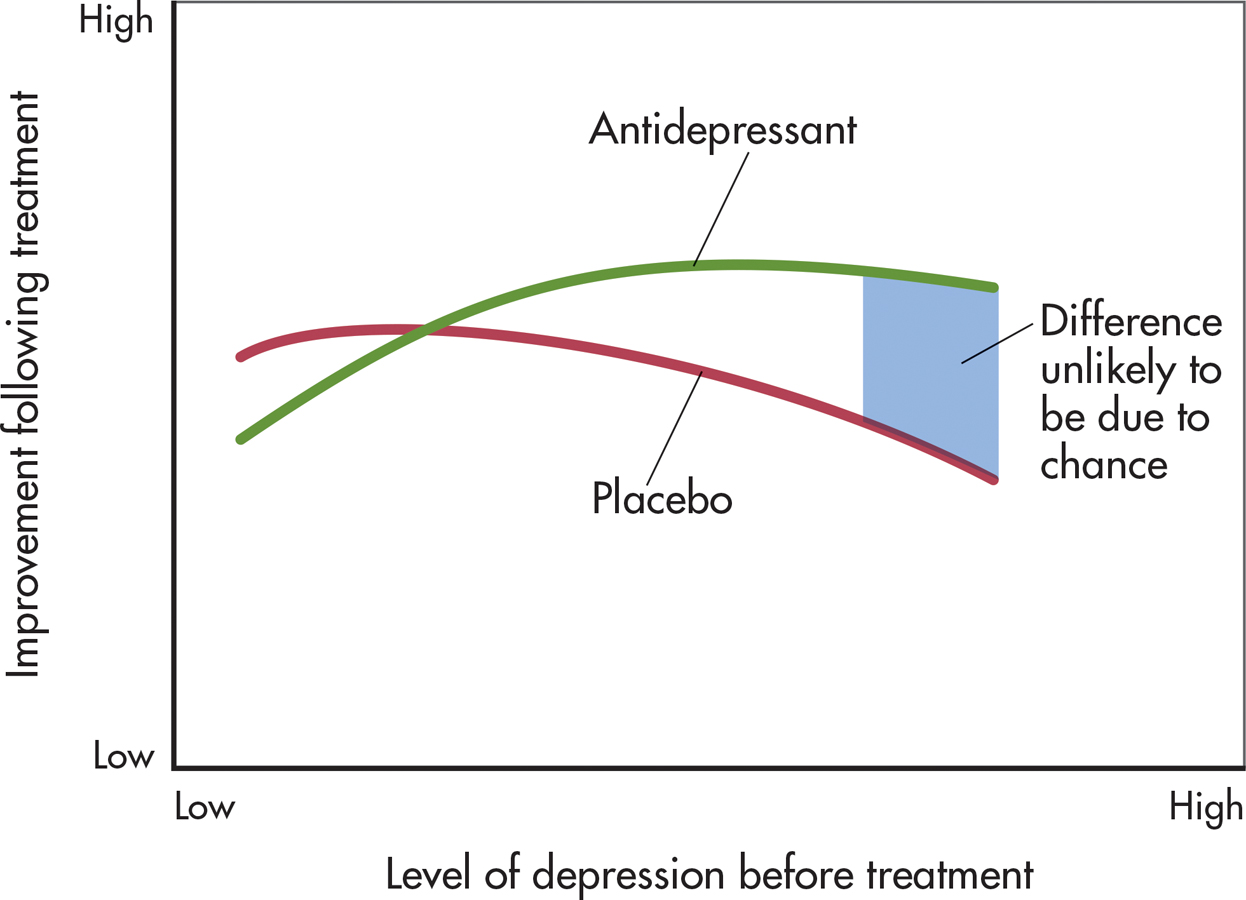
Kirsch and his colleagues found that most patients improved with either antidepressants or placebos (see graph). Antidepressants were found to work better than placebos for some patients—but only those with very high levels of depression, the area shown in blue. Except in that area, the difference between the lines could have simply occurred by chance. Overall, according to Kirsch and his colleagues, about 80% of the improvement from antidepressants seems to be due to a placebo effect.
The placebo effect, as discussed in Chapter 1 on pages 28–
You may now be thinking that the placebo effect means that any improvements are just imaginary. But as described in Chapter 13 on page 544, brain imaging shows that placebos lead to real biological changes (Meissner & others, 2011). In response to a placebo, patients with Parkinson’s disease experience increased dopamine activation, pain patients saw less neural activity in the parts of the brain associated with pain, and depressed patients experienced metabolic increases in the same parts of the brain that respond to antidepressants (Price & others, 2008). Even better, improvements tend to come without the side effects and potentially high costs of “real” medication.
MYTH !lhtriangle! SCIENCE
Is it true that antidepressants are a much more effective treatment than placebos for the vast majority of cases of depression?
Kirsch argues that we should question whether it’s worth the risk of giving a “real” drug when a placebo is just as effective for some people. But this may be a hard sell to physicians and patients who believe that antidepressants are the most effective treatment for depression. Other researchers view the pharmaceutical industry, which has immense resources, as contributing to exaggerated reports of the effects of medications (Cuijpers & others, 2010). Pharmaceutical companies have billions of dollars at stake in convincing physicians and patients that their medications are effective, and they spend more than $25 billion each year just in the United States marketing their drugs (Kornfield & others, 2013).
While acknowledging concerns about the influence of the pharmaceutical industry, other researchers have found that antidepressants are superior to placebos. Using different statistical methods, several researchers identified a subset of about 20% of patients who benefited from antidepressants over placebos at all levels of depression severity (Horder & others, 2011; Thase & others, 2011). But even these researchers don’t entirely dispute Kirsch’s findings.
As more is known about the effects of placebos, there is more discussion about how to harness their power. Researchers suggest that clinicians should receive training on ethical ways to openly and successfully prescribe placebos by educating patients about their effectiveness (Brody & Miller, 2011). In the past, clinicians believed that successful treatment with placebos required that the patients believe the placebo was real, but recent research questions this premise. One study on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) observed improvement in patients even after they were told they were receiving “placebo pills made of an inert substance, like sugar pills, that have been shown in clinical studies to produce significant improvement in IBS symptoms through mind–
Research on the placebo effect continues to accumulate. However, despite Kirsch’s argument, it’s important to remember that many people have been and continue to be helped by antidepressant medication. Other treatment options, such as psychotherapy, may be unavailable. So, if antidepressants are helping you, you should continue to take them as directed by your physician. It can be dangerous to stop taking antidepressant medications without guidance from a physician.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS
Why do you think studies that found differences are more likely to be published than studies that found no differences?
What is the ethical problem with giving a patient a placebo and saying it is an antidepressant?
Why might simply giving a patient a placebo openly not work without additional education?
Electroconvulsive Therapy
As we have just seen, millions of prescriptions are written for antidepressant medications in the United States every year. In contrast, a much smaller number of patients receive electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, as a medical treatment for severe cases of major depressive disorder. Also known as electroshock therapy or shock therapy, electroconvulsive therapy involves using a brief burst of electric current to induce a seizure in the brain, much like an epileptic seizure. Although ECT is most commonly used to treat major depressive disorder, it is occasionally used to treat mania, schizophrenia, and other severe mental disorders (Nahas & Anderson, 2011).
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
A biomedical therapy used primarily in the treatment of major depressive disorder that involves electrically inducing a brief brain seizure; also called electroshock therapy.
ECT is a relatively simple and quick medical procedure, usually performed in a hospital. The patient lies on a table. Electrodes are placed on one or both of the patient’s temples, and the patient is given a short-term, light anesthetic and muscle-relaxing drugs. To ensure adequate airflow, a breathing tube is sometimes placed in the patient’s throat.
While the patient is unconscious, a split-second burst of electricity induces a seizure. The seizure lasts for about a minute. Outwardly, the seizure typically produces mild muscle tremors. After the anesthesia wears off and the patient wakes up, confusion and disorientation may be present for a few hours. Some patients experience a temporary or permanent memory loss for the events leading up to the treatment. To treat major depressive disorder, the patient typically receives two to three treatments per week for two to seven weeks, with less frequent follow-up treatments for several additional months (Fink, 2009).
In the short term, ECT is a very effective treatment for severe cases of major depressive disorder: About 80 percent of patients improve (Rasmussen, 2009). ECT also relieves the symptoms of depression very quickly, typically within days. And as the symptoms of depression decrease, ECT patients’ quality of life tends to increase to a level similar to that in people without depression (McCall & others, 2013). Because of its rapid therapeutic effects, ECT can be a lifesaving procedure for extremely suicidal or severely depressed patients (Nahas & Anderson, 2011). Such patients may not survive for the several weeks it takes for antidepressant drugs to alleviate symptoms.
MYTH !lhtriangle! SCIENCE
Is it true that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), once called “shock therapy,” causes permanent brain damage and memory loss?
Typically, ECT is used only after other forms of treatment, including both psychotherapy and medication, have failed to help the patient, especially when depressive symptoms are severe. For some people, such as elderly individuals, ECT may be less dangerous than antidepressant drugs. In general, the complication rate from ECT is very low.
Nevertheless, inducing a brain seizure is not a matter to be taken lightly. ECT has potential dangers. Serious cognitive impairments can occur, such as extensive amnesia and disturbances in language and verbal abilities. However, fears that ECT might produce brain damage have not been confirmed by research (Eschweiler & others, 2007; McDonald & others, 2009).
Perhaps ECT’s biggest drawback is that its antidepressive effects can be short-lived. Relapses within four months are relatively common (Glass, 2001). About half the patients treated for major depressive disorder experience a relapse within six months. Today, patients are often treated with long-term antidepressant medication following ECT, which reduces the relapse rate (McCall & others, 2011). In severe, recurrent cases of major depressive disorder, ECT may also be periodically readministered to prevent the return of depressive symptoms.
At this point, you may be wondering why ECT is not in wider use. The reason is that ECT is considered controversial (Dukart & others, 2014; Shorter, 2009). Not everyone agrees that ECT is either safe or effective.
Some have been quite outspoken against it, arguing that its safety and effectiveness are not as great as its supporters have claimed (Andre, 2009). The controversy over ECT is tied to its portrayal in popular media over time. The use of ECT declined drastically in the 1960s and 1970s when it was depicted in many popular books and movies, including One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest, as a brutal treatment with debilitating side effects (Swartz, 2009). Its use has increased greatly since that time, especially in the past decade or two, with ECT now available in most major metropolitan areas in the United States (Shorter, 2009).
How does ECT work? Despite many decades of research, it’s still not known exactly why electrically inducing a convulsion relieves the symptoms of major depressive disorder (Michael, 2009). One theory is that ECT seizures may somehow “reboot” the brain by depleting and then replacing important neurotransmitters (Swartz, 2009).
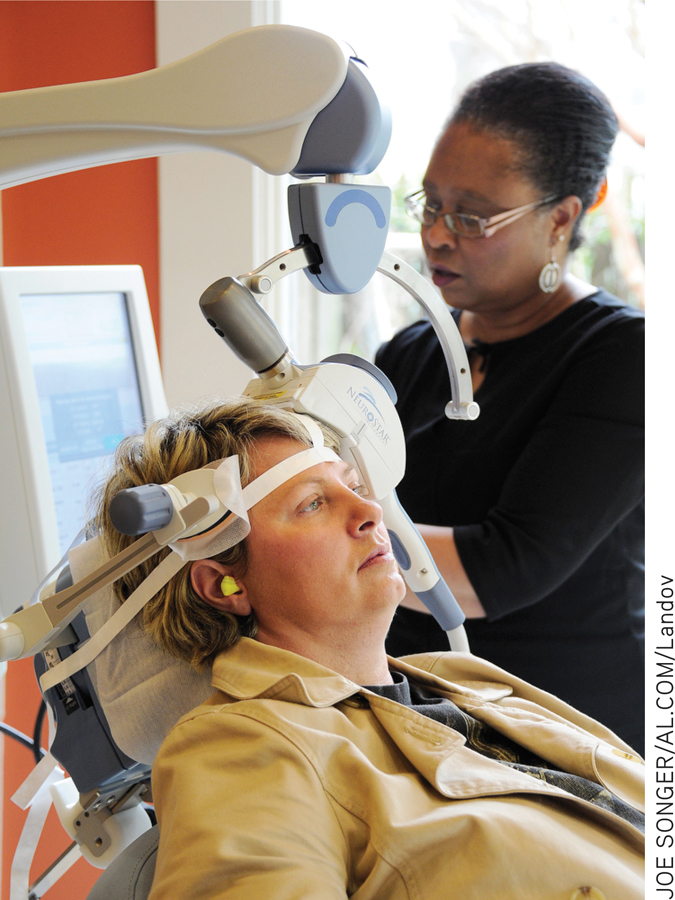
Some new, experimental treatments suggest that those seizures may not actually be necessary. That is, it may be possible to provide lower levels of electrical current to the brain than traditional ECT delivers and still reduce severe symptoms of depression and other mental illnesses. For example, transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is similar to ECT, but uses a small fraction of the electricity (Brunoni & others, 2012). Another, related treatment is transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), which involves stimulation of certain regions of the brain with magnetic pulses of various frequencies. Unlike ECT, both tDCS and TMS require no anesthetic, induce no seizures, and can be conducted in a private doctor’s office rather than a hospital (Janicak & others, 2010; Rosenberg & Dannon, 2009).
Yet another experimental treatment, vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), involves the surgical implantation of a device about the size of a pacemaker into the left chest wall. The device provides brief, intermittent electrical stimulation to the left vagus nerve, which runs through the neck and connects to the brain stem (McClintock & others, 2009). Finally, deep brain stimulation (DBS) utilizes electrodes surgically implanted in the brain and a battery-powered neurostimulator surgically implanted in the chest. Wires under the skin connect the two implants, and the neurostimulator sends electrical signals to the brain (Fink, 2009; Schläpfer & Bewernick, 2009).
Keep in mind that tDCS, TMS, VNS, and DBS are still experimental. And like ECT, the specific mechanism by which they may work is not entirely clear. Still, researchers are hopeful that these techniques will provide additional viable treatment options for people suffering from severe psychological symptoms (McDonald & others, 2009).
Question 15.17
NYcPVu/6neu904dB/sbnPgJTg2ptyw+1QU0FyoCRpAuvHsUCXPzz4jXyKf3SPOWAvEGLHxj+45iMvGRVHYLkoTRouE6qUpCORDnmyMp4/hy6CUGuWnwBhc3f/dcfgyzUFdEAE7toDG61HaUw2wneZJaCAsIvy9KAAaEUe2ml+PrD1HnK1qxZc7x+p04v8rl0Rep7w0KuVKrujlOR2EgmiqU9BElmLOzSvjlEV9Qii78qWyXWqD635dMve19RqbOwk7pY3d2p14yc5qvpoKva3BewmjqVZk31yoU8Z0cwuAU8nY9+f8n9VNJPWdV6WARj5Taz251YRgI3GB/rAZJI6sTEPHgFtW3FeE4PGDQKUPgE0wCuCONCEPT REVIEW 15.3
Biomedical Therapies
Match each description below with one of the following treatments: (a) atypical antipsychotic medications, (b) antipsychotic medications, (c) antidepressant medications, (d) ECT, (e) antianxiety medications, (f) lithium.
ECT
lithium
antipsychotic medications
antianxiety medications
atypical antipsychotic medications
antidepressant medications
lithium
Question 15.18
| 1. | ____ Medication that stabilizes the availability of the neurotransmitter called glutamate. |
Question 15.19
| 2. | ____ A category of psychotropic drugs that includes SSRIs and MAO inhibitors. |
Question 15.20
| 3. | ____ Drugs that are effective in reducing positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. |
Question 15.21
| 4. | ____ Drugs that produce their effects by increasing brain levels of GABA. |
Question 15.22
| 5. | ____ Drugs that globally reduce dopamine levels in the brain. |
Question 15.23
| 6. | ____ Used in the treatment of bipolar disorder. |
Question 15.24
| 7. | ____ Controversial biomedical therapy that induces a brief brain seizure. |
Test your understanding of Biomedical Therapies with
 .
.
Closing Thoughts
As you’ve seen throughout this chapter, a wide range of therapies is available to help people who are troubled by psychological symptoms and disorders. Like our friend Marcia, whose story we told in the Prologue, many people benefit psychologically from psychotherapy. As the first part of the chapter showed, psychotherapy can help people by providing insight, developing more effective behaviors and coping strategies, and changing thought patterns.
The biomedical therapies, discussed in the second part of the chapter, can also help people with psychological problems. This was also true in Marcia’s case, when she reluctantly agreed to try an antidepressant medication. For almost a year, Marcia took a low dose of one of the SSRI antidepressant medications. It helped in the short term, lessening the feelings of depression and anxiety and giving her time to work through various issues in therapy and develop greater psychological resilience. Today, people are increasingly being helped by a combination of psychotherapy and one of the psychotropic medications.
As our discussion of the effectiveness of psychotherapy has shown, characteristics of both the therapist and the client are important to the success of psychotherapy. In the Psych for Your Life section at the end of this chapter, we describe the attitudes that should be brought to the therapeutic relationship, discuss some general ground rules of psychotherapy, and dispel some common misunderstandings. The Psych for Your Life section will help you understand the nature of the therapeutic relationship and provide information useful to anyone who may be considering entering psychotherapy.
