Strands of nucleic acids hybridize to complementary sequences
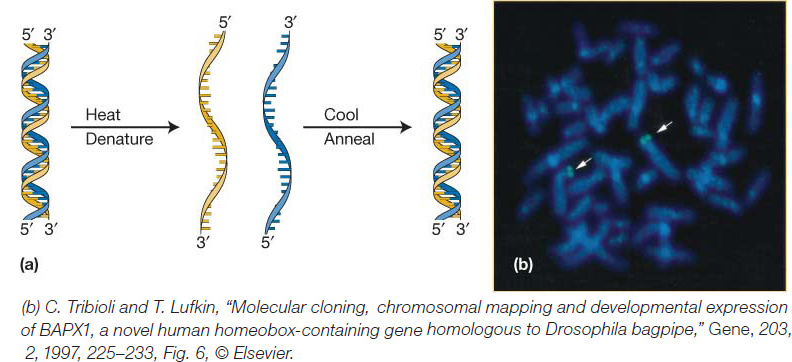
Figure 1-13: (a) The two strands of the DNA double helix can be dissociated by heat in aqueous solutions. Upon cooling under controlled conditions, strands reassociate, or hybridize, with their complement. (b) A cloned copy of the human BAPX1 gene was tagged with a green fluorescent dye. The fluorescent- tagged DNA was then denatured and allowed to hybridize to the chromosomes in a single cell. The fluorescent- tagged clone hybridized to the location on chromosome 4 (green fluorescent regions) where the gene is located.
[(b) C. Tribioliand T. Lufkin, “Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping and developmental expression of BAPX1, a novel human homeobox- containing gene homologous to Drosophila bagpipe,” Gene, 203, 2, 1997, 225- 233, Fig. 6, © Elsevier .
[Leave] [Close]