Using fine mapping to identify a gene
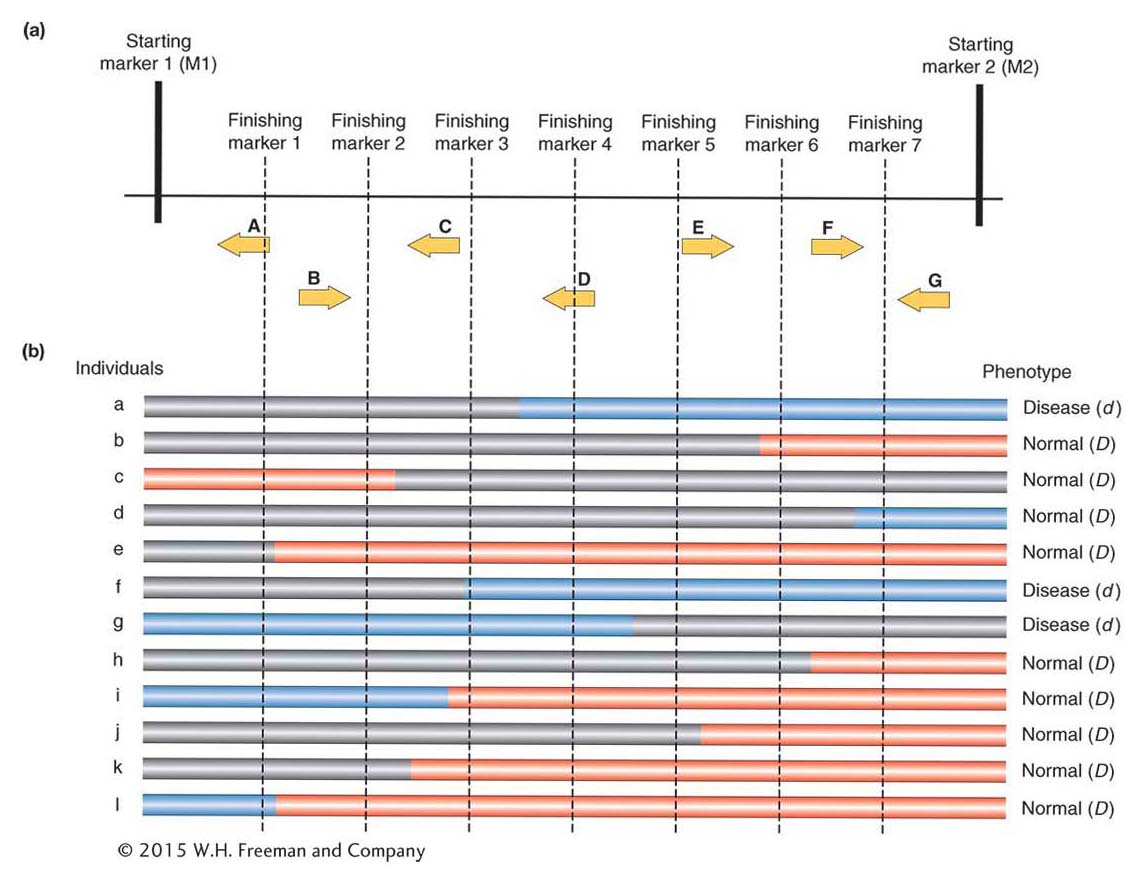
Figure 10-20: A modern gene hunt uses markers and sequences obtained from online databases to determine the genotypes within a region of DNA for large numbers of individuals with and without the disease trait. The individuals shown here were derived from the F2 progeny in Figure 10-21. The target gene is the gene allele shared by all with the disease, gene D. Red is homozygous for the dominant D allele of Parent 1 (normal); blue is homozygous for the recessive d allele of Parent 2 (disease, mutant); gray is heterozygous.
[Leave] [Close]