RNA polymerase contacts the promoter at specific sequences
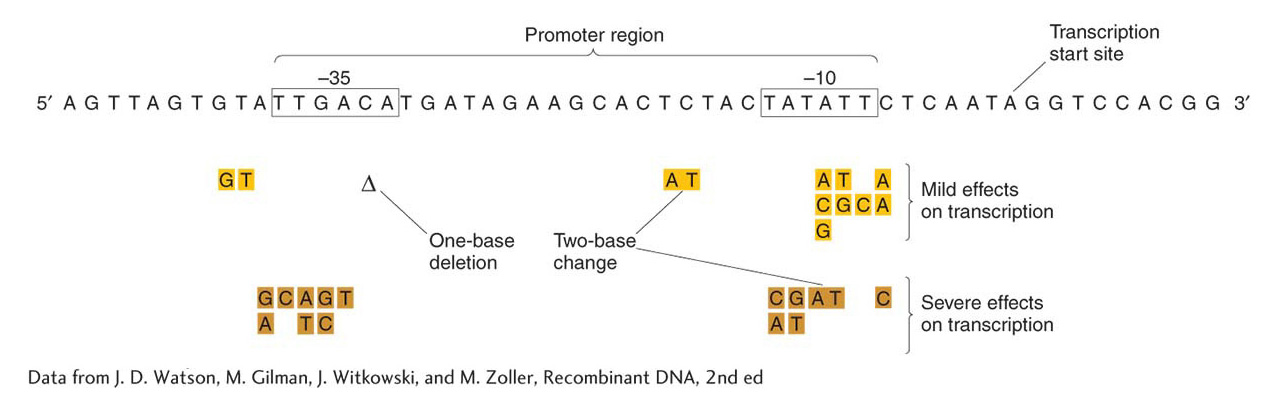
Figure 11-11: Specific DNA sequences are important for the efficient transcription of E. coli genes by RNA polymerase. Only the non- template strand is shown here (see Figure 8- 4). Transcription would proceed from left to right (5′ to 3′), and the mRNA transcript would be homologous to the sequence shown. The boxed sequences are highly conserved in all E. coli promoters, an indication of their role as contact sites on the DNA for RNA polymerase binding, and contacts are made with both strands (not shown). Mutations in these regions have mild (gold) and severe (brown) effects on transcription. The mutations may be changes of single nucleotides or pairs of nucleotides, or a deletion (Δ) may occur.
[Data from J. D. Watson, M. Gilman, J. Witkowski, and M. Zoller, Recombinant DNA, 2nd ed.]
[Leave] [Close]