The structure of DNA
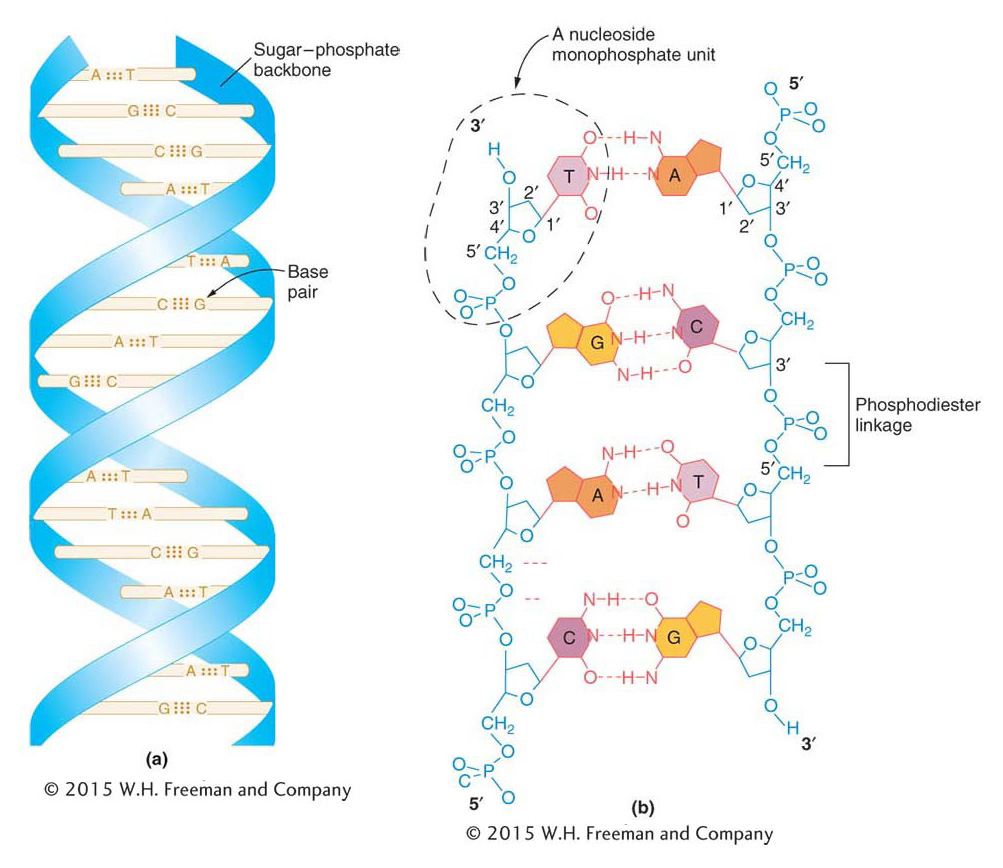
Figure 7-8: (a) A simplified model showing the helical structure of DNA. The sticks represent base pairs, and the ribbons represent the sugar– phosphate backbones of the two antiparallel chains. (b) An accurate chemical diagram of the DNA double helix, unrolled to show the sugar– phosphate backbones (blue) and base- pair rungs (purple, orange). The backbones run in opposite directions; the 5′ and 3′ ends are named for the orientation of the 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of the sugar rings. Each base pair has one purine base, adenine (A) or guanine (G), and one pyrimidine base, thymine (T) or cytosine (C), connected by hydrogen bonds (red dashed lines).
[Leave] [Close]