Chapter 20
9. The three principles are (1) individuals within any one population vary from one another, (2) offspring resemble their parents more than they resemble unrelated individuals, and (3) some forms are more successful at surviving and reproducing than other forms in a given environment.
11. The relative rate of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions would not be higher than expected in a globin pseudogene because a pseudogene is inactive and has no function to be preserved.
13. A population will not differentiate from other populations by local inbreeding if:
μ ≥ 1/N
and so
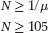
17. When amino acid changes have been driven by positive adaptive selection, there should be an excess of nonsynonymous changes. The MC1R gene (melanocortin 1 receptor) encodes a key protein controlling the amount of melanin in skin and hair. Asian and European populations appear to have experienced positive adaptive selection for more lightly pigmented skin relative to their African counterparts.
19. Noncoding sequences. A major constraint on gene evolution comprises the potential pleiotropic effects of mutations in coding regions. These effects can be circumvented by mutations in regulatory sequences, which play a major role in the evolution of body form. Changes in noncoding sequences provide a mechanism for altering one aspect of gene expression while preserving the role of pleiotropic proteins in other essential developmental processes.
21.
The HbS mutation has arisen independently in five different haplotypes in different regions and then increased to high frequency.
Two independent lines of bacteriophage evolved the ability to reproduce at high temperatures in a new host.
23. A new gene duplicate can (1) evolve a new function, (2) become inactivated, or (3) perform part of the original function, sharing full function with the original gene.
25. For polymorphic sites with a species, let nonsynonymous = a and synonymous = b. For polymorphic sites between the species, let nonsynonymous = c and synonymous = d. If divergence is due to neutral evolution, then
a/b = c/d
If divergence is due to selection, then
a/b < c/d
However, in this example, a/b = 20/50 > c/d = 2/18, which fits neither expectation. Because the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous polymorphisms (a/b) is relatively high, the gene being studied may encode a protein tolerant of relatively fewer species differences. The relatively fewer species differences may suggest that speciation was a recent event so new polymorphisms have been fixed in one species that are not variants in the other.