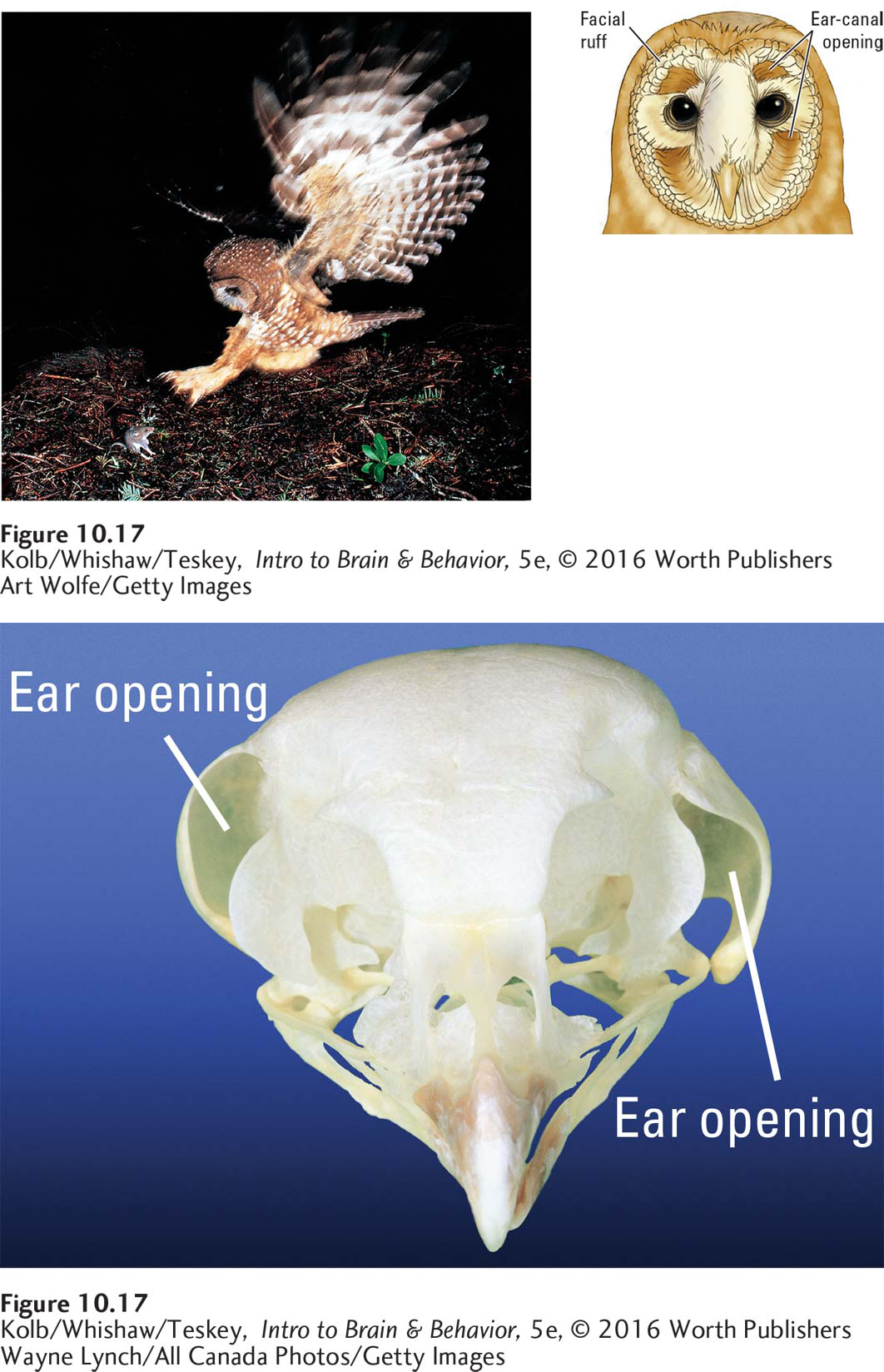
FIGURE 10- t-
Art Wolfe/Getty Images
Wayne Lynch/All Canada Photos/Getty Images
Wayne Lynch/All Canada Photos/Getty Images