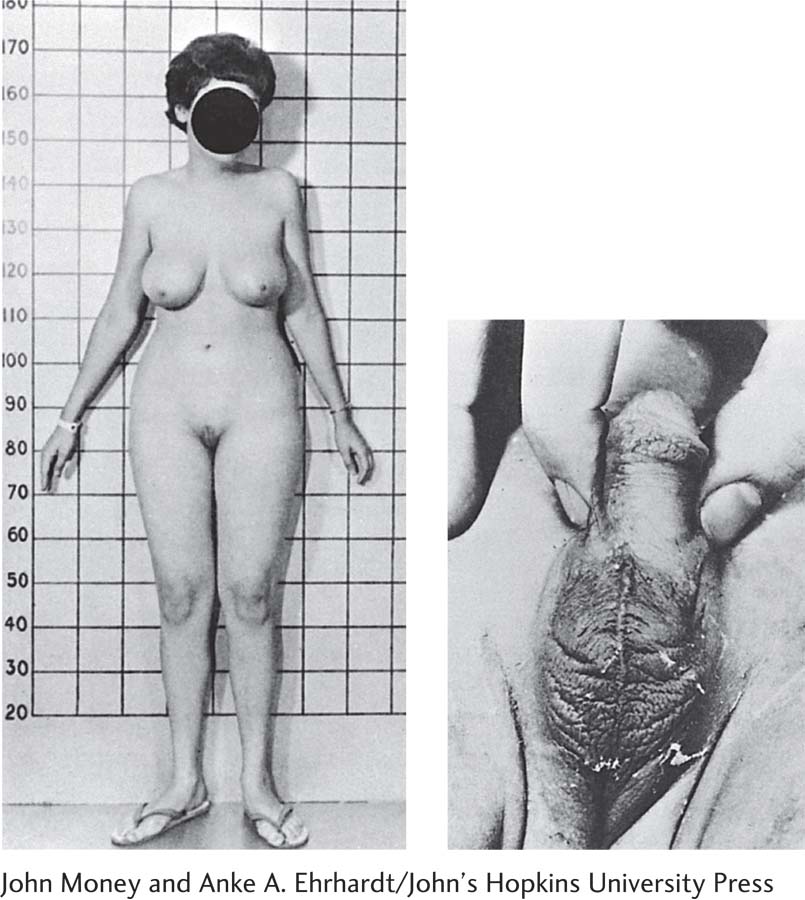
Left: In androgen insensitivity syndrome, a genetic male (XY) is insensitive to gonadal androgens but remains sensitive to estrogens, which leads to the development of a female phenotype. Right: In congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a genetic female (XX) is exposed to androgens produced by the adrenal gland embryonically, which leads to the partial development of male external genitalia.
Reprinted from J. Money & A. A. Ehrhardt (1972). Man and Woman, Boy and Girl (p. 116). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
John Money and Anke A. Ehrhardt/John’s Hopkins University Press
John Money and Anke A. Ehrhardt/John’s Hopkins University Press