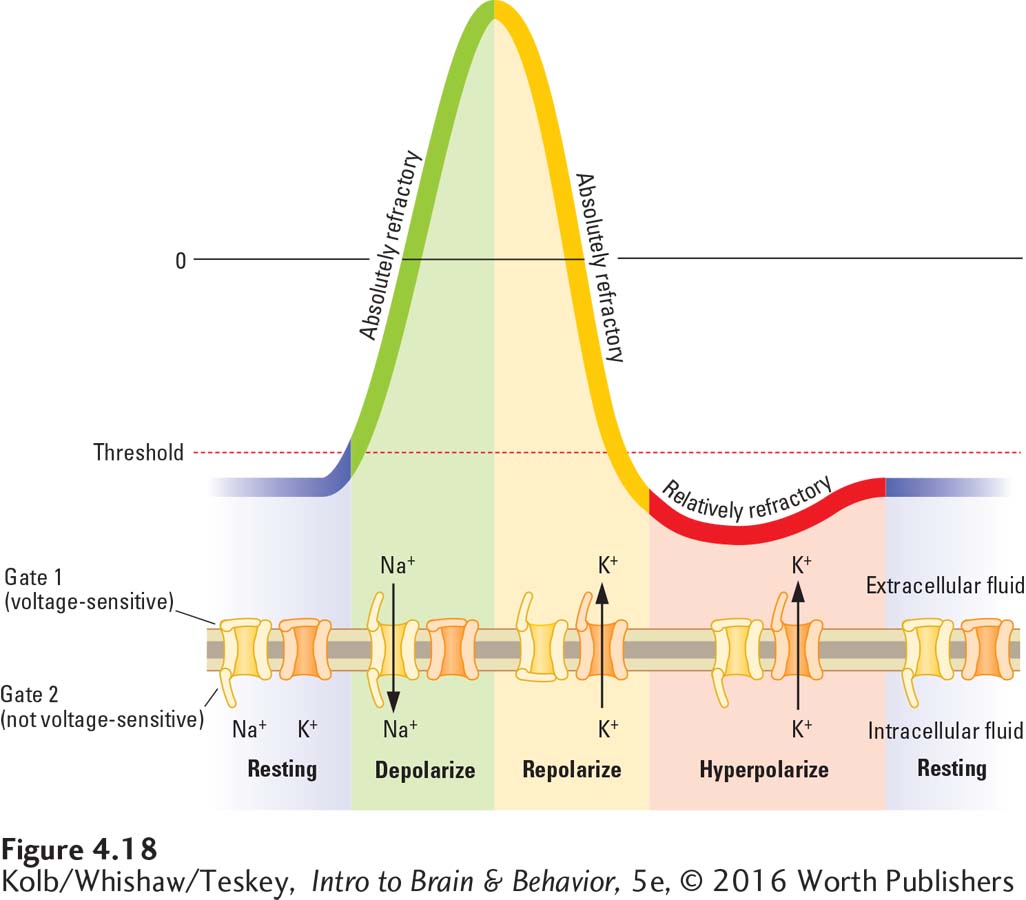
FIGURE 4- 18 Phases of an Action Potential Initiated by changes in voltage- sensitive sodium and potassium channels, an action potential begins with a depolarization: gate 1 of the sodium channel opens and then gate 2 closes. The slower- opening potassium channel gate contributes to repolarization and hyperpolarization until the resting membrane potential is restored.