| Figure 50.4 | Changing the Quantity Lowers Total Surplus |
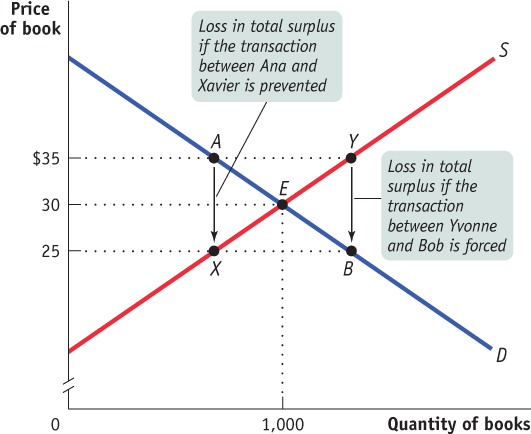
Changing the Quantity Lowers Total SurplusIf Xavier (point X) were prevented from selling his book to someone like Ana (point A), total surplus would fall by $10, the difference between Ana’s willingness to pay ($35) and Xavier’s cost ($25). This means that total surplus falls whenever fewer than 1,000 books— the equilibrium quantity— are transacted. Likewise, if Yvonne (point Y) were compelled to sell her book to someone like Bob (point B), total surplus would also fall by $10, the difference between Yvonne’s cost ($35) and Bob’s willingness to pay ($25). This means that total surplus falls whenever more than 1,000 books are transacted. These two examples show that at market equilibrium, all mutually beneficial transactions— and only mutually beneficial transactions— occur.
[Leave] [Close]