| Figure 62.2 | Unregulated and Regulated Natural Monopoly |
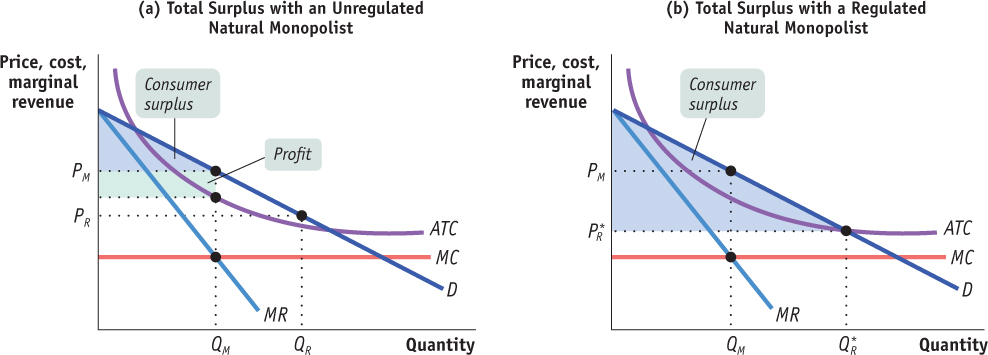
Unregulated and Regulated Natural MonopolyThis figure shows the case of a natural monopolist. In panel (a), if the monopolist is allowed to charge PM, it makes a profit, shown by the green area; consumer surplus is shown by the blue area. If it is regulated and must charge the lower price, PR, output increases from QM to QR and consumer surplus increases. Panel (b) shows what happens when the monopolist must charge a price equal to average total cost, the price P*R. Output expands to Q*R, and consumer surplus is now the entire blue area. The monopolist makes zero profit. This is the greatest total surplus possible without the monopoly incurring losses.
[Leave] [Close]