Printed Page 310(cont.)
Check Your Understanding
Question
Assume that there is an increase in the demand for money at every interest rate. Using a diagram, show what effect this will have on the equilibrium interest rate for a given money supply.
In the accompanying diagram, the increase in the demand for money is shown as a rightward shift of the money demand curve, from MD1 to MD2 . This raises the equilibrium interest rate from r1 to r2.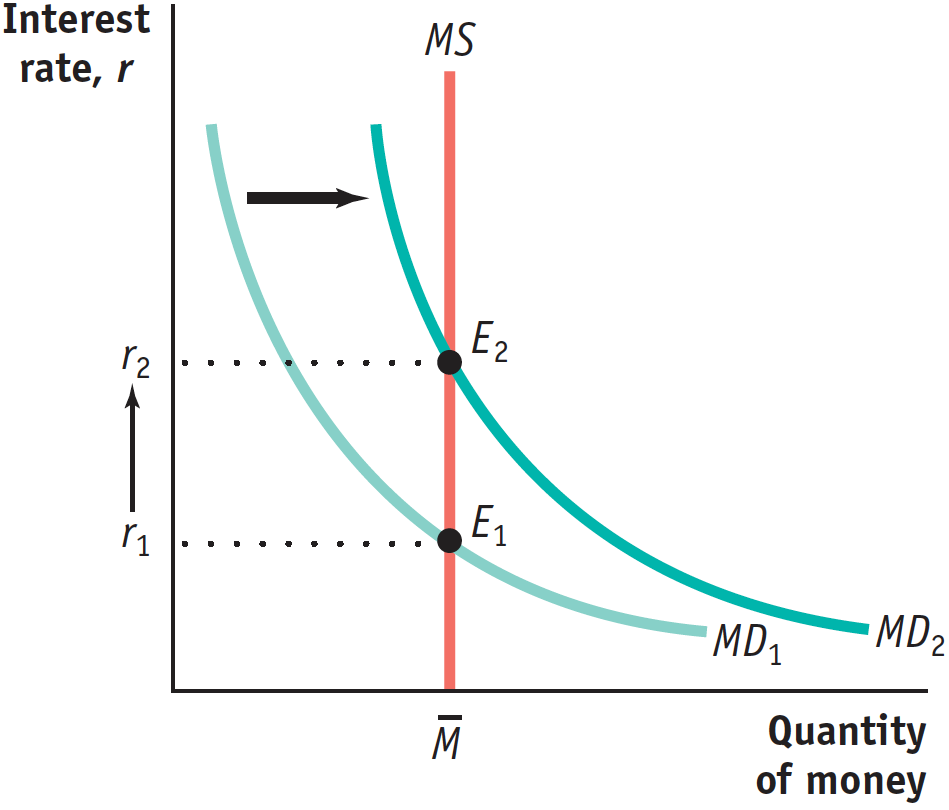
Question
Now assume that the Fed is following a policy of targeting the federal funds rate. What will the Fed do in the situation described in Question 1 to keep the federal funds rate unchanged? Illustrate with a diagram.
In order to prevent the interest rate from rising, the Federal Reserve must make an open-market purchase of Treasury bills, shifting the money supply curve rightward. This is shown in the accompanying diagram as the move from MS1 to MS2.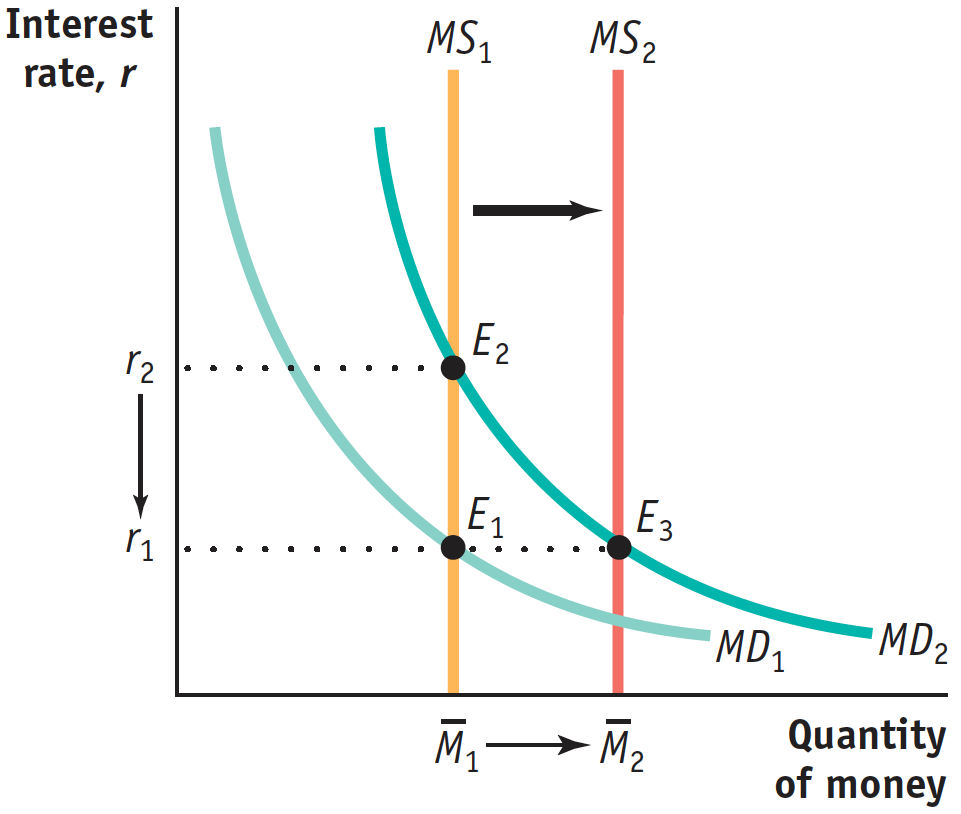
Question
Suppose the economy is currently suffering from a recessionary gap and the Federal Reserve uses an expansionary monetary policy to close that gap. Describe the short-
run effect of this policy on the following. the money supply curve
The money supply curve shifts to the right.the equilibrium interest rate
The equilibrium interest rate falls.investment spending
Investment spending rises due to the fall in the interest rate.consumer spending
Consumer spending rises due to the multiplier process.aggregate output
Aggregate output rises because of the rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve that results from the increase in investment and consumer spending.
[Leave] [Close]