Printed Page 451(cont.)
Check Your Understanding
Question
The economy is operating in long-
run macroeconomic equilibrium. Illustrate this situation using a correctly labeled aggregate demand–
aggregate supply graph. 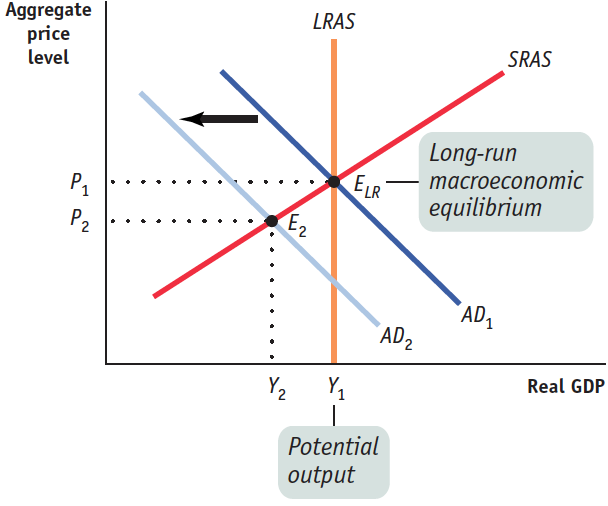
Use your graph to show the short-
run effect on real GDP and the aggregate price level if there is a decrease in government spending. Aggregate demand shifts left; real GDP and the aggregate price level fall.What will happen to the aggregate price level and real GDP in the long run? Explain.
Nominal wages will decrease as a result of the recessionary gap and the decrease in the aggregate price level, leading to an increase in short-run aggregate supply. The rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve moves the economy back to long-run equilibrium at potential output and a lower aggregate price level.Suppose the government is experiencing a persistent budget deficit. How will the decrease in government spending affect that deficit? Use a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market to show the effect of a decrease in government spending on the interest rate.
Lower government spending will decrease the government budget deficit. With less borrowing by the government, the demand for loanable funds will decrease, shifting the demand curve from D 1 to D 2 and decreasing the interest rate from r 1 to r 2 in the accompanying figure.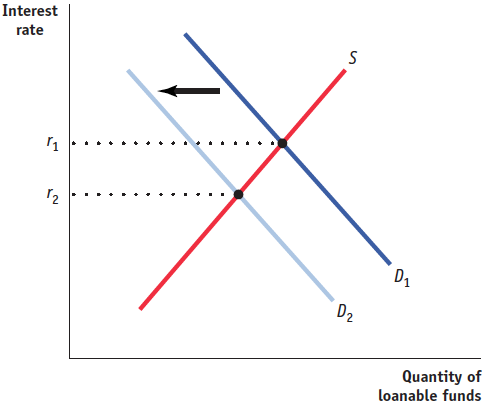
[Leave] [Close]