Printed Page 482(cont.)
An Elasticity Menagerie
We’ve just run through quite a few different types of elasticity. Keeping them all straight can be a challenge, but all of these elasticities are important. So we provide a summary of all the types of elasticity we have discussed and their implications in Table 48.1.
Table 48.1An Elasticity Menagerie
| Name | Elasticity values | Significance |
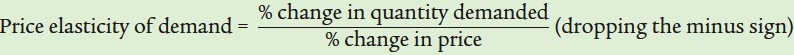
|
||
| Perfectly inelastic demand | 0 | Price has no effect on quantity demanded (vertical demand curve). |
| Inelastic demand | Between 0 and 1 | A rise in price increases total revenue. |
| Unit- |
Exactly 1 | Changes in price have no effect on total revenue. |
| Elastic demand | Greater than 1, less than ∞ | A rise in price reduces total revenue. |
| Perfectly elastic demand | ∞ | A rise in price causes quantity demanded to fall to 0. A fall in price leads to an infinite quantity demanded (horizontal demand curve). |
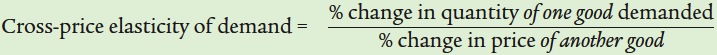
|
||
| Complements | Negative | Quantity demanded of one good falls when the price of another rises. |
| Substitutes | Positive | Quantity demanded of one good rises when the price of another rises. |
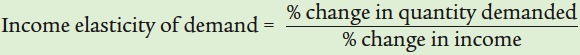
|
||
| Inferior good | Negative | Quantity demanded falls when income rises. |
| Normal good, income- |
Positive,less than 1 | Quantity demanded rises when income rises,but not as rapidly as income. |
| Normal good, income- |
Greater than 1 | Quantity demanded rises when income rises, and more rapidly than income. |
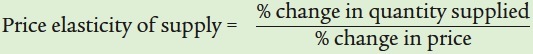
|
||
| Perfectly inelastic supply | 0 | Price has no effect on quantity supplied (vertical supply curve). |
| Inelastic supply | Between 0 and 1 | Upward- |
| Unit- |
Exactly 1 | Upward- |
| Elastic supply | Greater than 1, less than ∞ | Upward- |
| Perfectly elastic supply | ∞ | Any fall in price causes quantity supplied to fall to 0. Any rise in price elicits an infinite quantity supplied (horizontal supply curve). |
Table 48.1: Table 48.1 An Elasticity Menagerie
[Leave] [Close]