Multiple-Choice Questions
Question
When the price of a normal good falls, consumers will ______ the quantity they want, in part because they now have more money to spend on these units, which economists call ______ .
A. B. C. D. E. When the price of a normal good falls, consumers will ______ the quantity they want, in part because they now have more money to spend on these units, which economists call ______ .Question
Suppose market prices for potatoes were to increase by 10%, and potato farmers wanted to know whether or not their overall total revenues would rise or fall as a consequence. The farmers could figure this out by calculating which of the following economic concepts?
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose market prices for potatoes were to increase by 10%, and potato farmers wanted to know whether or not their overall total revenues would rise or fall as a consequence. The farmers could figure this out by calculating which of the following economic concepts?Question
Suppose Jolene buys apples weekly. If the price of apples were to drop, Jolene would experience ______ in _____ .
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose Jolene buys apples weekly. If the price of apples were to drop, Jolene would experience ______ in _____ .Question
Pizza and soda are often consumed together at Joe’s Diner. Suppose that the price of pizza rises from $0.75 a slice to $1.25 a slice, and consequently April sales of pizza drop from 1,050 to 950 slices. Using the midpoint method and this information, an economist could conclude the following:
A. B. C. D. E. Pizza and soda are often consumed together at Joe’s Diner. Suppose that the price of pizza rises from $0.75 a slice to $1.25 a slice, and consequently April sales of pizza drop from 1,050 to 950 slices. Using the midpoint method and this information, an economist could conclude the following:- Page 529
Question
Use the following information to answer Questions 5–
8. Suppose the government levies a tax of $0.50 per pack on the buyers of cigarettes. Suppose also that the price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is 1.2 and the price elasticity of supply is 0.7.
Because this tax is levied on the sale of a specific good, it is
A. B. C. D. E. Use the following information to answer Questions Question
After this tax is levied, total surplus will _______ , and the price received by producers (not including the tax) will ________ .
A. B. C. D. E. After this tax is levied, total surplus will _______ , and the price received by producers (not including the tax) will ________ .Question
If economists were to study the tax incidence in this cigarette market, they would conclude which of the following?
A. B. C. D. E. If economists were to study the tax incidence in this cigarette market, they would conclude which of the following?Question
In this example, cigarettes have
A. B. C. D. E. In this example, cigarettes haveQuestion
Jill is willing to sell her used calculator for $20. Her friend Jack is willing to pay $90 for a used calculator. They agree and trade at a price of $50. Which of the following is correct?
A. B. C. D. E. Jill is willing to sell her used calculator for $20. Her friend Jack is willing to pay $90 for a used calculator. They agree and trade at a price of $50. Which of the following is correct?Question
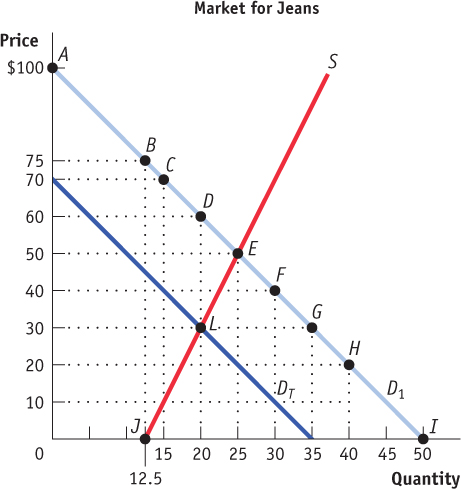
Refer to the figure for Questions 10–
17. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points C and E is _______ and economists would classify it as ______.
A. B. C. D. E. Refer to the figure for Questions 1Question
Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of supply between points J and E is _______ and economists would classify it as ______ .
A. B. C. D. E. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of supply between pointsQuestion
Suppose the government levies a tax on the buyers of jeans that shifts the demand curve from D1 to DT. Using the diagram, determine the amount of the tax per pair of jeans sold.
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose the government levies a tax on the buyers of jeans that shifts the demand curve from- Page 530
Question
Which of the following statements about the tax on jeans is true?
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following statements about the tax on jeans is true? Question
How much revenue would the government collect from the tax on jeans?
A. B. C. D. E. How much revenue would the government collect from the tax on jeans?Question
Buyers in the jeans market gain ______ in consumer surplus before the imposition of the tax, and they gain ______ in consumer surplus after the imposition of the tax.
A. B. C. D. E. Buyers in the jeans market gain ______ in consumer surplus before the imposition of the tax, and they gain ______ in consumer surplus after the imposition of the tax.Question
Jeans and product X (not shown) have a cross price elasticity of 3.7. After the imposition of the tax on jeans, buyers’ consumption of product X would ______ because jeans and product X are ______ .
A. B. C. D. E. Jeans and product X (not shown) have a cross price elasticity of 3.7. After the imposition of the tax on jeans, buyers’ consumption of product X would ______ because jeans and product X are ______ .Question
The deadweight loss caused by the tax on jeans is
A. B. C. D. E. The deadweight loss caused by the tax on jeans isQuestion
Quantity of ball toss games Total utility (utils) 0 0 1 70 2 130 3 180 4 220 5 250 6 270 7 280 Quantity of video games Total utility (utils) 0 0 1 30 2 55 3 75 4 90 5 100 6 105 7 109 8 112 9 114 Use the information from the tables above to complete Questions 18–
20. If Jill purchased 5 video games and 1 ball toss game, she would receive _______ and _______ .
A. B. C. D. E. - Page 531
Question
At the arcade, Jill likes the video games, which cost $0.50 to play, and the ball toss, which costs $2 to play. She has $6 to spend at the arcade. If Jill maximizes her utility, she will
A. B. C. D. E. At the arcade, Jill likes the video games, which cost $0.50 to play, and the ball toss, which costs $2 to play. She has $6 to spend at the arcade. If Jill maximizes her utility, she will Question
Suppose that video games still cost $0.50 and the ball toss still costs $2, but Jill now has $10.50 to spend at the arcade. If Jill chooses her optimal consumption bundle, she will purchase 9 video games and 3 games of ball toss.
A. B. C. D. Suppose that video games still cost $0.50 and the ball toss still costs $2, but Jill now has $10.50 to spend at the arcade. If Jill chooses her optimal consumption bundle, she will purchase 9 video games and 3 games of ball toss.