Multiple-Choice Questions
Question
Consider the data about the cost of each year of college in the table below:
Opportunity Cost of a Year of College
Explicit cost Implicit cost Tuition $17,000 Forgone salary $35,000 Books and supplies 1,000 Computer 1,500 Total explicit cost 19,500 Total implicit cost 35,000 Total opportunity cost = Total explicit cost + Total implicit cost = $54,500 A rational person would attend another year of college if the additional income expected plus the value of improved quality of life were worth at least
A. B. C. D. E. Consider the data about the cost of each year of college in the table below:Question
Comparing accounting profit to economic profit, accounting profit can
A. B. C. D. E. Comparing accounting profit to economic profit, accounting profit canQuestion
Which kind of profit is just enough to keep a firm operating in the long run?
A. B. C. D. E. Which kind of profit is just enough to keep a firm operating in the long run?- Page 585
Question
Refer to the cost data in the table below to answer Question 4.
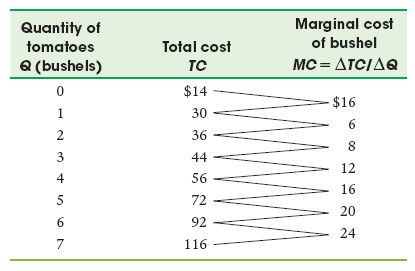
If this business can sell all it can produce at a market price of $16, the firm should produce how many units in order to maximize profits?
A. B. C. D. E. If this business can sell all it can produce at a market price of $16, the firm should produce how many units in order to maximize profits? Question
Assume a perfectly competitive firm is producing at a level of output where marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. To maximize profits, the firm should
A. B. C. D. E. Assume a perfectly competitive firm is producing at a level of output where marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. To maximize profits, the firm shouldQuestion
When a firm is producing where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue, the firm
A. B. C. D. E. When a firm is producing where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue, the firmQuestion
A fixed input
A. B. C. D. E. A fixed inputQuestion
If marginal product is positive and declining as more workers are hired, then total product is
A. B. C. D. E. If marginal product is positive and declining as more workers are hired, then total product isQuestion
Diminishing marginal returns always involve
A. B. C. D. E. Diminishing marginal returns always involveQuestion
If marginal cost is positive and rising as more output is produced, then total cost is
A. B. C. D. E. If marginal cost is positive and rising as more output is produced, then total cost isQuestion
Marginal cost rises due to
A. B. C. D. E. Marginal cost rises due toQuestion
The relationship between the marginal cost curve and the average cost curve is that when marginal cost is
A. B. C. D. E. The relationship between the marginal cost curve and the average cost curve is that when marginal cost isQuestion
In the short-
run, as output increases, average fixed cost A. B. C. D. E. In the shorQuestion
If at the current level of output of 200 units, average variable cost is $10 per unit and average total cost is $15 per unit, then
A. B. C. D. E. If at the current level of output of 200 units, average variable cost is $10 per unit and average total cost is $15 per unit, thenQuestion
If labor is the only variable input and the wage rate is constant, marginal cost reaches its minimum when
A. B. C. D. E. If labor is the only variable input and the wage rate is constant, marginal cost reaches its minimum whenQuestion
The spreading effect causes the average total cost curve to
A. B. C. D. E. The spreading effect causes the average total cost curve to- Page 586
Question
If marginal cost is rising and lies above average variable cost, then average total cost
A. B. C. D. E. If marginal cost is rising and lies above average variable cost, then average total cost Question
If the average product of labor is rising as more workers are hired, then
A. B. C. D. E. If the average product of labor is rising as more workers are hired, thenQuestion
The long-
run average cost curve eventually slopes up due to A. B. C. D. E. The lonQuestion
When a firm makes production decisions, the sunk cost should be
A. B. C. D. E. When a firm makes production decisions, the sunk cost should beQuestion
Monopolistically competitive industries are characterized by
A. B. C. D. E. Monopolistically competitive industries are characterized byQuestion
Compared to a monopolistically competitive industry, an oligopoly has
A. B. C. D. E. Compared to a monopolistically competitive industry, an oligopoly hasQuestion
Compared to a monopoly, an oligopoly has
A. B. C. D. E. Compared to a monopoly, an oligopoly hasQuestion
Diseconomies of scale can be caused by
A. B. C. D. E. Diseconomies of scale can be caused by