Multiple-Choice Questions
Question
According to the price-
taking firm’s optimal output rule, a perfectly competitive firm should produce the quantity at which marginal cost is equal to A. B. C. D. E. According to the pricQuestion
A perfectly competitive firm is a price-
taker because A. B. C. D. E. A perfectly competitive firm is a pricQuestion
Because a perfectly competitive firm is a price-
taker, its short- run demand curve is A. B. C. D. E. Because a perfectly competitive firm is a pricQuestion
A perfectly competitive firm is guaranteed to be profitable when it produces a level of output where
A. B. C. D. E. A perfectly competitive firm is guaranteed to be profitable when it produces a level of output whereQuestion
Average total cost is minimized by producing the level of output where the marginal cost
A. B. C. D. E. Average total cost is minimized by producing the level of output where the marginal costQuestion
Consider the data below for Questions 6, 7, and 8 for a perfectly competitive firm.
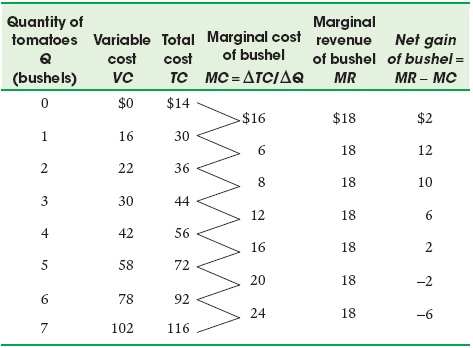
Suppose an increase in the demand for tomatoes brings the market price up to $22. How many tomatoes should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose an increase in the demand for tomatoes brings the market price up to $22. How many tomatoes should be produced in order to maximize profit?Question
Now suppose a decrease in the demand for tomatoes brings the market price down to $15. How many tomatoes should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A. B. C. D. E. Now suppose a decrease in the demand for tomatoes brings the market price down to $15. How many tomatoes should be produced in order to maximize profit?- Page 639
Question
What price represents the shut-
down price in the short run? A. B. C. D. E. What price represents the shu Question
Oscar sells bicycles in a perfectly competitive market. In the short run, at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost, the market price is above Oscar’s average variable cost and below his average total cost. Oscar should
A. B. C. D. E. Oscar sells bicycles in a perfectly competitive market. In the short run, at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost, the market price is above Oscar’s average variable cost and below his average total cost. Oscar shouldQuestion
The short-
run supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is its A. B. C. D. E. The shorQuestion
For a perfectly competitive industry, the short-
run industry supply curve is determined by A. B. C. D. E. For a perfectly competitive industry, the shorQuestion
Tia sells hats in a perfectly competitive market. If, in the long run, the market price exceeds the minimum of Tia’s average variable cost but is below the minimum of her average total cost, Tia should
A. B. C. D. E. Tia sells hats in a perfectly competitive market. If, in the long run, the market price exceeds the minimum of Tia’s average variable cost but is below the minimum of her average total cost, Tia shouldQuestion
In the long run for a perfectly competitive constant-
cost industry, if existing firms are producing where price is greater than average total cost, firms will enter the industry, price will A. B. C. D. E. In the long run for a perfectly competitive constanQuestion
For a perfectly competitive increasing-
cost industry, an increase in demand will cause the price to A. B. C. D. E. For a perfectly competitive increasinQuestion
The long-
run industry supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is A. B. C. D. E. The lonQuestion
The demand curve for a monopolist producing a normal good is downward-
sloping because of A. B. C. D. E. The demand curve for a monopolist producing a normal good is downwarQuestion
The marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve because of
A. B. C. D. E. The marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve because ofQuestion
If a monopolist is charging a price such that marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, then the monopolist
A. B. C. D. E. If a monopolist is charging a price such that marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, then the monopolist- Page 640
Question
For a monopolist, when marginal revenue is positive
A. B. C. D. E. For a monopolist, when marginal revenue is positive Question
Relative to a competitive industry with the same costs, a monopolist charges
A. B. C. D. E. Relative to a competitive industry with the same costs, a monopolist chargesQuestion
If a monopolist finds that demand is elastic at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, the monopolist will
A. B. C. D. E. If a monopolist finds that demand is elastic at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, the monopolist willQuestion
A perfectly competitive industry will likely have
A. B. C. D. E. A perfectly competitive industry will likely haveQuestion
If a regulatory commission wants to ensure that a monopolist produces the largest quantity of output that is consistent with earning a normal profit, it will require the monopolist to charge a price equal to its
A. B. C. D. E. If a regulatory commission wants to ensure that a monopolist produces the largest quantity of output that is consistent with earning a normal profit, it will require the monopolist to charge a price equal to itsQuestion
In order to practice price discrimination, a firm must have
A. B. C. D. E. In order to practice price discrimination, a firm must haveQuestion
Perfect price discrimination will result in
A. B. C. D. E. Perfect price discrimination will result in