Multiple-Choice Questions
Question
A difference between oligopolists and monopolistic competitors is that only
A. B. C. D. E. A difference between oligopolists and monopolistic competitors is that onlyQuestion
In studying market structures, economists have observed that when an industry has a relatively large number of firms, the firms are more likely to engage in _____ and prices are likely be relatively_____.
A. B. C. D. E. In studying market structures, economists have observed that when an industry has a relatively large number of firms, the firms are more likely to engage in _____ and prices are likely be relatively_____.Question
The government would attempt to enforce antitrust policy under which of the following circumstances?
A. B. C. D. E. The government would attempt to enforce antitrust policy under which of the following circumstances?Question
Government regulators should be concerned with _____ if firms in an industry have _____.
A. B. C. D. E. Government regulators should be concerned with _____ if firms in an industry have _____.Question
Brand names can lead to higher prices because
A. B. C. D. E. Brand names can lead to higher prices because- Page 684
Question
Which of the following is the most likely to lead to lower prices in an oligopoly?
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is the most likely to lead to lower prices in an oligopoly? Question
Use the information and table below to answer Questions 7 and 8.
Suppose that Firm A and Firm B are the only companies that make a common food preservative. The marginal cost of production is zero and the industry demand schedule for the preservative in a typical month is as follows:
Price (per pound) Quantity demanded (millions of pounds) $6 0 $5 10 $4 20 $3 30 $2 40 $1 50 $0 60 If the two companies agree to each produce half of the quantity that maximizes their combined profits and to share the revenue equally, what is the dollar amount (in millions) of revenue that each firm collects?
A. B. C. D. E. Use the information and table below to answer Questions 7 and 8.Question
Suppose Firm A continues to honor the production agreement from Question 7 while Firm B breaks it and produces more. Now what is the maximum dollar amount (in millions) that Firm B would collect?
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose Firm A continues to honor the production agreement from Question 7 while Firm B breaks it and produces more. Now what is the maximum dollar amount (in millions) that Firm B would collect?Question
Suppose a breakfast cereal market consists of only two firms, Firm X and Firm Y. Each firm sets either high prices or low prices for one month at a time. Use the information on each firm’s monthly profit in the payoff matrix below to answer Questions 9–
12. 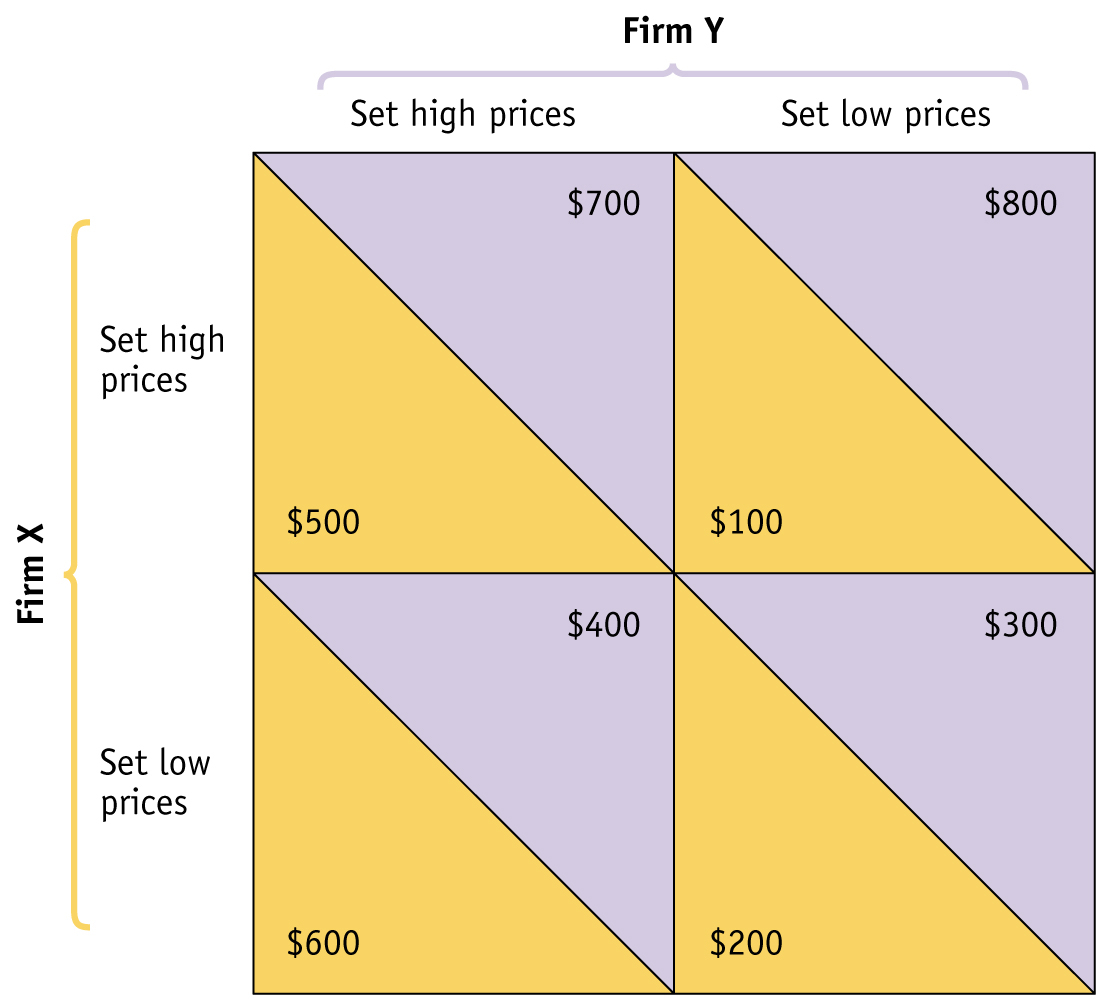
Which of the following statements is true?
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following statements is true?Question
Which of the following accurately describes the dominant strategies of Firm X and Firm Y?
Dominant strategy for Firm XDominant strategy for Firm YA. B. C. D. E. Which of the following accurately describes the dominant strategies of Firm X and Firm Y?Question
Suppose the same payoff matrix applies every month. For the current month, Firm X has set low prices and Firm Y has set high prices. If each firm follows a tit for tat strategy, then
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose the same payoff matrix applies every month. For the current month, Firm X has set low prices and Firm Y has set high prices. If each firm follows a tit for tat strategy, then- Page 685
Question
Suppose all the profit payoffs for Firm X double, but they remain the same for Firm Y. Which of the following is a true statement?
A. B. C. D. E. Suppose all the profit payoffs for Firm X double, but they remain the same for Firm Y. Which of the following is a true statement? Question
Which of the following works in favor of tacit collusion in an oligopolistic industry?
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following works in favor of tacit collusion in an oligopolistic industry?Question
Which of the following business tactics are ways that firms in an oligopolistic industry attempt to legally collude?
engaging in nonprice competition
utilizing price leadership for signaling
following the actions of others in a price war
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following business tactics are ways that firms in an oligopolistic industry attempt to legally collude?Question
In a monopolistically competitive soda industry, assume the following facts: a typical firm produces 10,000 beverage cans in a month; the price per can is $1.00; average total cost is $0.50 at the current production level, and marginal cost is $0.25 at the current production level. What will happen to the equilibrium quantity and profits for a typical firm in the soda industry in the long run?
Equilibrium quantity for a typical firmProfits for a typical firmA. B. C. D. E. In a monopolistically competitive soda industry, assume the following facts: a typical firm produces 10,000 beverage cans in a month; the price per can is $1.00; average total cost is $0.50 at the current production level, and marginal cost is $0.25 at the current production level. What will happen to the equilibrium quantity and profits for a typical firm in the soda industry in the long run?Question
Economists have argued that there may be inefficiencies in industries that are monopolistically competitive. Which of the following are some of the reasons cited for this inefficiency?
Prices are set above marginal cost.
There is excess capacity at current production levels.
There are zero profits in the long run.
A. B. C. D. E. Economists have argued that there may be inefficiencies in industries that are monopolistically competitive. Which of the following are some of the reasons cited for this inefficiency?Question
Use the following graph of a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive industry for Questions 17–
19. 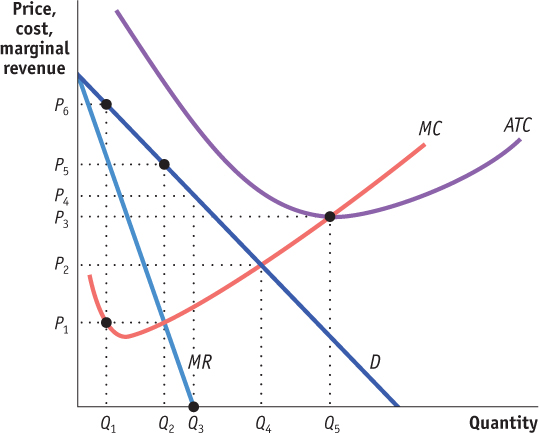
What price and quantity combination would we expect from a profit-
maximizing firm in this monopolistically competitive industry? A. B. C. D. E. What price and quantity combination would we expect from a profiQuestion
Firms in this industry are earning ______ and over time we would expect these profits or losses to _____.
A. B. C. D. E. Firms in this industry are earning ______ and over time we would expect these profits or losses to _____.- Page 686
Question
Over time, what will happen to the number of firms in this industry and the output per firm?
Number of firms in the industryOutput per firmA. B. C. D. E. Over time, what will happen to the number of firms in this industry and the output per firm? Question
Which of the following is NOT an example of product differentiation?
A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is NOT an example of product differentiation?