Check Your Understanding
Question
In the following three situations, the market is initially in equilibrium. After each event described below, does a surplus or shortage exist at the original equilibrium price? What will happen to the equilibrium price as a result?
In 2014 there was a bumper crop of wine grapes.
This is an increase in supply, so the supply curve shifts rightward. At the original equilibrium price of the year before, the quantity of grapes supplied exceeds the quantity demanded, and the result is a surplus. The price of grapes will fall.After a hurricane, Florida hoteliers often find that many people cancel their upcoming vacations, leaving them with empty hotel rooms.
This is a decrease in demand, so the demand curve shifts leftward. At the original equilibrium price, the quantity of hotel rooms supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. The result is a surplus. The rates for hotel rooms will fall.After a heavy snowfall, many people want to buy second-
hand snowblowers at the local tool shop. The snowfall increases the demand for snow blowers, so the demand curve shifts rightward. At the original equilibrium price, the quantity of snow blowers demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. The result is a shortage. The price of snow blowers will rise.
Question
For each of the following examples, explain how the indicated change affects supply or demand for the good in question and how the shift you describe affects the equilibrium price and quantity.
As the price of gasoline fell in the United States during the 1990s, more people bought large cars.
The decrease in the price of gasoline caused a rightward shift in the demand for large cars. As a result of the shift, the equilibrium price of large cars rose and the equilibrium quantity of large cars bought and sold also rose.Technological innovation in the use of recycled paper has lowered the cost of paper production.
The technological innovation causes a rightward shift in the supply of fresh paper made from recycled stock. As a result of this shift, the equilibrium price of fresh paper made from recycled stock falls and the equilibrium quantity bought and sold rises.When a local cable company offers cheaper pay-
per- view films, local movie theaters have more unfilled seats. The fall in the price of pay-per-view movies causes a leftward shift in the demand for movies at local movie theaters. As a result of this shift, the equilibrium price of movie tickets falls and the equilibrium number of people who go to the movies also falls.
Question
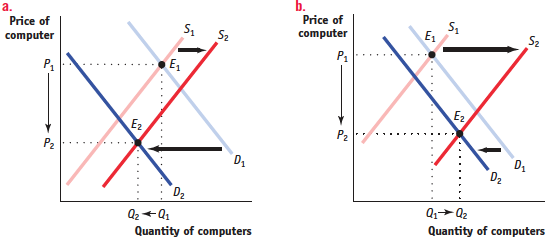
Periodically, a computer chip maker like Intel introduces a new chip that is faster than the previous one. In response, demand for computers using the earlier chip decreases as customers put off purchases in anticipation of machines containing the new chip. Simultaneously, computer makers increase their production of computers containing the earlier chip in order to clear out their stocks of those chips.
Draw two diagrams of the market for computers containing the earlier chip: (a) one in which the equilibrium quantity falls in response to these events and (b) one in which the equilibrium quantity rises. What happens to the equilibrium price in each diagram?
Upon announcement of the new chip, the demand curve for computers using the earlier chip shifts leftward (demand decreases), and the supply curve for these computers shifts rightward (supply increases).
a. If demand decreases relatively more than supply increases, then the equilibrium quantity falls, as shown in graph a.
b. If supply increases relatively more than demand decreases, then the equilibrium quantity rises, as shown in graph b. In both cases, the equilibrium price falls.