Check Your Understanding
Question
Draw a circular-
flow diagram that includes households, firms, factor markets, markets for goods and services, and financial markets. Circle the section of the diagram that illustrates maturity transformation and briefly explain the maturity transformation process. 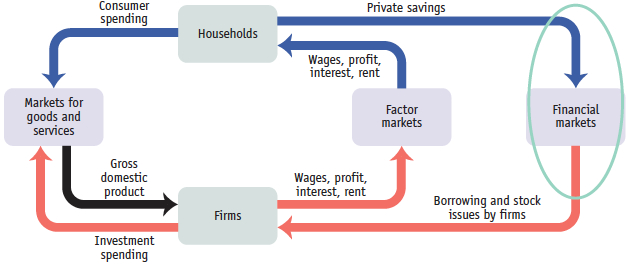 Financial markets take private savings in the form of short-term deposits and inject that money back into the economy through long-term loans.
Financial markets take private savings in the form of short-term deposits and inject that money back into the economy through long-term loans.Question
What are the four major causes of the 2008 financial crisis? Briefly describe each one.
Macroeconomic conditions: The economy experienced a long period of low inflation, stable growth, and low global interest rates prior to the 2008 financial crisis. These macroeconomic conditions encouraged risk-taking by shadow banks by making it easy and cheap to borrow money. Housing bubble: Housing prices increased to a high level due to expectations of future price gains, creating a housing bubble. When the housing bubble burst, people began to default on their subprime mortgages and the value of the collateralized debt obligations fell. Financial system linkages: When the housing bubble burst, the large number of defaults that resulted had the effect of a traditional bank run in the shadow banking system. Failure of government regulation: Relaxed regulation of investment banks in the shadow banking sector failed to prevent the start and spread of the financial crisis.Question
What are the four main elements of the Dodd-
Frank Act? Briefly describe each one. Consumer protection: The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau was created by the Dodd-Frank Act to protect borrowers from abusive practices that became prevalent leading up to the crisis. Derivatives regulation: The new law also contains stipulations designed to make financial markets transparent so that a derivative’s risk is no longer concealed. Shadow bank regulation: The shadow bank regulation extends government control during financial crises to cover nonbank financial institutions. Resolution authority: The government now has the authority to seize control of financial institutions that require a bailout during a crisis, the way it already did with commercial banks. Resolution authority allows governments to guarantee a wide range of financial institutions' debts in a crisis.
Discussion Starters
Question
Explain why an efficient financial system is important.
The financial system improves efficiency and leads to long-run economic growth by reducing transaction costs, reducing risk, and providing liquidity.Question
What is a shadow bank? Give several specific examples of shadow banks.
A shadow bank is a financial institution that engages in maturity transformation but does not accept deposits. Examples include: JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, Merrill Lynch, and Goldman Sachs.Question
Explain how an asset bubble can lead to an economy-
wide banking crisis. When the price of an asset like housing is pushed above a reasonable level by investor expectations of future price increases, eventually the market runs out of new buyers and the future price increases do not materialize. This causes the bubble to burst, leading to a decrease in the asset price. People who borrowed money to purchase the asset based on the expectation that prices would rise instead end up with a large debt on an asset that is now worth much less when prices decrease. When many asset owners default on their loans, it can lead to an economy-wide crisis.Question
What are some of the possible consequences of a financial crisis?
Domestic and possibly worldwide recession; reduced real GDP and high unemployment.Question
Define moral hazard. Explain the role of moral hazard in the 2008 financial crisis.
Moral hazard involves a distortion of incentives when someone else bears the costs of a lack of care or effort. Banks may have taken excessive risks because some people believed the banks would be protected by the government because they were “too big to fail.”