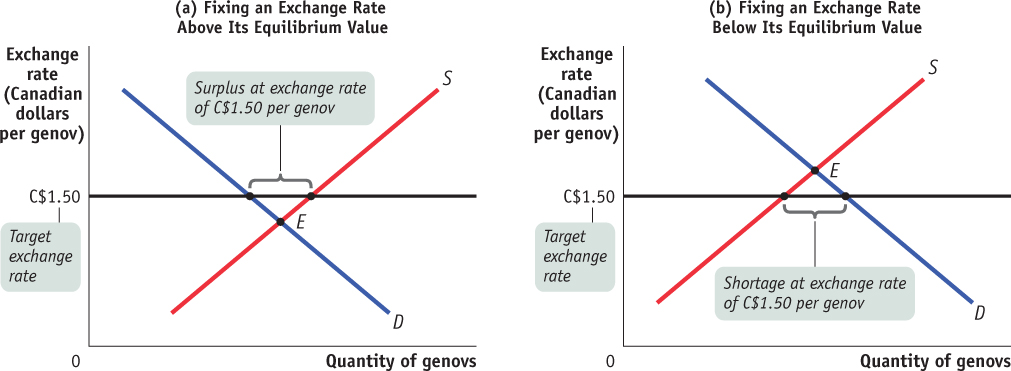
Figure19-10Exchange Market Intervention In both panels, the imaginary country of Genovia is trying to keep the exchange rate of the genov fixed at C$1.50 per genov. In panel (a), the equilibrium exchange rate is below C$1.50, leading to a surplus of genovs on the foreign exchange market. To keep the genov from falling below C$1.50, the Genovian government can buy genovs and sell Canadian dollars. In panel (b), the equilibrium exchange rate is above C$1.50, leading to a shortage of genovs on the foreign exchange market. To keep the genov from rising above C$1.50, the Genovian government can sell genovs and buy Canadian dollars.
[Leave] [Close]