Producer Surplus and the Supply Curve
Just as some buyers of a good would be willing to pay more for their purchase than the price they actually pay, some sellers of a good would be willing to sell it for less than the price they actually receive. So just as there are consumers who receive consumer surplus from buying in a market, there are producers who receive producer surplus from selling in a market.
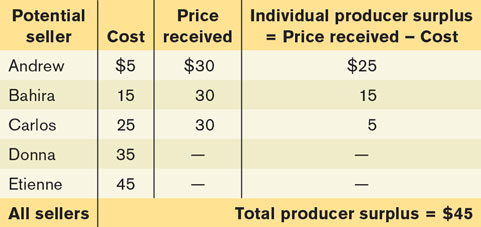
Cost and Producer Surplus Consider a group of students who are potential sellers of used textbooks. Because they have different preferences, the various potential sellers differ in the price at which they are willing to sell their books. Table 3B-2 shows the prices at which several different students would be willing to sell. Andrew is willing to sell his book as long as he can get at least $5; Bahira won’t sell unless she can get at least $15; Carlos, unless he can get $25; Donna, unless she can get $35; Etienne, unless he can get $45.
An individual seller’s cost is the lowest price at which he or she is willing to sell a good.
The lowest price at which a potential seller is willing to sell has a special name in economics: it is called the seller’s cost. So Andrew’s cost is $5, Bahira’s is $15, and so on.
Using the term cost, which people normally associate with the monetary cost of producing a good, may sound a little strange when applied to sellers of used textbooks. The students don’t have to manufacture the books, so it doesn’t cost the student who sells a used textbook anything to make that book available for sale, does it?
Yes, it does. A student who sells a book won’t have it later, as part of his or her personal collection. So there is an opportunity cost to selling a textbook, even if the owner has completed the course for which it was required. And remember that one of the basic principles of economics is that the true measure of the cost of doing something is always its opportunity cost. That is, the real cost of something is what you must give up to get it.
Individual producer surplus is the net gain to an individual seller from selling a good. It is equal to the difference between the price received and the seller’s cost.
Getting back to the example, suppose that Andrew sells his book for $30. Clearly he has gained from the transaction: he was willing to sell for only $5, so he has gained $25. This net gain, the difference between the price he actually gets and his cost, is known as his individual producer surplus.
Total producer surplus is the sum of the individual producer surpluses of all the sellers of a good in a market.
As in the case of consumer surplus, we can add the individual producer surpluses of sellers to calculate the total producer surplus, the total net gain to all sellers in the market. Economists use the term producer surplus to refer to either individual or total producer surplus. Table 3B-2 shows the net gain to each of the students who would sell a used book at a price of $30: $25 for Andrew, $15 for Bahira, and $5 for Carlos. The total producer surplus is $25 + $15 + $5 = $45.
Economists use the term producer surplus to refer to either total or individual producer surplus.
As with consumer surplus, the producer surplus gained by those who sell used books can be represented graphically. Just as we derived the demand curve from the willingness of different consumers to pay, we derive the supply curve from the cost of different producers. The step-
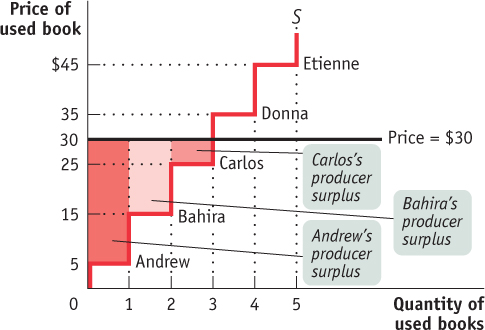
Let’s assume that the campus bookstore is willing to buy all the used copies of this book that students are willing to sell at a price of $30. Then, in addition to Andrew, Bahira and Carlos will also sell their books. They will also benefit from their sales, though not as much as Andrew, because they have higher costs. Andrew, as we have seen, gains $25. Bahira gains a smaller amount: since her cost is $15, she gains only $15. Carlos gains even less, only $5.
Again, as with consumer surplus, we have a general rule for determining the total producer surplus from sales of a good: the total producer surplus from sales of a good at a given price is the area above the supply curve but below that price.
This rule applies both to examples like the one shown in Figure 3B-3, where there are a small number of producers and a step-
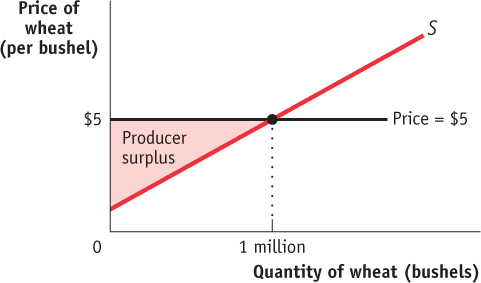
Consider, for example, the supply of wheat. Figure 3B-4 shows how producer surplus depends on the price per bushel. Suppose that, as shown in the figure, the price is $5 per bushel and farmers supply 1 million bushels. What is the benefit to the farmers from selling their wheat at a price of $5? Their producer surplus is equal to the shaded area in the figure—