Question 20.3
1. Due to a strike by truckers, trade in food between the United States and Mexico is halted. In autarky, the price of Mexican grapes is lower than that of U.S. grapes. Using a diagram of the U.S. domestic demand curve and the U.S. domestic supply curve for grapes, explain the effect of the strike on the following.
U.S. grape consumers’ surplus
U.S. grape producers’ surplus
U.S. total surplus
In the accompanying diagram, PA is the U.S. price of grapes in autarky and PW is the world price of grapes under international trade. With trade, U.S. consumers pay a price of PW for grapes and consume quantity QD, U.S. grape producers produce quantity QS, and the difference, QD − QS, represents imports of Mexican grapes. As a consequence of the strike by truckers, imports are halted, the price paid by American consumers rises to the autarky price, PA, and U.S. consumption falls to the autarky quantity, QA.
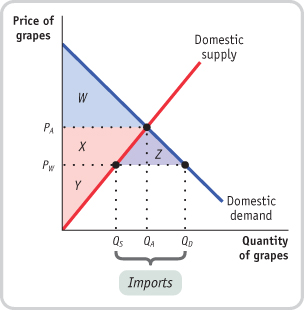
Before the strike, U.S. consumers enjoyed consumer surplus equal to areas W + X + Z. After the strike, their consumer surplus shrinks to W. So consumers are worse off, losing consumer surplus represented by X + Z.
Before the strike, U.S. producers had producer surplus equal to the area Y. After the strike, their producer surplus increases to Y + X. So U.S. producers are better off, gaining producer surplus represented by X.
U.S. total surplus falls as a result of the strike by an amount represented by area Z, the loss in consumer surplus that does not accrue to producers.