FIGURE 8- 8 Monopoly Causes Inefficiency
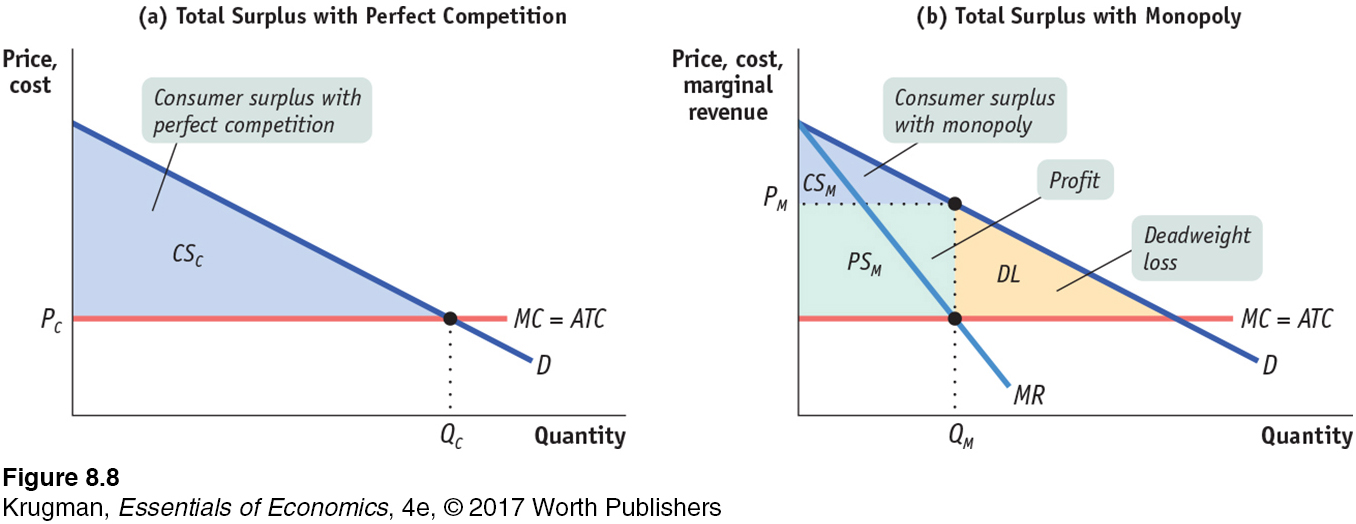 Panel (a) depicts a perfectly competitive industry: output is QC, and market price, PC, is equal to MC. Since price is exactly equal to each producer’s average total cost of production per unit, there is no profit and no producer surplus. So total surplus is equal to consumer surplus, the entire shaded area. Panel (b) depicts the industry under monopoly: the monopolist decreases output to QM and charges PM. Consumer surplus (blue area) has shrunk: a portion of it has been captured as profit (green area), and a portion of it has been lost to deadweight loss (yellow area), the value of mutually beneficial transactions that do not occur because of monopoly behavior. As a result, total surplus falls.
Panel (a) depicts a perfectly competitive industry: output is QC, and market price, PC, is equal to MC. Since price is exactly equal to each producer’s average total cost of production per unit, there is no profit and no producer surplus. So total surplus is equal to consumer surplus, the entire shaded area. Panel (b) depicts the industry under monopoly: the monopolist decreases output to QM and charges PM. Consumer surplus (blue area) has shrunk: a portion of it has been captured as profit (green area), and a portion of it has been lost to deadweight loss (yellow area), the value of mutually beneficial transactions that do not occur because of monopoly behavior. As a result, total surplus falls.