Problems
Question
Each month, usually on the first Friday of the month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the Employment Situation Summary for the previous month. Go to www.bls.gov and find the latest report. On the Bureau of Labor Statistics home page, at the top of the page, select the “Subject Areas” tab, find “Unemployment,” and select “National Unemployment Rate.” You will find the Employment Situation Summary under “CPS News Releases” on the left side of the page. How does the unemployment rate compare to the rate one month earlier? How does the unemployment rate compare to the rate one year earlier?
Prob 12 1. Each month, usually on the first Friday of the month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the Employment Situation Summary for the previous month. Go to www.bls.gov and find the latest report. On the Bureau of Labor Statistics home page, at the top of the page, select the “Subject Areas” tab, find “Unemployment,” and select “National Unemployment Rate.” You will find the Employment Situation Summary under “CPS News Releases” on the left side of the page. How does the unemployment rate compare to the rate one month earlier? How does the unemployment rate compare to the rate one year earlier?Question
In general, how do changes in the unemployment rate vary with changes in real GDP? After several quarters of a severe recession, explain why we might observe a decrease in the official unemployment rate. Explain why we could see an increase in the official unemployment rate after several quarters of a strong expansion.
Prob 12 2. In general, how do changes in the unemployment rate vary with changes in real GDP? After several quarters of a severe recession, explain why we might observe a decrease in the official unemployment rate. Explain why we could see an increase in the official unemployment rate after several quarters of a strong expansion.- In each of the following situations, what type of unemployment is Melanie facing?
Question
After completing a complex programming project, Melanie is laid off. Her prospects for a new job requiring similar skills are good, and she has signed up with a programmer placement service. She has passed up offers for low-paying jobs.
Prob 12 3a. After completing a complex programming project, Melanie is laid off. Her prospects for a new job requiring similar skills are good, and she has signed up with a programmer placement service. She has passed up offers for low-paying jobs.Question
When Melanie and her co-workers refused to accept pay cuts, her employer outsourced their programming tasks to workers in another country. This phenomenon is occurring throughout the programming industry.
Prob 12 3b. When Melanie and her co-workers refused to accept pay cuts, her employer outsourced their programming tasks to workers in another country. This phenomenon is occurring throughout the programming industry.Question
Due to the current slump, Melanie has been laid off from her programming job. Her employer promises to rehire her when business picks up.
Prob 12 3c. Due to the current slump, Melanie has been laid off from her programming job. Her employer promises to rehire her when business picks up.
- Part of the information released in the Employment Situation Summary concerns how long individuals have been unemployed. Go to www.bls.gov to find the latest report. Use the same technique as in Problem 1 to find the Employment Situation Summary. Near the end of the Employment Situation, click on Table A-12, titled “Unemployed persons by duration of unemployment.” Use the seasonally adjusted numbers to answer the following questions.
Question
How many workers were unemployed less than 5 weeks? What percentage of all unemployed workers do these workers represent? How do these numbers compare to the previous month’s data?
Prob 12 4a. How many workers were unemployed less than 5 weeks? What percentage of all unemployed workers do these workers represent? How do these numbers compare to the previous month’s data?Question
How many workers were unemployed for 27 or more weeks? What percentage of all unemployed workers do these workers represent? How do these numbers compare to the previous month’s data?
Prob 12 4b.How many workers were unemployed for 27 or more weeks? What percentage of all unemployed workers do these workers represent? How do these numbers compare to the previous month’s data?Question
How long has the average worker been unemployed (average duration, in weeks)? How does this compare to the average for the previous month’s data?
Prob 12 4c. How long has the average worker been unemployed (average duration, in weeks)? How does this compare to the average for the previous month’s data?Question
Comparing the latest month for which there are data with the previous month, has the problem of long-term unemployment improved or deteriorated?
Prob 12 4d. Comparing the latest month for which there are data with the previous month, has the problem of long-term unemployment improved or deteriorated?
- There is only one labor market in Profunctia. All workers have the same skills, and all firms hire workers with these skills. Use the accompanying diagram, which shows the supply of and demand for labor, to answer the following questions. Illustrate each answer with a diagram.
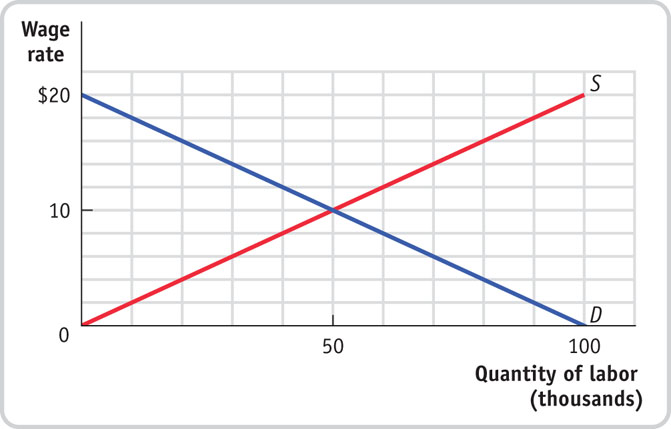
Question
What is the equilibrium wage rate in Profunctia? At this wage rate, what are the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?
Prob 12 5a. What is the equilibrium wage rate in Profunctia? At this wage rate, what are the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?Question
If the government of Profunctia sets a minimum wage equal to $12, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?
Prob 12 5b. If the government of Profunctia sets a minimum wage equal to $12, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?Question
If unions bargain with the firms in Profunctia and set a wage rate equal to $14, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?
Prob 12 5c. If the concern for retaining workers and encouraging high-quality work leads firms to set a wage rate equal to $16, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?Question
If the concern for retaining workers and encouraging high-quality work leads firms to set a wage rate equal to $16, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?
Prob 12 5d. If the concern for retaining workers and encouraging high-quality work leads firms to set a wage rate equal to $16, what will be the level of employment, the size of the labor force, and the unemployment rate?
- A country’s labor force is the sum of the number of employed and unemployed workers. The accompanying table provides data on the size of the labor force and the number of unemployed workers for different regions of the United States.
Labor force(thousands) Unemployed(thousands) Region May 2010 May 2011 May 2010 May 2011 Northeast 28,303.7 28,201.9 2,482.7 2,254.1 South 55,223.5 55,544.1 5,126.3 4,896.6 Midwest 34,520.2 34,430.0 3,305.7 2,803.7 West 35,827.2 35,613.0 3,954.0 3,664.4 Question
Calculate the number of workers employed in each of the regions in May 2010 and May 2011. Use your answers to calculate the change in the total number of workers employed between May 2010 and May 2011.
Prob 12 6a. Calculate the number of workers employed in each of the regions in May 2010 and May 2011. Use your answers to calculate the change in the total number of workers employed between May 2010 and May 2011.Question
For each region, calculate the growth in the labor force from May 2010 to May 2011.
Prob 12 6b. For each region, calculate the growth in the labor force from May 2010 to May 2011.Question
Compute unemployment rates in the different regions of the country in May 2010 and May 2011.
Prob 12 6c. Compute unemployment rates in the different regions of the country in May 2010 and May 2011.Question
What can you infer about the fall in unemployment rates over this period? Was it caused by a net gain in the number of jobs or by a large fall in the number of people seeking jobs?
Prob 12 6d. What can you infer about the fall in unemployment rates over this period? Was it caused by a net gain in the number of jobs or by a large fall in the number of people seeking jobs?
- In which of the following cases is it more likely for efficiency wages to exist? Why?
Question
Jane and her boss work as a team selling ice cream.
Prob 12 7a. Jane and her boss work as a team selling ice cream.Question
Jane sells ice cream without any direct supervision by her boss.
Prob 12 7b. Jane sells ice cream without any direct supervision by her boss.Question
Jane speaks Korean and sells ice cream in a neighborhood in which Korean is the primary language. It is difficult to find another worker who speaks Korean.
Prob 12 7c. Jane speaks Korean and sells ice cream in a neighborhood in which Korean is the primary language. It is difficult to find another worker who speaks Korean.
- How will the following changes affect the natural rate of unemployment?
Question
The government reduces the time during which an unemployed worker can receive unemployment benefits.
Prob 12 8a. The government reduces the time during which an unemployed worker can receive unemployment benefits.Question
More teenagers focus on their studies and do not look for jobs until after college.
Prob 12 8b. More teenagers focus on their studies and do not look for jobs until after college.Question
Greater access to the Internet leads both potential employers and potential employees to use the Internet to list and find jobs.
Prob 12 8c. Greater access to the Internet leads both potential employers and potential employees to use the Internet to list and find jobs.Question
Union membership declines.
Prob 12 8d. Union membership declines.
- With its tradition of a job for life for most citizens, Japan once had a much lower unemployment rate than that of the United States; from 1960 to 1995, the unemployment rate in Japan exceeded 3% only once. However, since the crash of its stock market in 1989 and slow economic growth in the 1990s, the job-for-life system has broken down and unemployment rose to more than 5% in 2003.
Question
Explain the likely effect of the breakdown of the job-for-life system in Japan on the Japanese natural rate of unemployment.
Prob 12 9a. Explain the likely effect of the breakdown of the job-for-life system in Japan on the Japanese natural rate of unemployment.Question
As the accompanying diagram shows, the rate of growth of real GDP picked up in Japan after 2001 and before the global economic crisis of 2007–2009. Explain the likely effect of this increase in real GDP growth on the unemployment rate. Was the likely cause of the change in the unemployment rate during this period a change in the natural rate of unemployment or a change in the cyclical unemployment rate?
Prob 12 9b. As the accompanying diagram shows, the rate of growth of real GDP picked up in Japan after 2001 and before the global economic crisis of 2007–2009. Explain the likely effect of this increase in real GDP growth on the unemployment rate. Was the likely cause of the change in the unemployment rate during this period a change in the natural rate of unemployment or a change in the cyclical unemployment rate?
Page 373 Source: OECD.
Source: OECD. - In the following examples, is inflation creating winners and losers at no net cost to the economy or is inflation imposing a net cost on the economy? If a net cost is being imposed, which type of cost is involved?
Question
When inflation is expected to be high, workers get paid more frequently and make more trips to the bank.
Prob 12 10a. When inflation is expected to be high, workers get paid more frequently and make more trips to the bank.Question
Lanwei is reimbursed by her company for her work-related travel expenses. Sometimes, however, the company takes a long time to reimburse her. So when inflation is high, she is less willing to travel for her job.
Prob 12 10b. Lanwei is reimbursed by her company for her work-related travel expenses. Sometimes, however, the company takes a long time to reimburse her. So when inflation is high, she is less willing to travel for her job.Question
Hector Homeowner has a mortgage with a fixed nominal 6% interest rate that he took out five years ago. Over the years, the inflation rate has crept up unexpectedly to its present level of 7%.
Prob 12 10c. Hector Homeowner has a mortgage with a fixed nominal 6% interest rate that he took out five years ago. Over the years, the inflation rate has crept up unexpectedly to its present level of 7%.Question
In response to unexpectedly high inflation, the manager of Cozy Cottages of Cape Cod must reprint and resend expensive color brochures correcting the price of rentals this season.
Prob 12 10d. In response to unexpectedly high inflation, the manager of Cozy Cottages of Cape Cod must reprint and resend expensive color brochures correcting the price of rentals this season.
The accompanying diagram shows the interest rate on one-year loans and inflation during 1995–2010 in the economy of Albernia. When would one-year loans have been especially attractive and why?
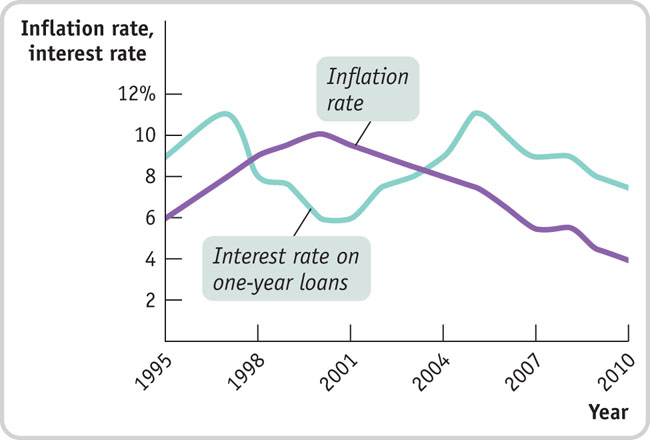
Question
Prob 12 11. The accompanying diagram shows the interest rate on one-year loans and inflation during 1995–2010 in the economy of Albernia. When would one-year loans have been especially attractive and why?- The accompanying table provides the inflation rate in the year 2000 and the average inflation rate over the period 2001–2010 for seven different countries.
Country Inflation rate in 2000 Average inflation rate in 2001–2010 Brazil 7.06% 6.70% China 0.4 2.16 France 1.83 1.86 Indonesia 3.77 8.55 Japan −0.78 −0.25 Turkey 55.03 18.51 United States 3.37 2.40 Question
Given the expected relationship between average inflation and menu costs, rank the countries in descending order of menu costs using average inflation over the period 2001–2010.
Prob 12 11a. Given the expected relationship between average inflation and menu costs, rank the countries in descending order of menu costs using average inflation over the period 2001–2010.Question
Rank the countries in order of inflation rates that most favored borrowers with ten-year loans that were taken out in 2000. Assume that the loans were agreed upon with the expectation that the inflation rate for 2001 to 2010 would be the same as the inflation rate in 2000.
Prob 12 11b. Rank the countries in order of inflation rates that most favored borrowers with ten-year loans that were taken out in 2000. Assume that the loans were agreed upon with the expectation that the inflation rate for 2001 to 2010 would be the same as the inflation rate in 2000.Question
Did borrowers who took out ten-year loans in Japan gain or lose overall versus lenders? Explain.
Prob 12 11c. Did borrowers who took out ten-year loans in Japan gain or lose overall versus lenders? Explain.
- The accompanying diagram shows the inflation rate in the United Kingdom from 1980 to 2010.
 Source: IMF.
Source: IMF.Question
Between 1980 and 1985, policy makers in the United Kingdom worked to lower the inflation rate. What would you predict happened to unemployment between 1980 and 1985?
Prob 12 13a. Between 1980 and 1985, policy makers in the United Kingdom worked to lower the inflation rate. What would you predict happened to unemployment between 1980 and 1985?Question
Question
Prob 12 13b. Policy makers in the United Kingdom react forcefully when the inflation rate rises above a target rate of 2%. Why would it be harmful if inflation rose from 3.4% (the level in 2010) to, say, a level of 5%?