Problems
Question
A fall in the value of the dollar against other currencies makes U.S. final goods and services cheaper to foreigners even though the U.S. aggregate price level stays the same. As a result, foreigners demand more American aggregate output. Your study partner says that this represents a movement down the aggregate demand curve because foreigners are demanding more in response to a lower price. You, however, insist that this represents a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve. Who is right? Explain.
Prob 14 1. A fall in the value of the dollar against other currencies makes U.S. final goods and services cheaper to foreigners even though the U.S. aggregate price level stays the same. As a result, foreigners demand more American aggregate output. Your study partner says that this represents a movement down the aggregate demand curve because foreigners are demanding more in response to a lower price. You, however, insist that this represents a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve. Who is right? Explain.Question
Your study partner is confused by the upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve. How would you explain this?
Prob 14 2. Your study partner is confused by the upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve. How would you explain this?- Suppose that in Wageland all workers sign annual wage contracts each year on January 1. No matter what happens to prices of final goods and services during the year, all workers earn the wage specified in their annual contract. This year, prices of final goods and services fall unexpectedly after the contracts are signed. Answer the following questions using a diagram and assume that the economy starts at potential output.
Question
In the short run, how will the quantity of aggregate output supplied respond to the fall in prices?
Prob 14 3a. In the short run, how will the quantity of aggregate output supplied respond to the fall in prices?Question
What will happen when firms and workers renegotiate their wages?
Prob 14 3b. What will happen when firms and workers renegotiate their wages?
- In each of the following cases, in the short run, determine whether the events cause a shift of a curve or a movement along a curve. Determine which curve is involved and the direction of the change.
Question
As a result of an increase in the value of the dollar in relation to other currencies, American producers now pay less in dollar terms for foreign steel, a major commodity used in production.
Prob 14 4a. As a result of an increase in the value of the dollar in relation to other currencies, American producers now pay less in dollar terms for foreign steel, a major commodity used in production.Question
An increase in the quantity of money by the Federal Reserve increases the quantity of money that people wish to lend, lowering interest rates.
Prob 14 4b. An increase in the quantity of money by the Federal Reserve increases the quantity of money that people wish to lend, lowering interest rates.Question
Greater union activity leads to higher nominal wages.
Prob 14 4c. Greater union activity leads to higher nominal wages.Question
A fall in the aggregate price level increases the purchasing power of households’ and firms’ money holdings. As a result, they borrow less and lend more.
Prob 14 4d. A fall in the aggregate price level increases the purchasing power of households’ and firms’ money holdings. As a result, they borrow less and lend more.
Question
The economy is at point A in the accompanying diagram. Suppose that the aggregate price level rises from P1 to P2. How will aggregate supply adjust in the short run and in the long run to the increase in the aggregate price level? Illustrate with a diagram.
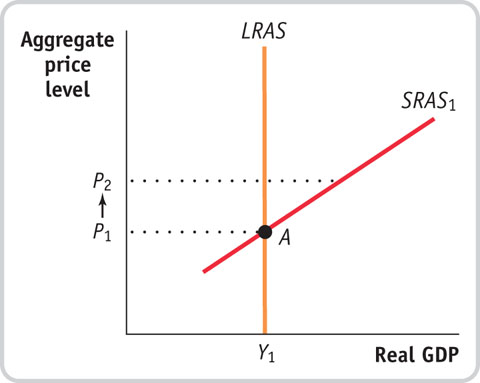 Prob 14 5. The economy is at point A in the accompanying diagram. Suppose that the aggregate price level rises from P1 to P2. How will aggregate supply adjust in the short run and in the long run to the increase in the aggregate price level? Illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 14 5. The economy is at point A in the accompanying diagram. Suppose that the aggregate price level rises from P1 to P2. How will aggregate supply adjust in the short run and in the long run to the increase in the aggregate price level? Illustrate with a diagram.Question
Suppose that all households hold all their wealth in assets that automatically rise in value when the aggregate price level rises (an example of this is what is called an “inflation-indexed bond”—a bond whose interest rate, among other things, changes one-for-one with the inflation rate). What happens to the wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level as a result of this allocation of assets? What happens to the slope of the aggregate demand curve? Will it still slope downward? Explain.
Prob 14 6. Suppose that all households hold all their wealth in assets that automatically rise in value when the aggregate price level rises (an example of this is what is called an “inflation-indexed bond”—a bond whose interest rate, among other things, changes one-for-one with the inflation rate). What happens to the wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level as a result of this allocation of assets? What happens to the slope of the aggregate demand curve? Will it still slope downward? Explain.Question
Suppose that the economy is currently at potential output. Also suppose that you are an economic policy maker and that a college economics student asks you to rank, if possible, your most preferred to least preferred type of shock: positive demand shock, negative demand shock, positive supply shock, negative supply shock. How would you rank them and why?
Prob 14 7. Suppose that the economy is currently at potential output. Also suppose that you are an economic policy maker and that a college economics student asks you to rank, if possible, your most preferred to least preferred type of shock: positive demand shock, negative demand shock, positive supply shock, negative supply shock. How would you rank them and why?- Explain whether the following government policies affect the aggregate demand curve or the short-run aggregate supply curve and how.
Question
The government reduces the minimum nominal wage.
Prob 14 8a. The government reduces the minimum nominal wage.Question
The government increases Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (TANF) payments, government transfers to families with dependent children.
Prob 14 8b. The government increases Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (TANF) payments, government transfers to families with dependent children.Question
To reduce the budget deficit, the government announces that households will pay much higher taxes beginning next year.
Prob 14 8c. To reduce the budget deficit, the government announces that households will pay much higher taxes beginning next year.Question
The government reduces military spending.
Prob 14 8d. The government reduces military spending.
Question
In Wageland, all workers sign an annual wage contract each year on January 1. In late January, a new computer operating system is introduced that increases labor productivity dramatically. Explain how Wageland will move from one short-run macroeconomic equilibrium to another. Illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 14 9. In Wageland, all workers sign an annual wage contract each year on January 1. In late January, a new computer operating system is introduced that increases labor productivity dramatically. Explain how Wageland will move from one short-run macroeconomic equilibrium to another. Illustrate with a diagram.- The Conference Board publishes the Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) every month based on a survey of 5,000 representative U.S. households. It is used by many economists to track the state of the economy. A press release by the Board on June 28, 2011 stated: “The Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index, which had declined in May, decreased again in June. The Index now stands at 58.5 (1985 = 100), down from 61.7 in May.”
Question
As an economist, is this news encouraging for economic growth?
Prob 14 10a. As an economist, is this news encouraging for economic growth?Question
Explain your answer to part a with the help of the AD–AS model. Draw a typical diagram showing two equilibrium points (E1) and (E2). Label the vertical axis “Aggregate price level” and the horizontal axis “Real GDP.” Assume that all other major macroeconomic factors remain unchanged.
Prob 14 10b. Explain your answer to part a with the help of the AD–AS model. Draw a typical diagram showing two equilibrium points (E1) and (E2). Label the vertical axis “Aggregate price level” and the horizontal axis “Real GDP.” Assume that all other major macroeconomic factors remain unchanged.Question
How should the government respond to this news? What are some policy measures that could be used to help neutralize the effect of falling consumer confidence?
Prob 14 10c. How should the government respond to this news? What are some policy measures that could be used to help neutralize the effect of falling consumer confidence?
- There were two major shocks to the U.S. economy in 2007, leading to the severe recession of 2007–2009. One shock was related to oil prices; the other was the slump in the housing market. This question analyzes the effect of these two shocks on GDP using the AD–AS framework.
Question
Draw typical aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves. Label the horizontal axis “Real GDP” and the vertical axis “Aggregate price level.” Label the equilibrium point E1, the equilibrium quantity Y1, and equilibrium price P1.
Prob 14 11a. Draw typical aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves. Label the horizontal axis “Real GDP” and the vertical axis “Aggregate price level.” Label the equilibrium point E1, the equilibrium quantity Y1, and equilibrium price P1.Question
Data taken from the Department of Energy indicate that the average price of crude oil in the world increased from $54.63 per barrel on January 5, 2007, to $92.93 on December 28, 2007. Would an increase in oil prices cause a demand shock or a supply shock? Redraw the diagram from part a to illustrate the effect of this shock by shifting the appropriate curve.
Prob 14 11b. Data taken from the Department of Energy indicate that the average price of crude oil in the world increased from $54.63 per barrel on January 5, 2007, to $92.93 on December 28, 2007. Would an increase in oil prices cause a demand shock or a supply shock? Redraw the diagram from part a to illustrate the effect of this shock by shifting the appropriate curve.Question
The Housing Price Index, published by the Office of Federal Housing Enterprise Oversight, calculates that U.S. home prices fell by an average of 3.0% in the 12 months between January 2007 and January 2008. Would the fall in home prices cause a supply shock or demand shock? Redraw the diagram from part b to illustrate the effect of this shock by shifting the appropriate curve. Label the new equilibrium point E3, the equilibrium quantity Y3, and equilibrium price P3.
Prob 14 11c. The Housing Price Index, published by the Office of Federal Housing Enterprise Oversight, calculates that U.S. home prices fell by an average of 3.0% in the 12 months between January 2007 and January 2008. Would the fall in home prices cause a supply shock or demand shock? Redraw the diagram from part b to illustrate the effect of this shock by shifting the appropriate curve. Label the new equilibrium point E3, the equilibrium quantity Y3, and equilibrium price P3.Question
Compare the equilibrium points E1 and E3 in your diagram for part c. What was the effect of the two shocks on real GDP and the aggregate price level (increase, decrease, or indeterminate)?
Prob 14 11d. Compare the equilibrium points E1 and E3 in your diagram for part c. What was the effect of the two shocks on real GDP and the aggregate price level (increase, decrease, or indeterminate)?
Extend Your Understanding
- Using aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply curves, explain the process by which each of the following economic events will move the economy from one long-run macroeconomic equilibrium to another. Illustrate with diagrams. In each case, what are the short-run and long-run effects on the aggregate price level and aggregate output?
Question
There is a decrease in households’ wealth due to a decline in the stock market.
Prob 14 12a. There is a decrease in households’ wealth due to a decline in the stock market.Question
The government lowers taxes, leaving households with more disposable income, with no corresponding reduction in government purchases.
Prob 14 12b. The government lowers taxes, leaving households with more disposable income, with no corresponding reduction in government purchases.
- Using aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply curves, explain the process by which each of the following government policies will move the economy from one long-run macroeconomic equilibrium to another. Illustrate with diagrams. In each case, what are the short-run and long-run effects on the aggregate price level and aggregate output?
Question
There is an increase in taxes on households.
Prob 14 13a. There is an increase in taxes on households.Question
There is an increase in the quantity of money.
Prob 14 13b. There is an increase in the quantity of money.Question
There is an increase in government spending.
Prob 14 13c. There is an increase in government spending.
- The economy is in short-run macroeconomic equilibrium at point E1 in the accompanying diagram. Based on the diagram, answer the following questions.
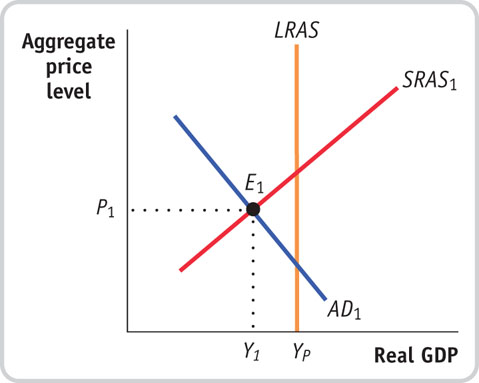
Question
Is the economy facing an inflationary or a recessionary gap?
Prob 14 14a. Is the economy facing an inflationary or a recessionary gap?Question
What policies can the government implement that might bring the economy back to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 14 14b. What policies can the government implement that might bring the economy back to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Illustrate with a diagram.Question
If the government did not intervene to close this gap, would the economy return to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Explain and illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 14 14c. If the government did not intervene to close this gap, would the economy return to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Explain and illustrate with a diagram.Question
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the government implementing policies to close the gap?
Prob 14 14d. What are the advantages and disadvantages of the government implementing policies to close the gap?
- In the accompanying diagram, the economy is in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium at point E1 when an oil shock shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to SRAS2. Based on the diagram, answer the following questions.
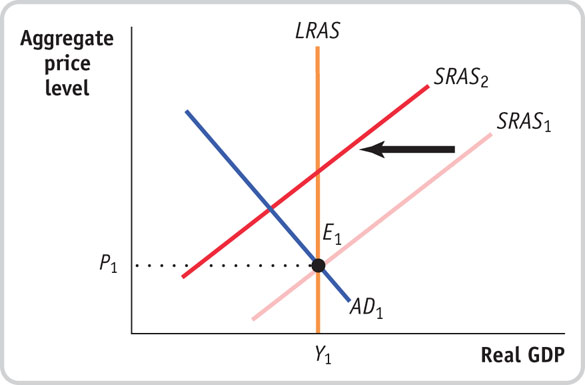
Question
How do the aggregate price level and aggregate output change in the short run as a result of the oil shock? What is this phenomenon known as?
Prob 14 15a. How do the aggregate price level and aggregate output change in the short run as a result of the oil shock? What is this phenomenon known as?Question
What fiscal or monetary policies can the government use to address the effects of the supply shock? Use a diagram that shows the effect of policies chosen to address the change in real GDP. Use another diagram to show the effect of policies chosen to address the change in the aggregate price level.
Prob 14 15b. What fiscal or monetary policies can the government use to address the effects of the supply shock? Use a diagram that shows the effect of policies chosen to address the change in real GDP. Use another diagram to show the effect of policies chosen to address the change in the aggregate price level.Question
Why do supply shocks present a dilemma for government policy makers?
Prob 14 15c. Why do supply shocks present a dilemma for government policy makers?
Question
The late 1990s in the United States was characterized by substantial economic growth with low inflation; that is, real GDP increased with little, if any, increase in the aggregate price level. Explain this experience using aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. Illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 14 16. The late 1990s in the United States was characterized by substantial economic growth with low inflation; that is, real GDP increased with little, if any, increase in the aggregate price level. Explain this experience using aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. Illustrate with a diagram.