Problems
- Marty’s Frozen Yogurt is a small shop that sells cups of frozen yogurt in a university town. Marty owns three frozen-yogurt machines. His other inputs are refrigerators, frozen-yogurt mix, cups, sprinkle toppings, and, of course, workers. He estimates that his daily production function when he varies the number of workers employed (and at the same time, of course, yogurt mix, cups, and so on) is as shown in the accompanying table.
Quantity of labor (workers) Quantity of frozen yogurt (cups) 0 0 1 110 2 200 3 270 4 300 5 320 6 330 Question
What are the fixed inputs and variable inputs in the production of cups of frozen yogurt?
Prob 6 1a. What are the fixed inputs and variable inputs in the production of cups of frozen yogurt?Question
Draw the total product curve. Put the quantity of labor on the horizontal axis and the quantity of frozen yogurt on the vertical axis.
Prob 6 1b. Draw the total product curve. Put the quantity of labor on the horizontal axis and the quantity of frozen yogurt on the vertical axis.Question
What is the marginal product of the first worker? The second worker? The third worker? Why does marginal product decline as the number of workers increases?
Prob 6 1c. What is the marginal product of the first worker? The second worker? The third worker? Why does marginal product decline as the number of workers increases?
- The production function for Marty’s Frozen Yogurt is given in Problem 1. Marty pays each of his workers $80 per day. The cost of his other variable inputs is $0.50 per cup of yogurt. His fixed cost is $100 per day.
Question
What is Marty’s variable cost and total cost when he produces 110 cups of yogurt? 200 cups? Calculate variable and total cost for every level of output given in Problem 1.
Prob 6 2a. What is Marty’s variable cost and total cost when he produces 110 cups of yogurt? 200 cups? Calculate variable and total cost for every level of output given in Problem 1.Question
Draw Marty’s variable cost curve. On the same diagram, draw his total cost curve.
Prob 6 2b. Draw Marty’s variable cost curve. On the same diagram, draw his total cost curve.Question
What is the marginal cost per cup for the first 110 cups of yogurt? For the next 90 cups? Calculate the marginal cost for all remaining levels of output.
Prob 6 2c. What is the marginal cost per cup for the first 110 cups of yogurt? For the next 90 cups? Calculate the marginal cost for all remaining levels of output.
- The production function for Marty’s Frozen Yogurt is given in Problem 1. The costs are given in Problem 2.
Question
For each of the given levels of output, calculate the average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC), and average total cost (ATC) per cup of frozen yogurt.
Prob 6 3a. For each of the given levels of output, calculate the average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC), and average total cost (ATC) per cup of frozen yogurt.Question
On one diagram, draw the AFC, AVC, and ATC curves.
Prob 6 3b. On one diagram, draw the AFC, AVC, and ATC curves.Question
What principle explains why the AFC declines as output increases? What principle explains why the AVC increases as output increases? Explain your answers.
Prob 6 3c. What principle explains why the AFC declines as output increases? What principle explains why the AVC increases as output increases? Explain your answers.Question
How many cups of frozen yogurt are produced when average total cost is minimized?
Prob 6 3d. How many cups of frozen yogurt are produced when average total cost is minimized?
- The accompanying table shows a car manufacturer’s total cost of producing cars.
Quantity of cars TC 0 $500,000 1 540,000 2 560,000 3 570,000 4 590,000 5 620,000 6 660,000 7 720,000 8 800,000 9 920,000 10 1,100,000 Question
What is this manufacturer’s fixed cost?
Prob 6 4a. What is this manufacturer’s fixed cost?Question
For each level of output, calculate the variable cost (VC). For each level of output except zero output, calculate the average variable cost (AVC), average total cost (ATC), and average fixed cost (AFC). What is the minimum-cost output?
Prob 6 4b. For each level of output, calculate the variable cost (VC). For each level of output except zero output, calculate the average variable cost (AVC), average total cost (ATC), and average fixed cost (AFC). What is the minimum-cost output?Question
For each level of output, calculate this manufacturer’s marginal cost (MC).
Prob 6 4c. For each level of output, calculate this manufacturer’s marginal cost (MC).Question
On one diagram, draw the manufacturer’s AVC, ATC, and MC curves.
Prob 6 4d. On one diagram, draw the manufacturer’s AVC, ATC, and MC curves.
- Magnificent Blooms is a florist specializing in floral arrangements for weddings, graduations, and other events. Magnificent Blooms has a fixed cost associated with space and equipment of $100 per day. Each worker is paid $50 per day. The daily production function for Magnificent Blooms is shown in the accompanying table.
Quantity of labor (workers) Quantity of floral arrangements 0 0 1 5 2 9 3 12 4 14 5 15 Question
Calculate the marginal product of each worker. What principle explains why the marginal product per worker declines as the number of workers employed increases?
Prob 6 5a. Calculate the marginal product of each worker. What principle explains why the marginal product per worker declines as the number of workers employed increases?Question
Calculate the marginal cost of each level of output. What principle explains why the marginal cost per floral arrangement increases as the number of arrangements increases?
Prob 6 5b. Calculate the marginal cost of each level of output. What principle explains why the marginal cost per floral arrangement increases as the number of arrangements increases?
You have the information shown in the accompanying table about a firm’s costs. Complete the missing data.
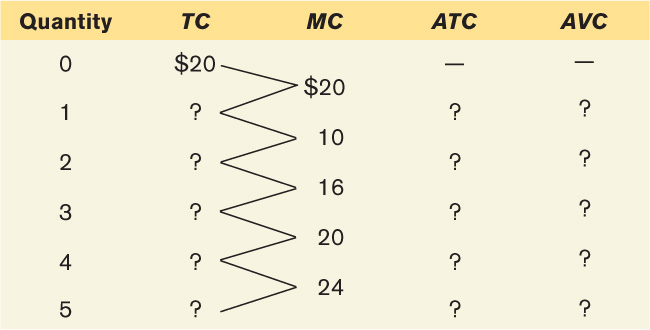
Question
Prob 6 6. You have the information shown in the accompanying table about a firm’s costs. Complete the missing data.- Evaluate each of the following statements. If a statement is true, explain why; if it is false, identify the mistake and try to correct it.
Question
A decreasing marginal product tells us that marginal cost must be rising.
Prob 6 7a. A decreasing marginal product tells us that marginal cost must be rising.Question
An increase in fixed cost increases the minimum-cost output.
Prob 6 7b. An increase in fixed cost increases the minimum-cost output.Question
An increase in fixed cost increases marginal cost.
Prob 6 7c. An increase in fixed cost increases marginal cost.Question
When marginal cost is above average total cost, average total cost must be falling.
Prob 6 7d. When marginal cost is above average total cost, average total cost must be falling.
- Mark and Jeff operate a small company that produces souvenir footballs. Their fixed cost is $2,000 per month. They can hire workers for $1,000 per worker per month. Their monthly production function for footballs is as given in the accompanying table.
Quantity of labor (workers) Quantity of footballs 0 0 1 300 2 800 3 1,200 4 1,400 5 1,500 Question
For each quantity of labor, calculate average variable cost (AVC), average fixed cost (AFC), average total cost (ATC), and marginal cost (MC).
Prob 6 8a. For each quantity of labor, calculate average variable cost (AVC), average fixed cost (AFC), average total cost (ATC), and marginal cost (MC).Question
On one diagram, draw the AVC, ATC, and MC curves.
Prob 6 8b. On one diagram, draw the AVC, ATC, and MC curves.Question
At what level of output is Mark and Jeff’s average total cost minimized?
Prob 6 8c. At what level of output is Mark and Jeff’s average total cost minimized?
- You produce widgets. Currently you produce 4 widgets at a total cost of $40.
Question
What is your average total cost?
Prob 6 9a. What is your average total cost?Question
Suppose you could produce one more (the fifth) widget at a marginal cost of $5. If you do produce that fifth widget, what will your average total cost be? Has your average total cost increased or decreased? Why?
Prob 6 9b. Suppose you could produce one more (the fifth) widget at a marginal cost of $5. If you do produce that fifth widget, what will your average total cost be? Has your average total cost increased or decreased? Why?Question
Suppose instead that you could produce one more (the fifth) widget at a marginal cost of $20. If you do produce that fifth widget, what will your average total cost be? Has your average total cost increased or decreased? Why?
Prob 6 9c. Suppose instead that you could produce one more (the fifth) widget at a marginal cost of $20. If you do produce that fifth widget, what will your average total cost be? Has your average total cost increased or decreased? Why?
Question
In your economics class, each homework problem set is graded on the basis of a maximum score of 100. You have completed 9 out of 10 of the problem sets for the term, and your current average grade is 88. What range of grades for your 10th problem set will raise your overall average? What range will lower your overall average? Explain your answer.
Prob 6 10. In your economics class, each homework problem set is graded on the basis of a maximum score of 100. You have completed 9 out of 10 of the problem sets for the term, and your current average grade is 88. What range of grades for your 10th problem set will raise your overall average? What range will lower your overall average? Explain your answer.- Don owns a small concrete-mixing company. His fixed cost is the cost of the concrete-batching machinery and his mixer trucks. His variable cost is the cost of the sand, gravel, and other inputs for producing concrete; the gas and maintenance for the machinery and trucks; and his workers. He is trying to decide how many mixer trucks to purchase. He has estimated the costs shown in the accompanying table based on estimates of the number of orders his company will receive per week.
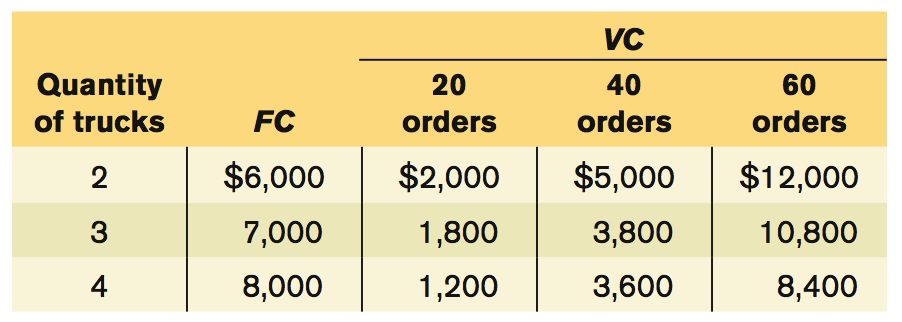 Page 207
Page 207Question
For each level of fixed cost, calculate Don’s total cost for producing 20, 40, and 60 orders per week.
Prob 6 11a. For each level of fixed cost, calculate Don’s total cost for producing 20, 40, and 60 orders per week.Question
If Don is producing 20 orders per week, how many trucks should he purchase and what will his average total cost be? Answer the same questions for 40 and 60 orders per week.
Prob 6 11b. If Don is producing 20 orders per week, how many trucks should he purchase and what will his average total cost be? Answer the same questions for 40 and 60 orders per week.
- Consider Don’s concrete-mixing business described in Problem 11. Assume that Don purchased 3 trucks, expecting to produce 40 orders per week.
Question
Suppose that, in the short run, business declines to 20 orders per week. What is Don’s average total cost per order in the short run? What will his average total cost per order in the short run be if his business booms to 60 orders per week?
Prob 6 12a. Suppose that, in the short run, business declines to 20 orders per week. What is Don’s average total cost per order in the short run? What will his average total cost per order in the short run be if his business booms to 60 orders per week?Question
What is Don’s long-run average total cost for 20 orders per week? Explain why his short-run average total cost of producing 20 orders per week when the number of trucks is fixed at 3 is greater than his long-run average total cost of producing 20 orders per week.
Prob 6 12b. What is Don’s long-run average total cost for 20 orders per week? Explain why his short-run average total cost of producing 20 orders per week when the number of trucks is fixed at 3 is greater than his long-run average total cost of producing 20 orders per week.Question
Draw Don’s long-run average total cost curve. Draw his short-run average total cost curve if he owns 3 trucks.
Prob 6 12c. Draw Don’s long-run average total cost curve. Draw his short-run average total cost curve if he owns 3 trucks.
- True or false? Explain your reasoning.
Question
The short-run average total cost can never be less than the long-run average total cost.
Prob 6 13a. The short-run average total cost can never be less than the long-run average total cost.Question
The short-run average variable cost can never be less than the long-run average total cost.
Prob 6 13b. The short-run average variable cost can never be less than the long-run average total cost.Question
In the long run, choosing a higher level of fixed cost shifts the long-run average total cost curve upward.
Prob 6 13c. In the long run, choosing a higher level of fixed cost shifts the long-run average total cost curve upward.
- Wolfsburg Wagon (WW) is a small automaker. The accompanying table shows WW’s long-run average total cost.
Quantity of cars LRATC of car 1 $30,000 2 20,000 3 15,000 4 12,000 5 12,000 6 12,000 7 14,000 8 18,000 Question
For which levels of output does WW experience increasing returns to scale?
Prob 6 14a. For which levels of output does WW experience increasing returns to scale?Question
For which levels of output does WW experience decreasing returns to scale?
Prob 6 14b. For which levels of output does WW experience decreasing returns to scale?Question
For which levels of output does WW experience constant returns to scale?
Prob 6 14c. For which levels of output does WW experience constant returns to scale?
- Changes in the prices of key commodities can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line. But, changes in the price of energy produced from oil, gas, and electricity are not the only concern for companies. According to an August 16, 2012, Bloomberg article, “ethanol requirements are aggravating the rise in food costs and spreading it to the price of gasoline, which is up almost 40 cents a gallon since the start of July.” The U.S. government mandates that gasoline contain ethanol, which is derived from corn.
Question
Explain how the cost of energy can be both a fixed cost and a variable cost for a company.
Prob 6 15a. Explain how the cost of energy can be both a fixed cost and a variable cost for a company.Question
Suppose energy is a fixed cost and energy prices rise. What happens to the company’s average total cost curve? What happens to its marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Prob 6 15b. Suppose energy is a fixed cost and energy prices rise. What happens to the company’s average total cost curve? What happens to its marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.Question
Explain why the cost of corn is a variable cost but not a fixed cost for an ethanol producer.
Prob 6 15c. Explain why the cost of corn is a variable cost but not a fixed cost for an ethanol producer.Question
When the cost of corn goes up, what happens to the average total cost curve of an ethanol producer? What happens to its marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Prob 6 15d. When the cost of corn goes up, what happens to the average total cost curve of an ethanol producer? What happens to its marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Extend Your Understanding
- Labor costs represent a large percentage of total costs for many firms. According to a July 29, 2011, Wall Street Journal article, U.S. labor costs were up 0.7% during the second quarter of 2011, compared to the first quarter of 2011.
Question
When labor costs increase, what happens to average total cost and marginal cost? Consider a case in which labor costs are only variable costs and a case in which they are both variable and fixed costs.
An increase in labor productivity means each worker can produce more output. Recent data on productivity show that labor productivity in the U.S. nonfarm business sector grew by 1.7% between 1970 and 1999, by 2.6% between 2000 and 2010, and by 4.1% in 2010.Prob 6 16a. When labor costs increase, what happens to average total cost and marginal cost? Consider a case in which labor costs are only variable costs and a case in which they are both variable and fixed costs.
An increase in labor productivity means each worker can produce more output. Recent data on productivity show that labor productivity in the U.S. nonfarm business sector grew by 1.7% between 1970 and 1999, by 2.6% between 2000 and 2010, and by 4.1% in 2010.Question
When productivity growth is positive, what happens to the total product curve and the marginal product of labor curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Prob 6 16b. When productivity growth is positive, what happens to the total product curve and the marginal product of labor curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.Question
When productivity growth is positive, what happens to the marginal cost curve and the average total cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Prob 6 16c. When productivity growth is positive, what happens to the marginal cost curve and the average total cost curve? Illustrate your answer with a diagram.Question
If labor costs are rising over time on average, why would a company want to adopt equipment and methods that increase labor productivity?
Prob 6 16d. If labor costs are rising over time on average, why would a company want to adopt equipment and methods that increase labor productivity?