Problems
- For each of the following, is the business a price-taking producer? Explain your answers.
Question
A cappuccino café in a university town where there are dozens of very similar cappuccino cafés
Prob 7 1a. A cappuccino café in a university town where there are dozens of very similar cappuccino cafésQuestion
The makers of Pepsi-Cola
Prob 7 1b. The makers of Pepsi-ColaQuestion
One of many sellers of zucchini at a local farmers’ market
Prob 7 1c. One of many sellers of zucchini at a local farmers’ market
- For each of the following, is the industry perfectly competitive? Referring to market share, standardization of the product, and/or free entry and exit, explain your answers.
Question
Aspirin
Prob 7 2a. AspirinQuestion
Alicia Keys concerts
Prob 7 2b. Alicia Keys concertsQuestion
SUVs
Prob 7 2c. SUVs
- Kate’s Katering provides catered meals, and the catered meals industry is perfectly competitive. Kate’s machinery costs $100 per day and is the only fixed input. Her variable cost consists of the wages paid to the cooks and the food ingredients. The variable cost per day associated with each level of output is given in the accompanying table.
Quantity of meals VC 0 0 10 2 20 4 30 10 40 10 50 10 Question
Calculate the total cost, the average variable cost, the average total cost, and the marginal cost for each quantity of output.
Prob 7 3a. Calculate the total cost, the average variable cost, the average total cost, and the marginal cost for each quantity of output.Question
What is the break-even price? What is the shut-down price?
Prob 7 3b. What is the break-even price? What is the shut-down price?Question
Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $21 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?
Prob 7 3c. Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $21 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?Question
Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $17 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?
Prob 7 3d. Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $17 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?Question
Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $13 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?
Prob 7 3e. Suppose that the price at which Kate can sell catered meals is $13 per meal. In the short run, will Kate earn a profit? In the short run, should she produce or shut down?
Page 234 - Bob produces DVD movies for sale, which requires a building and a machine that copies the original movie onto a DVD. Bob rents a building for $30,000 per month and rents a machine for $20,000 a month. Those are his fixed costs. His variable cost per month is given in the accompanying table.
Quantity of DVDs VC 0 $0 1,000 5,000 2,000 8,000 3,000 9,000 4,000 14,000 5,000 20,000 6,000 33,000 7,000 49,000 8,000 72,000 9,000 99,000 10,000 150,000 Question
Calculate Bob’s average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost for each quantity of output.
Prob 7 4a. Calculate Bob’s average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost for each quantity of output.Question
There is free entry into the industry, and anyone who enters will face the same costs as Bob. Suppose that currently the price of a DVD is $25. What will Bob’s profit be? Is this a long-run equilibrium? If not, what will the price of DVD movies be in the long run?
Prob 7 4b. There is free entry into the industry, and anyone who enters will face the same costs as Bob. Suppose that currently the price of a DVD is $25. What will Bob’s profit be? Is this a long-run equilibrium? If not, what will the price of DVD movies be in the long run?
- Consider Bob’s DVD company described in Problem 4. Assume that DVD production is a perfectly competitive industry. For each of the following questions, explain your answers.
Question
What is Bob’s break-even price? What is his shut-down price?
Prob 7 5a. What is Bob’s break-even price? What is his shut-down price?Question
Suppose the price of a DVD is $2. What should Bob do in the short run?
Prob 7 5b. Suppose the price of a DVD is $2. What should Bob do in the short run?Question
Suppose the price of a DVD is $7. What is the profit-maximizing quantity of DVDs that Bob should produce? What will his total profit be? Will he produce or shut down in the short run? Will he stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
Prob 7 5c. Suppose the price of a DVD is $7. What is the profit-maximizing quantity of DVDs that Bob should produce? What will his total profit be? Will he produce or shut down in the short run? Will he stay in the industry or exit in the long run?Question
Suppose instead that the price of DVDs is $20. Now what is the profit-maximizing quantity of DVDs that Bob should produce? What will his total profit be now? Will he produce or shut down in the short run? Will he stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
Prob 7 5d. Suppose instead that the price of DVDs is $20. Now what is the profit-maximizing quantity of DVDs that Bob should produce? What will his total profit be now? Will he produce or shut down in the short run? Will he stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
- Consider again Bob’s DVD company described in Problem 4.
Question
Draw Bob’s marginal cost curve.
Prob 7 6a. Draw Bob’s marginal cost curve.Question
Over what range of prices will Bob produce no DVDs in the short run?
Prob 7 6b. Over what range of prices will Bob produce no DVDs in the short run?Question
Draw Bob’s individual supply curve.
Prob 7 6c. Draw Bob’s individual supply curve.
Question
A profit-maximizing business incurs an economic loss of $10,000 per year. Its fixed cost is $15,000 per year. Should it produce or shut down in the short run? Should it stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
Prob 7 7a. A profit-maximizing business incurs an economic loss of $10,000 per year. Its fixed cost is $15,000 per year. Should it produce or shut down in the short run? Should it stay in the industry or exit in the long run?Question
Suppose instead that this business has a fixed cost of $6,000 per year. Should it produce or shut down in the short run? Should it stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
Prob 7 7b. Suppose instead that this business has a fixed cost of $6,000 per year. Should it produce or shut down in the short run? Should it stay in the industry or exit in the long run?
- The first sushi restaurant opens in town. Initially people are very cautious about eating tiny portions of raw fish, as this is a town where large portions of grilled meat have always been popular. Soon, however, an influential health report warns consumers against grilled meat and suggests that they increase their consumption of fish, especially raw fish. The sushi restaurant becomes very popular and its profit increases.
Question
What will happen to the short-run profit of the sushi restaurant? What will happen to the number of sushi restaurants in town in the long run? Will the first sushi restaurant be able to sustain its short-run profit over the long run? Explain your answers.
Prob 7 8a. What will happen to the short-run profit of the sushi restaurant? What will happen to the number of sushi restaurants in town in the long run? Will the first sushi restaurant be able to sustain its short-run profit over the long run? Explain your answers.Question
Local steakhouses suffer from the popularity of sushi and start incurring losses. What will happen to the number of steakhouses in town in the long run? Explain your answer.
Prob 7 8b. Local steakhouses suffer from the popularity of sushi and start incurring losses. What will happen to the number of steakhouses in town in the long run? Explain your answer.
- A perfectly competitive firm has the following short-run total cost:
Quantity TC 0 $5 1 10 2 13 3 18 4 25 5 34 6 45 Market demand for the firm’s product is given by the following market demand schedule:
Price Quantity demanded $12 300 10 500 8 800 6 1,200 4 1,800 Question
Calculate this firm’s marginal cost and, for all output levels except zero, the firm’s average variable cost and average total cost.
Prob 7 9a. Calculate this firm’s marginal cost and, for all output levels except zero, the firm’s average variable cost and average total cost.Question
There are 100 firms in this industry that all have costs identical to those of this firm. Draw the short-run industry supply curve. In the same diagram, draw the market demand curve.
Prob 7 9b. There are 100 firms in this industry that all have costs identical to those of this firm. Draw the short-run industry supply curve. In the same diagram, draw the market demand curve.Question
What is the market price, and how much profit will each firm make?
Prob 7 9c. What is the market price, and how much profit will each firm make?
Page 235 - Evaluate each of the following statements. If a statement is true, explain why; if it is false, identify the mistake and try to correct it.
Question
A profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive industry should select the output level at which the difference between the market price and marginal cost is greatest.
Prob 7 10a. A profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive industry should select the output level at which the difference between the market price and marginal cost is greatest.Question
An increase in fixed cost lowers the profit-maximizing quantity of output produced in the short run.
Prob 7 10b. An increase in fixed cost lowers the profit-maximizing quantity of output produced in the short run.
Extend Your Understanding
- A new vaccine against a deadly disease has just been discovered. Presently, 55 people die from the disease each year. The new vaccine will save lives, but it is not completely safe. Some recipients of the shots will die from adverse reactions. The projected effects of the inoculation are given in the accompanying table:
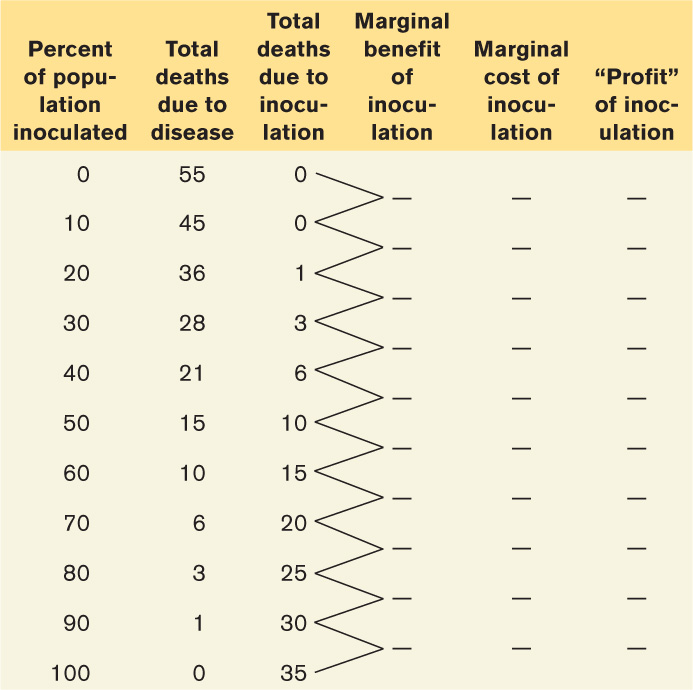
Question
What are the interpretations of “marginal benefit” and “marginal cost” here? Calculate marginal benefit and marginal cost per each 10% increase in the rate of inoculation. Write your answers in the table.
Prob 7 11a. What are the interpretations of “marginal benefit” and “marginal cost” here? Calculate marginal benefit and marginal cost per each 10% increase in the rate of inoculation. Write your answers in the table.Question
What proportion of the population should optimally be inoculated?
Prob 7 11b. What proportion of the population should optimally be inoculated?Question
What is the interpretation of “profit” here? Calculate the profit for all levels of inoculation.
Prob 7 11c. What is the interpretation of “profit” here? Calculate the profit for all levels of inoculation.
- The production of agricultural products like wheat is one of the few examples of a perfectly competitive industry. In this question, we analyze results from a study released by the U.S. Department of Agriculture about wheat production in the United States in 1998.
Question
The average variable cost per acre planted with wheat was $107 per acre. Assuming a yield of 50 bushels per acre, calculate the average variable cost per bushel of wheat.
Prob 7 12a. The average variable cost per acre planted with wheat was $107 per acre. Assuming a yield of 50 bushels per acre, calculate the average variable cost per bushel of wheat.Question
The average price of wheat received by a farmer in 1998 was $2.65 per bushel. Do you think the average farm would have exited the industry in the short run? Explain.
Prob 7 12b. The average price of wheat received by a farmer in 1998 was $2.65 per bushel. Do you think the average farm would have exited the industry in the short run? Explain.Question
With a yield of 50 bushels of wheat per acre, the average total cost per farm was $3.80 per bushel. The harvested acreage for rye (a type of wheat) in the United States fell from 418,000 acres in 1998 to 274,000 in 2006. Using the information on prices and costs here and in parts a and b, explain why this might have happened.
Prob 7 12c. With a yield of 50 bushels of wheat per acre, the average total cost per farm was $3.80 per bushel. The harvested acreage for rye (a type of wheat) in the United States fell from 418,000 acres in 1998 to 274,000 in 2006. Using the information on prices and costs here and in parts a and b, explain why this might have happened.Question
Using the above information, do you think the prices of wheat were higher or lower prior to 1998? Why?
Prob 7 12d. Using the above information, do you think the prices of wheat were higher or lower prior to 1998? Why?
- The accompanying table presents prices for washing and ironing a man’s shirt taken from a survey of California dry cleaners.
Dry Cleaner City Price A-1 Cleaners Santa Barbara $1.50 Regal Cleaners Santa Barbara 1.95 St. Paul Cleaners Santa Barbara 1.95 Zip Kleen Dry Cleaners Santa Barbara 1.95 Effie the Tailor Santa Barbara 2.00 Magnolia Too Goleta 2.00 Master Cleaners Santa Barbara 2.00 Santa Barbara Cleaners Goleta 2.00 Sunny Cleaners Santa Barbara 2.00 Casitas Cleaners Carpinteria 2.10 Rockwell Cleaners Carpinteria 2.10 Norvelle Bass Cleaners Santa Barbara 2.15 Ablitt’s Fine Cleaners Santa Barbara 2.25 California Cleaners Goleta 2.25 Justo the Tailor Santa Barbara 2.25 Pressed 4 Time Goleta 2.50 King’s Cleaners Goleta 2.50 Question
What is the average price per shirt washed and ironed in Goleta? In Santa Barbara?
Prob 7 13a. What is the average price per shirt washed and ironed in Goleta? In Santa Barbara?Question
Draw typical marginal cost and average total cost curves for California Cleaners in Goleta, assuming it is a perfectly competitive firm but is making a profit on each shirt in the short run. Mark the short-run equilibrium point and shade the area that corresponds to the profit made by the dry cleaner.
Prob 7 13b. Draw typical marginal cost and average total cost curves for California Cleaners in Goleta, assuming it is a perfectly competitive firm but is making a profit on each shirt in the short run. Mark the short-run equilibrium point and shade the area that corresponds to the profit made by the dry cleaner.Question
Assume $2.25 is the short-run equilibrium price in Goleta. Draw a typical short-run demand and supply curve for the market. Label the equilibrium point.
Prob 7 13c. Assume $2.25 is the short-run equilibrium price in Goleta. Draw a typical short-run demand and supply curve for the market. Label the equilibrium point.Question
Observing profits in the Goleta area, another dry cleaning service, Diamond Cleaners, enters the market. It charges $1.95 per shirt. What is the new average price of washing and ironing a shirt in Goleta? Illustrate the effect of entry on the average Goleta price by a shift of the short-run supply curve, the demand curve, or both.
Prob 7 13d. Observing profits in the Goleta area, another dry cleaning service, Diamond Cleaners, enters the market. It charges $1.95 per shirt. What is the new average price of washing and ironing a shirt in Goleta? Illustrate the effect of entry on the average Goleta price by a shift of the short-run supply curve, the demand curve, or both.Question
Assume that California Cleaners now charges the new average price and just breaks even (that is, makes zero economic profit) at this price. Show the likely effect of the entry on your diagram in part b.
Prob 7 13e. Assume that California Cleaners now charges the new average price and just breaks even (that is, makes zero economic profit) at this price. Show the likely effect of the entry on your diagram in part b.Question
If the dry cleaning industry is perfectly competitive, what does the average difference in price between Goleta and Santa Barbara imply about costs in the two areas?
Prob 7 13f. If the dry cleaning industry is perfectly competitive, what does the average difference in price between Goleta and Santa Barbara imply about costs in the two areas?
Page 236