Problems
- Each of the following firms possesses market power. Explain its source.
Question
Merck, the producer of the patented cholesterol-lowering drug Zetia
Prob 8 1a. Merck, the producer of the patented cholesterol-lowering drug ZetiaQuestion
WaterWorks, a provider of piped water
Prob 8 1b. WaterWorks, a provider of piped waterQuestion
Chiquita, a supplier of bananas and owner of most banana plantations
Prob 8 1c. Chiquita, a supplier of bananas and owner of most banana plantationsQuestion
The Walt Disney Company, the creators of Mickey Mouse
Prob 8 1d. The Walt Disney Company, the creators of Mickey Mouse
Question
Skyscraper City has a subway system, for which a one-way fare is $1.50. There is pressure on the mayor to reduce the fare by one-third, to $1.00. The mayor is dismayed, thinking that this will mean Skyscraper City is losing one-third of its revenue from sales of subway tickets. The mayor’s economic adviser reminds her that she is focusing only on the price effect and ignoring the quantity effect. Explain why the mayor’s estimate of a one-third loss of revenue is likely to be an overestimate. Illustrate with a diagram.
Prob 8 2. Skyscraper City has a subway system, for which a one-way fare is $1.50. There is pressure on the mayor to reduce the fare by one-third, to $1.00. The mayor is dismayed, thinking that this will mean Skyscraper City is losing one-third of its revenue from sales of subway tickets. The mayor’s economic adviser reminds her that she is focusing only on the price effect and ignoring the quantity effect. Explain why the mayor’s estimate of a one-third loss of revenue is likely to be an overestimate. Illustrate with a diagram.- Consider an industry with the demand curve (D) and marginal cost curve (MC) shown in the accompanying diagram. There is no fixed cost. If the industry is a monopoly, the monopolist’s marginal revenue curve would be MR. Answer the following questions by naming the appropriate points or areas.
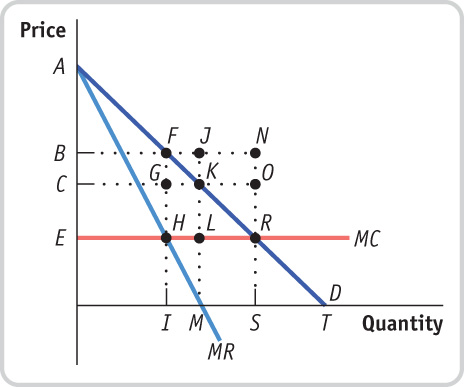
Question
If the industry is perfectly competitive, what will be the total quantity produced? At what price?
Prob 8 3a. If the industry is perfectly competitive, what will be the total quantity produced? At what price?Question
Which area reflects consumer surplus under perfect competition?
Prob 8 3b. Which area reflects consumer surplus under perfect competition?Question
If the industry is a monopoly, what quantity will the monopolist produce? Which price will it charge?
Prob 8 3c. If the industry is a monopoly, what quantity will the monopolist produce? Which price will it charge?Question
Which area reflects the monopolist’s profit?
Prob 8 3d. Which area reflects the monopolist’s profit?Question
Which area reflects consumer surplus under monopoly?
Prob 8 3e. Which area reflects consumer surplus under monopoly?Question
Which area reflects the deadweight loss to society from monopoly?
Prob 8 3f. Which area reflects the deadweight loss to society from monopoly?
- Bob, Bill, Ben, and Brad Baxter have just made a documentary movie about their basketball team. They are thinking about making the movie available for download on the Internet, and they can act as a monopolist if they choose to. Each time the movie is downloaded, their Internet service provider charges them a fee of $4. The Baxter brothers are arguing about which price to charge customers per download. The accompanying table shows the demand schedule for their film.
Price of download Quantity of downloads demanded $10 0 8 1 6 3 4 6 2 10 0 15 Question
Calculate the total revenue and the marginal revenue per download.
Prob 8 4a. Calculate the total revenue and the marginal revenue per download.Question
Bob is proud of the film and wants as many people as possible to download it. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?
Prob 8 4b. Bob is proud of the film and wants as many people as possible to download it. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?Question
Bill wants as much total revenue as possible. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?
Prob 8 4c. Bill wants as much total revenue as possible. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?Question
Ben wants to maximize profit. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?
Prob 8 4d. Ben wants to maximize profit. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?Question
Brad wants to charge the efficient price. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?
Prob 8 4e. Brad wants to charge the efficient price. Which price would he choose? How many downloads would be sold?
- Jimmy has a room that overlooks, from some distance, a major league baseball stadium. He decides to rent a telescope for $50.00 a week and charge his friends and classmates to use it to peep at the game for 30 seconds. He can act as a monopolist for renting out “peeps.” For each person who takes a 30-second peep, it costs Jimmy $0.20 to clean the eyepiece. The accompanying table shows the information Jimmy has gathered about the demand for the service in a given week.Page 271
Price of peep Quantity of peeps demanded $1.20 0 1.00 100 0.90 150 0.80 200 0.70 250 0.60 300 0.50 350 0.40 400 0.30 450 0.20 500 0.10 550 Question
For each price in the table, calculate the total revenue from selling peeps and the marginal revenue per peep.
Prob 8 5a. For each price in the table, calculate the total revenue from selling peeps and the marginal revenue per peep.Question
At what quantity will Jimmy’s profit be maximized? What price will he charge? What will his total profit be?
Prob 8 5b. At what quantity will Jimmy’s profit be maximized? What price will he charge? What will his total profit be?Question
Jimmy’s landlady complains about all the visitors coming into the building and tells Jimmy to stop selling peeps. Jimmy discovers, however, that if he gives the landlady $0.20 for every peep he sells, she will stop complaining. What effect does the $0.20-per-peep bribe have on Jimmy’s marginal cost per peep? What is the new profit-maximizing quantity of peeps? What effect does the $0.20-per-peep bribe have on Jimmy’s total profit?
Prob 8 5c. Jimmy’s landlady complains about all the visitors coming into the building and tells Jimmy to stop selling peeps. Jimmy discovers, however, that if he gives the landlady $0.20 for every peep he sells, she will stop complaining. What effect does the $0.20-per-peep bribe have on Jimmy’s marginal cost per peep? What is the new profit-maximizing quantity of peeps? What effect does the $0.20-per-peep bribe have on Jimmy’s total profit?
- Suppose that De Beers is a monopolist in the market for diamonds. De Beers has five potential customers: Raquel, Jackie, Joan, Mia, and Sophia. Each of these customers will buy at most one diamond—and only if the price is just equal to, or lower than, her willingness to pay. Raquel’s willingness to pay is $400; Jackie’s, $300; Joan’s, $200; Mia’s, $100; and Sophia’s, $0. De Beers’s marginal cost per diamond is $100. This leads to the demand schedule for diamonds shown in the accompanying table.
Price of diamond Quantity of diamonds demanded $500 0 400 1 300 2 200 3 100 4 0 5 Question
Calculate De Beers’s total revenue and its marginal revenue. From your calculation, draw the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve.
Prob 8 6a. Calculate De Beers’s total revenue and its marginal revenue. From your calculation, draw the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve.Question
Explain why De Beers faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
Prob 8 6b. Explain why De Beers faces a downward-sloping demand curve.Question
Explain why the marginal revenue from an additional diamond sale is less than the price of the diamond.
Prob 8 6c. Explain why the marginal revenue from an additional diamond sale is less than the price of the diamond.Question
Suppose De Beers currently charges $200 for its diamonds. If it lowers the price to $100, how large is the price effect? How large is the quantity effect?
Prob 8 6d. Suppose De Beers currently charges $200 for its diamonds. If it lowers the price to $100, how large is the price effect? How large is the quantity effect?Question
Add the marginal cost curve to your diagram from part a and determine which quantity maximizes De Beers’s profit and which price De Beers will charge.
Prob 8 6e. Add the marginal cost curve to your diagram from part a and determine which quantity maximizes De Beers’s profit and which price De Beers will charge.
- Use the demand schedule for diamonds given in Problem 6. The marginal cost of producing diamonds is constant at $100. There is no fixed cost.
Question
If De Beers charges the monopoly price, how large is the individual consumer surplus that each buyer experiences? Calculate total consumer surplus by summing the individual consumer surpluses. How large is producer surplus?
Prob 8 7a. If De Beers charges the monopoly price, how large is the individual consumer surplus that each buyer experiences? Calculate total consumer surplus by summing the individual consumer surpluses. How large is producer surplus?
Question
What is the perfectly competitive price? What quantity will be sold in this perfectly competitive market?
Prob 8 7b. What is the perfectly competitive price? What quantity will be sold in this perfectly competitive market?Question
At the competitive price and quantity, how large is the consumer surplus that each buyer experiences? How large is total consumer surplus? How large is producer surplus?
Prob 8 7c. At the competitive price and quantity, how large is the consumer surplus that each buyer experiences? How large is total consumer surplus? How large is producer surplus?Question
Compare your answer to part c to your answer to part a. How large is the deadweight loss associated with monopoly in this case?
Prob 8 7d. Compare your answer to part c to your answer to part a. How large is the deadweight loss associated with monopoly in this case?
Suppose that upstart Russian and Asian producers enter the market and the market becomes perfectly competitive.
- Download Records decides to release an album by the group Mary and the Little Lamb. It produces the album with no fixed cost, but the total cost of downloading an album to a CD and paying Mary her royalty is $6 per album. Download Records can act as a monopolist. Its marketing division finds that the demand schedule for the album is as shown in the accompanying table.
Price of album Quantity of albums demanded $22 0 20 1,000 18 2,000 16 3,000 14 4,000 12 5,000 10 6,000 8 7,000 Page 272Question
Calculate the total revenue and the marginal revenue per album.
Prob 8 8a. Calculate the total revenue and the marginal revenue per album.Question
The marginal cost of producing each album is constant at $6. To maximize profit, what level of output should Download Records choose, and which price should it charge for each album?
Prob 8 8b. The marginal cost of producing each album is constant at $6. To maximize profit, what level of output should Download Records choose, and which price should it charge for each album?Question
Mary renegotiates her contract and now needs to be paid a higher royalty per album. So the marginal cost rises to be constant at $14. To maximize profit, what level of output should Download Records now choose, and which price should it charge for each album?
Prob 8 8c. Mary renegotiates her contract and now needs to be paid a higher royalty per album. So the marginal cost rises to be constant at $14. To maximize profit, what level of output should Download Records now choose, and which price should it charge for each album?
- The accompanying diagram illustrates your local electricity company’s natural monopoly. The diagram shows the demand curve for kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity, the company’s marginal revenue (MR) curve, its marginal cost (MC) curve, and its average total cost (ATC) curve. The government wants to regulate the monopolist by imposing a price ceiling.
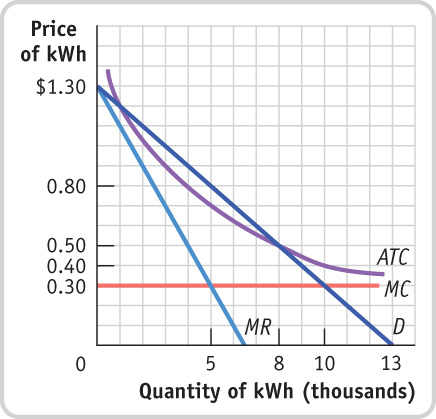
Question
If the government does not regulate this monopolist, which price will it charge? Illustrate the inefficiency this creates by shading the deadweight loss from monopoly.
Prob 8 9a. If the government does not regulate this monopolist, which price will it charge? Illustrate the inefficiency this creates by shading the deadweight loss from monopoly.Question
If the government imposes a price ceiling equal to the marginal cost, $0.30, will the monopolist make profits or lose money? Shade the area of profit (or loss) for the monopolist. If the government does impose this price ceiling, do you think the firm will continue to produce in the long run?
Prob 8 9b. If the government imposes a price ceiling equal to the marginal cost, $0.30, will the monopolist make profits or lose money? Shade the area of profit (or loss) for the monopolist. If the government does impose this price ceiling, do you think the firm will continue to produce in the long run?Question
If the government imposes a price ceiling of $0.50, will the monopolist make a profit, lose money, or break even?
Prob 8 9c. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $0.50, will the monopolist make a profit, lose money, or break even?
Question
A monopolist knows that in order to expand the quantity of output it produces from 8 to 9 units it must lower the price of its output from $2 to $1. Calculate the quantity effect and the price effect. Use these results to calculate the monopolist’s marginal revenue of producing the 9th unit. The marginal cost of producing the 9th unit is positive. Is it a good idea for the monopolist to produce the 9th unit?
Prob 8 10. A monopolist knows that in order to expand the quantity of output it produces from 8 to 9 units it must lower the price of its output from $2 to $1. Calculate the quantity effect and the price effect. Use these results to calculate the monopolist’s marginal revenue of producing the 9th unit. The marginal cost of producing the 9th unit is positive. Is it a good idea for the monopolist to produce the 9th unit?- In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is charged with promoting competition and challenging mergers that would likely lead to higher prices. Several years ago, Staples and Office Depot, two of the largest office supply superstores, announced their agreement to merge.
Question
Some critics of the merger argued that, in many parts of the country, a merger between the two companies would create a monopoly in the office supply superstore market. Based on the FTC’s argument and its mission to challenge mergers that would likely lead to higher prices, do you think it allowed the merger?
Prob 8 11a. Some critics of the merger argued that, in many parts of the country, a merger between the two companies would create a monopoly in the office supply superstore market. Based on the FTC’s argument and its mission to challenge mergers that would likely lead to higher prices, do you think it allowed the merger?Question
Staples and Office Depot argued that, while in some parts of the country they might create a monopoly in the office supply superstore market, the FTC should consider the larger market for all office supplies, which includes many smaller stores that sell office supplies (such as grocery stores and other retailers). In that market, Staples and Office Depot would face competition from many other, smaller stores. If the market for all office supplies is the relevant market that the FTC should consider, would it make the FTC more or less likely to allow the merger?
Prob 8 11b. Staples and Office Depot argued that, while in some parts of the country they might create a monopoly in the office supply superstore market, the FTC should consider the larger market for all office supplies, which includes many smaller stores that sell office supplies (such as grocery stores and other retailers). In that market, Staples and Office Depot would face competition from many other, smaller stores. If the market for all office supplies is the relevant market that the FTC should consider, would it make the FTC more or less likely to allow the merger?
- The accompanying table shows the demand schedule for vitamin D. Suppose that the marginal cost of producing vitamin D is zero.
Price of vitamin D(per ton) Quantity of vitamin D demanded(tons) $8 0 7 10 6 20 5 30 4 40 3 50 2 60 1 70 Question
Assume that BASF is the only producer of vitamin D and acts as a monopolist. It currently produces 40 tons of vitamin D at $4 per ton. If BASF were to produce 10 more tons, what would be the price effect for BASF? What would be the quantity effect? Would BASF have an incentive to produce those 10 additional tons?
Prob 8 12a. Assume that BASF is the only producer of vitamin D and acts as a monopolist. It currently produces 40 tons of vitamin D at $4 per ton. If BASF were to produce 10 more tons, what would be the price effect for BASF? What would be the quantity effect? Would BASF have an incentive to produce those 10 additional tons?Question
Now assume that Roche enters the market by also producing vitamin D and the market is now a duopoly. BASF and Roche agree to produce 40 tons of vitamin D in total, 20 tons each. BASF cannot be punished for deviating from the agreement with Roche. If BASF, on its own, were to deviate from that agreement and produce 10 more tons, what would be the price effect for BASF? What would be the quantity effect for BASF? Would BASF have an incentive to produce those 10 additional tons?
Prob 8 12b. Now assume that Roche enters the market by also producing vitamin D and the market is now a duopoly. BASF and Roche agree to produce 40 tons of vitamin D in total, 20 tons each. BASF cannot be punished for deviating from the agreement with Roche. If BASF, on its own, were to deviate from that agreement and produce 10 more tons, what would be the price effect for BASF? What would be the quantity effect for BASF? Would BASF have an incentive to produce those 10 additional tons?
- Suppose you are an economist working for the Antitrust Division of the Department of Justice. In each of the following cases you are given the task of determining whether the behavior warrants an antitrust investigation for possible illegal acts or is just an example of undesirable, but not illegal, tacit collusion. Explain your reasoning.Page 273
Question
Two companies dominate the industry for industrial lasers. Several people sit on the boards of directors of both companies.
Prob 8 13a. Two companies dominate the industry for industrial lasers. Several people sit on the boards of directors of both companies.Question
Three banks dominate the market for banking in a given state. Their profits have been going up recently as they add new fees for customer transactions. Advertising among the banks is fierce, and new branches are springing up in many locations.
Prob 8 13b. Three banks dominate the market for banking in a given state. Their profits have been going up recently as they add new fees for customer transactions. Advertising among the banks is fierce, and new branches are springing up in many locations.Question
The two oil companies that produce most of the petroleum for the western half of the United States have decided to forgo building their own pipelines and to share a common pipeline, the only means of transporting petroleum products to that market.
Prob 8 13c. The two oil companies that produce most of the petroleum for the western half of the United States have decided to forgo building their own pipelines and to share a common pipeline, the only means of transporting petroleum products to that market.Question
The two major companies that dominate the market for herbal supplements have each created a subsidiary that sells the same product as the parent company in large quantities but with a generic name.
Prob 8 13d. The two major companies that dominate the market for herbal supplements have each created a subsidiary that sells the same product as the parent company in large quantities but with a generic name.Question
The two largest credit card companies, Passport and OmniCard, have required all retailers who accept their cards to agree to limit their use of rival credit cards.
Prob 8 13e. The two largest credit card companies, Passport and OmniCard, have required all retailers who accept their cards to agree to limit their use of rival credit cards.
- Use the three conditions for monopolistic competition discussed in the chapter to decide which of the following firms are likely to be operating as monopolistic competitors. If they are not monopolistically competitive firms, are they monopolists, oligopolists, or perfectly competitive firms?
Question
A local band that plays for weddings, parties, and so on
Prob 8 14a. A local band that plays for weddings, parties, and so onQuestion
Minute Maid, a producer of individual-serving juice boxes
Prob 8 14b. Minute Maid, a producer of individual-serving juice boxesQuestion
Your local dry cleaner
Prob 8 14c. Your local dry cleanerQuestion
A farmer who produces soybeans
Prob 8 14d. A farmer who produces soybeans
Question
You are thinking of setting up a coffee shop. The market structure for coffee shops is monopolistic competition. There are three Starbucks shops and two other coffee shops very much like Starbucks in your town already. In order for you to have some degree of market power, you may want to differentiate your coffee shop. Thinking about the three different ways in which products can be differentiated, explain how you would decide whether you should copy Starbucks or whether you should sell coffee in a completely different way.
Prob 8 15. You are thinking of setting up a coffee shop. The market structure for coffee shops is monopolistic competition. There are three Starbucks shops and two other coffee shops very much like Starbucks in your town already. In order for you to have some degree of market power, you may want to differentiate your coffee shop. Thinking about the three different ways in which products can be differentiated, explain how you would decide whether you should copy Starbucks or whether you should sell coffee in a completely different way.
Extend Your Understanding
- Prior to the late 1990s, the same company that generated your electricity also distributed it to you over high-voltage lines. Since then, 16 states and the District of Columbia have begun separating the generation from the distribution of electricity, allowing competition between electricity generators and between electricity distributors.
Question
Assume that the market for electricity distribution was and remains a natural monopoly. Use a graph to illustrate the market for electricity distribution if the government sets price equal to average total cost.
Prob 8 16a. Assume that the market for electricity distribution was and remains a natural monopoly. Use a graph to illustrate the market for electricity distribution if the government sets price equal to average total cost.Question
Assume that deregulation of electricity generation creates a perfectly competitive market. Also assume that electricity generation does not exhibit the characteristics of a natural monopoly. Use a graph to illustrate the cost curves in the long-run equilibrium for an individual firm in this industry.
Prob 8 16b. Assume that deregulation of electricity generation creates a perfectly competitive market. Also assume that electricity generation does not exhibit the characteristics of a natural monopoly. Use a graph to illustrate the cost curves in the long-run equilibrium for an individual firm in this industry.
- The market for olive oil in New York City is controlled by two families, the Sopranos and the Contraltos. Both families will ruthlessly eliminate any other family that attempts to enter the New York City olive oil market. The marginal cost of producing olive oil is constant and equal to $40 per gallon. There is no fixed cost. The accompanying table gives the market demand schedule for olive oil.
Price of olive oil(per gallon) Quantity of olive oil demanded(gallons) $100 1,000 90 1,500 80 2,000 70 2,500 60 3,000 50 3,500 40 4,000 30 4,500 20 5,000 10 5,500 Question
Suppose the Sopranos and the Contraltos form a cartel. For each of the quantities given in the table, calculate the total revenue for their cartel and the marginal revenue for each additional gallon. How many gallons of olive oil would the cartel sell in total and at what price? The two families share the market equally (each produces half of the total output of the cartel). How much profit does each family make?
Prob 8 17a. Suppose the Sopranos and the Contraltos form a cartel. For each of the quantities given in the table, calculate the total revenue for their cartel and the marginal revenue for each additional gallon. How many gallons of olive oil would the cartel sell in total and at what price? The two families share the market equally (each produces half of the total output of the cartel). How much profit does each family make?Question
Uncle Junior, the head of the Soprano family, breaks the agreement and sells 500 more gallons of olive oil than under the cartel agreement. Assuming the Contraltos maintain the agreement, how does this affect the price for olive oil and the profit earned by each family?
Prob 8 17b. Uncle Junior, the head of the Soprano family, breaks the agreement and sells 500 more gallons of olive oil than under the cartel agreement. Assuming the Contraltos maintain the agreement, how does this affect the price for olive oil and the profit earned by each family?Question
Anthony Contralto, the head of the Contralto family, decides to punish Uncle Junior by increasing his sales by 500 gallons as well. How much profit does each family earn now?
Prob 8 17c. Anthony Contralto, the head of the Contralto family, decides to punish Uncle Junior by increasing his sales by 500 gallons as well. How much profit does each family earn now?