Comparative Advantage and International Trade
Goods and services purchased from other countries are imports; goods and services sold to other countries are exports.
The United States buys smartphones—
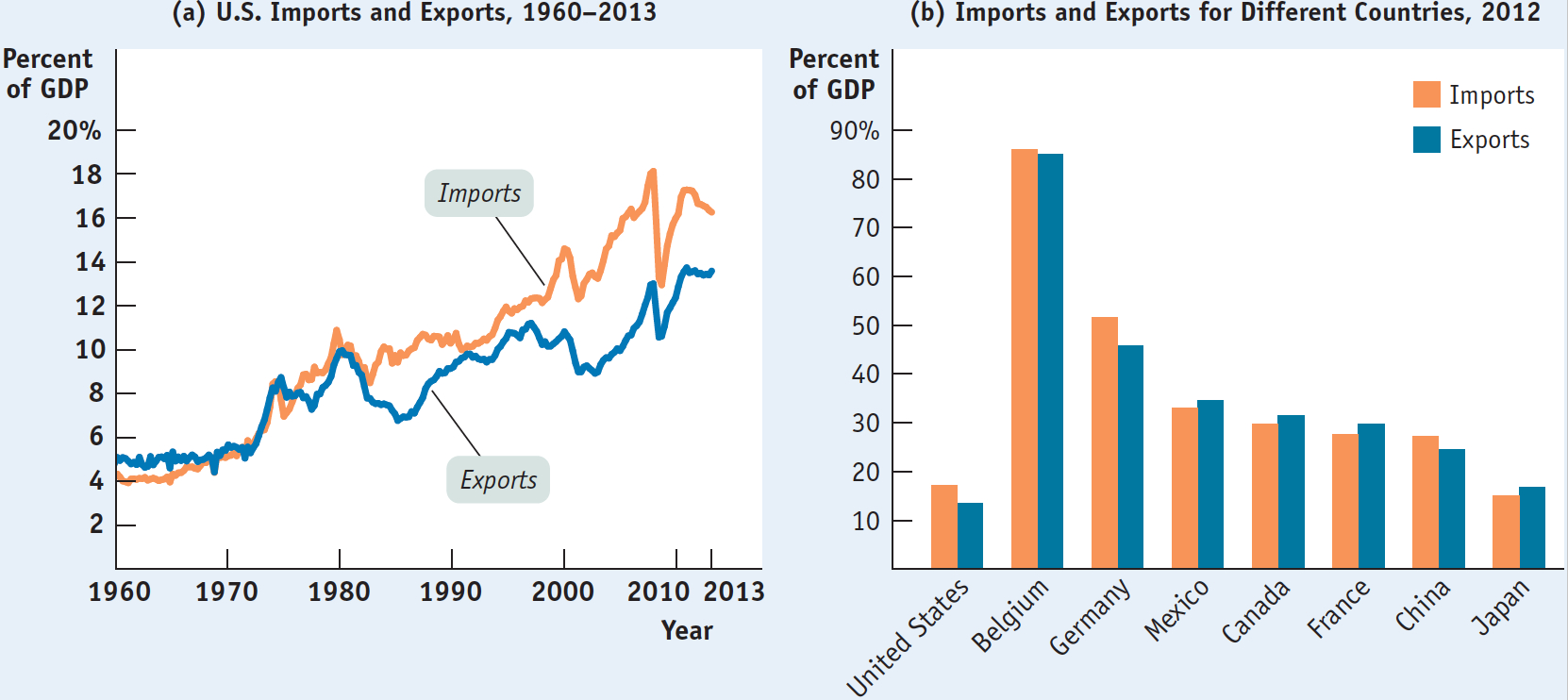
As illustrated by the opening story, imports and exports have taken on an increasingly important role in the U.S. economy. Over the last 50 years, both imports into and exports from the United States have grown faster than the U.S. economy. Panel (a) of Figure 8-1 shows how the values of U.S. imports and exports have grown as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP). Panel (b) shows imports and exports as a percentage of GDP for a number of countries. It shows that foreign trade is significantly more important for many other countries than it is for the United States. (Japan is the exception.)
8-1
The Growing Importance of International Trade
Globalization is the phenomenon of growing economic linkages among countries.
Hyperglobalization is the phenomenon of extremely high levels of international trade.
Foreign trade isn’t the only way countries interact economically. In the modern world, investors from one country often invest funds in another nation; many companies are multinational, with subsidiaries operating in several countries; and a growing number of individuals work in a country different from the one in which they were born. The growth of all these forms of economic linkages among countries is often called globalization. And as we saw in the opening story, certain sectors of the economy are characterized by extremely high levels of international trade. This hyperglobalization is often the result of supply chains of production that span the globe, in which each stage of a good’s production takes place in a different country—
In this chapter, however, we’ll focus mainly on international trade. To understand why international trade occurs and why economists believe it is beneficial to the economy, we will first review the concept of comparative advantage.
Production Possibilities and Comparative Advantage, Revisited
To produce phones, any country must use resources—
In some cases, it’s easy to see why the opportunity cost of producing a good is especially low in a given country. Consider, for example, shrimp—
Conversely, other goods are not produced as easily in Vietnam as in the United States. For example, Vietnam doesn’t have the base of skilled workers and technological know-

In other cases, matters are a bit less obvious. It’s as easy to assemble smartphones in the United States as it is in China, and Chinese electronics workers are, if anything, less efficient than their U.S. counterparts. But Chinese workers are a lot less productive than U.S. workers in other areas, such as automobile and chemical production. This means that diverting a Chinese worker into assembling phones reduces output of other goods less than diverting a U.S. worker into assembling phones. That is, the opportunity cost of assembling phones in China is less than it is in the United States.
Notice that we said the opportunity cost of assembling phones. As we’ve seen, most of the value of a “Chinese made” phone actually comes from other countries. For the sake of exposition, however, let’s ignore that complication and consider a hypothetical case in which China makes phones from scratch.
So we say that China has a comparative advantage in producing smartphones. Let’s repeat the definition of comparative advantage from Chapter 2: A country has a comparative advantage in producing a good or service if the opportunity cost of producing the good or service is lower for that country than for other countries.
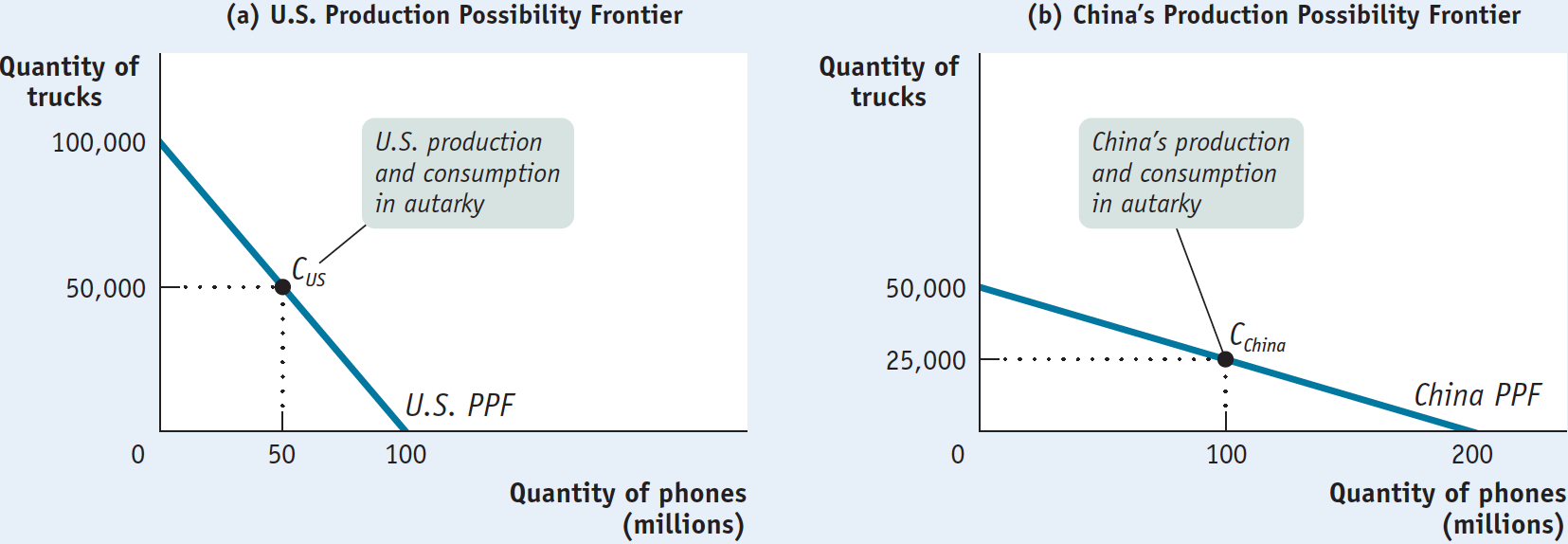
Figure 8-2 provides a hypothetical numerical example of comparative advantage in international trade. We assume that only two goods are produced and consumed, phones and Ford trucks, and that there are only two countries in the world, the United States and China. The figure shows hypothetical production possibility frontiers for the United States and China.
8-2
Comparative Advantage and the Production Possibility Frontier
The Ricardian model of international trade analyzes international trade under the assumption that opportunity costs are constant.
As in Chapter 2, we simplify the model by assuming that the production possibility frontiers are straight lines, as shown in Figure 2-1, rather than the more realistic bowed-
In Figure 8-2 we show a situation in which the United States can produce 100,000 trucks if it produces no phones, or 100 million phones if it produces no trucks. Thus, the slope of the U.S. production possibility frontier, or PPF, is −100,000/100 = −1,000. That is, to produce an additional million phones, the United States must forgo the production of 1,000 trucks.
Similarly, China can produce 50,000 trucks if it produces no phones or 200 million phones if it produces no trucks. Thus, the slope of China’s PPF is −50,000/200 = −250. That is, to produce an additional million phones, China must forgo the production of 250 trucks.
Autarky is a situation in which a country does not trade with other countries.
Economists use the term autarky to refer to a situation in which a country does not trade with other countries. We assume that in autarky the United States chooses to produce and consume 50 million phones and 50,000 trucks. We also assume that in autarky China produces 100 million phones and 25,000 trucks.
The trade-
8-1
U.S. and Chinese Opportunity Costs of Phones and Trucks
|
U.S. Opportunity Cost |
Chinese Opportunity Cost |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 million phones |
1,000 trucks |
> |
250 trucks |
|
1 truck |
1,000 phones |
< |
4,000 phones |
TABLE 8-
As we learned in Chapter 2, each country can do better by engaging in trade than it could by not trading. A country can accomplish this by specializing in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantage and exporting that good, while importing the good in which it has a comparative disadvantage.
Let’s see how this works.
The Gains from International Trade
Figure 8-3 illustrates how both countries can gain from specialization and trade, by showing a hypothetical rearrangement of production and consumption that allows each country to consume more of both goods. Again, panel (a) represents the United States and panel (b) represents China. In each panel we indicate again the autarky production and consumption assumed in Figure 8-2.
8-3
The Gains from International Trade
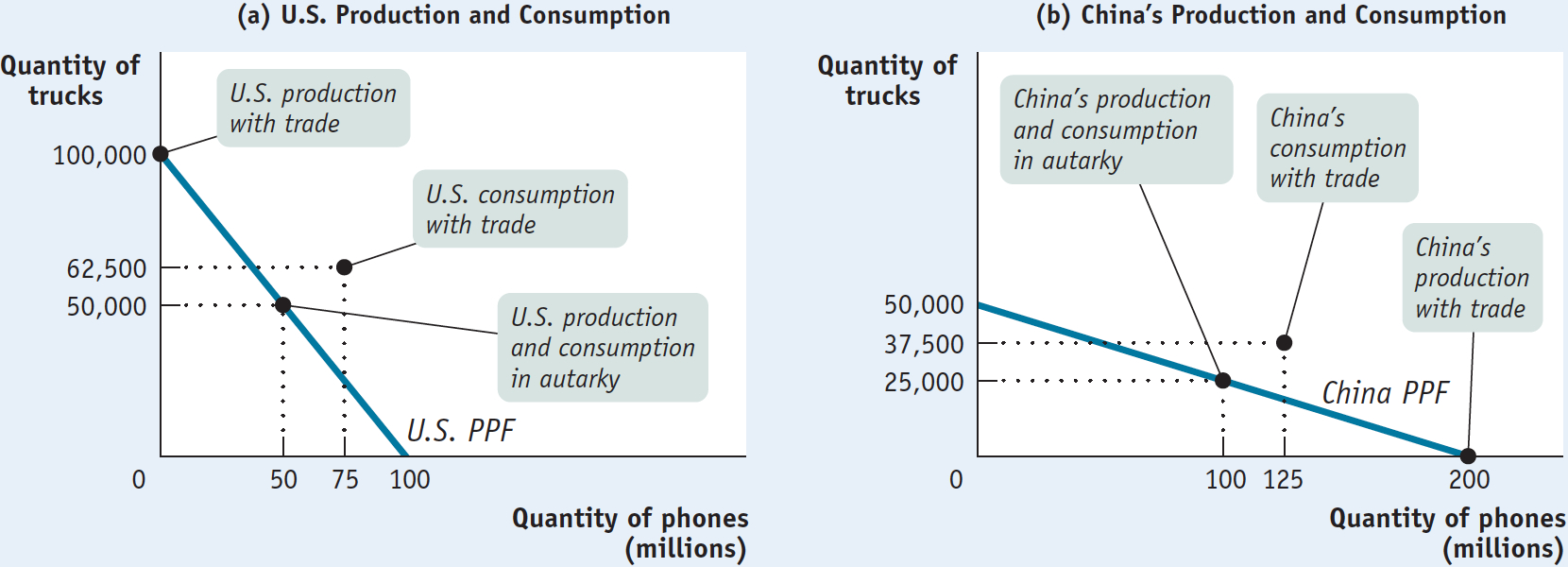
Once trade becomes possible, however, everything changes. With trade, each country can move to producing only the good in which it has a comparative advantage—
Table 8-2 sums up the changes as a result of trade and shows why both countries can gain. The left part of the table shows the autarky situation, before trade, in which each country must produce the goods it consumes. The right part of the table shows what happens as a result of trade. After trade, the United States specializes in the production of trucks, producing 100,000 trucks and no phones; China specializes in the production of phones, producing 200 million phones and no trucks.
8-2
How the United States and China Gain from Trade
|
In Autarky |
With Trade |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Production |
Consumption |
Production |
Consumption |
Gains from trade |
||
|
United States |
Million phones |
50 |
50 |
0 |
75 |
+25 |
|
Trucks |
50,000 |
50,000 |
100,000 |
62,500 |
+12,500 |
|
|
China |
Million phones |
100 |
100 |
200 |
125 |
+25 |
|
Trucks |
25,000 |
25,000 |
0 |
37,500 |
+12,500 |
|
TABLE 8-
The result is a rise in total world production of both goods. As you can see in the Table 8-2 column at far right showing consumption with trade, the United States is able to consume both more trucks and more phones than before, even though it no longer produces phones, because it can import phones from China. China can also consume more of both goods, even though it no longer produces trucks, because it can import trucks from the United States.
The key to this mutual gain is the fact that trade liberates both countries from self-
In this example we have simply assumed the post-
One requirement that the relative price must satisfy is that no country pays a relative price greater than its opportunity cost of obtaining the good in autarky. That is, the United States won’t pay more than 1,000 trucks for one million phones from China, and China won’t pay more than 4,000 phones for each truck from the United States. Once this requirement is satisfied, the actual relative price in international trade is determined by supply and demand—
Comparative Advantage versus Absolute Advantage
It’s easy to accept the idea that Vietnam and Thailand have a comparative advantage in shrimp production: they have a tropical climate that’s better suited to shrimp farming than that of the United States (even along the Gulf Coast), and they have a lot of usable coastal area. So the United States imports shrimp from Vietnam and Thailand. In other cases, however, it may be harder to understand why we import certain goods from abroad.
U.S. imports of phones from China are a case in point. There’s nothing about China’s climate or resources that makes it especially good at assembling electronic devices. In fact, it almost surely would take fewer hours of labor to assemble a smartphone or a tablet in the United States than in China.
Why, then, do we buy phones assembled in China? Because the gains from trade depend on comparative advantage, not absolute advantage. Yes, it would take less labor to assemble a phone in the United States than in China. That is, the productivity of Chinese electronics workers is less than that of their U.S. counterparts. But what determines comparative advantage is not the amount of resources used to produce a good but the opportunity cost of that good—

Here’s how it works: Chinese workers have low productivity compared with U.S. workers in the electronics industry. But Chinese workers have even lower productivity compared with U.S. workers in other industries. Because Chinese labor productivity in industries other than electronics is relatively very low, producing a phone in China, even though it takes a lot of labor, does not require forgoing the production of large quantities of other goods.
In the United States, the opposite is true: very high productivity in other industries (such as automobiles) means that assembling electronic products in the United States, even though it doesn’t require much labor, requires sacrificing lots of other goods. So the opportunity cost of producing electronics is less in China than in the United States. Despite its lower labor productivity, China has a comparative advantage in the production of many consumer electronics, although the United States has an absolute advantage.
The source of China’s comparative advantage in consumer electronics is reflected in global markets by the wages Chinese workers are paid. That’s because a country’s wage rates, in general, reflect its labor productivity. In countries where labor is highly productive in many industries, employers are willing to pay high wages to attract workers, so competition among employers leads to an overall high wage rate. In countries where labor is less productive, competition for workers is less intense and wage rates are correspondingly lower.
As the accompanying Global Comparison shows, there is indeed a strong relationship between overall levels of productivity and wage rates around the world. Because China has generally low productivity, it has a relatively low wage rate. Low wages, in turn, give China a cost advantage in producing goods where its productivity is only moderately low, like consumer electronics. As a result, it’s cheaper to produce these goods in China than in the United States.
The kind of trade that takes place between low-
 | Productivity and Wages Around the World |
Is it true that both the pauper labor argument and the sweatshop labor argument are fallacies? Yes, it is. The real explanation for low wages in poor countries is low overall productivity.
The graph shows estimates of labor productivity, measured by the value of output (GDP) per worker, and wages, measured by the hourly compensation of the average worker, for several countries in 2012. Both productivity and wages are expressed as percentages of U.S. productivity and wages; for example, productivity and wages in Japan were 70% and 101%, respectively, of their U.S. levels. You can see the strong positive relationship between productivity and wages. The relationship isn’t perfect. For example, Norway has higher wages than its productivity might lead you to expect. But simple comparisons of wages give a misleading sense of labor costs in poor countries: their low wage advantage is mostly offset by low productivity.
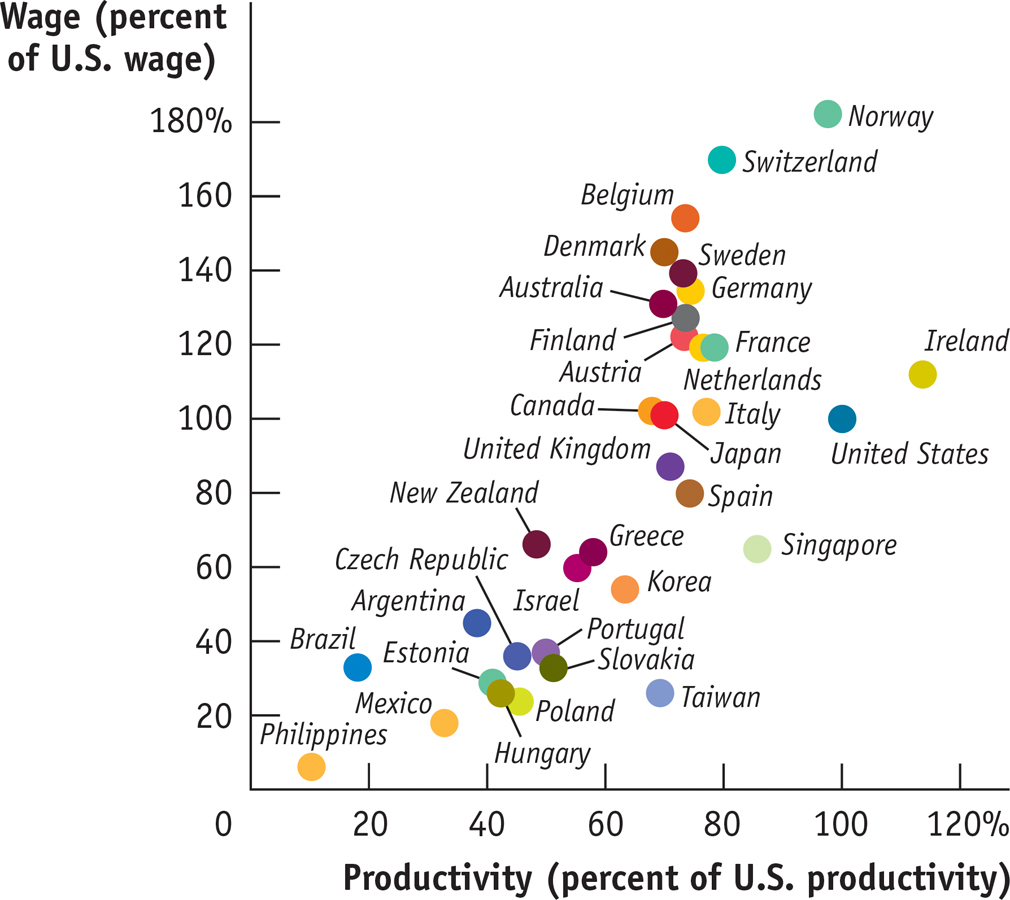
Sources: The Conference Board; Penn World Table 8.0.
Both fallacies miss the nature of gains from trade: it’s to the advantage of both countries if the poorer, lower-
It’s particularly important to understand that buying a good made by someone who is paid much lower wages than most U.S. workers doesn’t necessarily imply that you’re taking advantage of that person. It depends on the alternatives. Because workers in poor countries have low productivity across the board, they are offered low wages whether they produce goods exported to America or goods sold in local markets. A job that looks terrible by rich-
International trade that depends on low-
Sources of Comparative Advantage
International trade is driven by comparative advantage, but where does comparative advantage come from? Economists who study international trade have found three main sources of comparative advantage: international differences in climate, international differences in factor endowments, and international differences in technology.
Differences in Climate One key reason the opportunity cost of producing shrimp in Vietnam and Thailand is less than in the United States is that shrimp need warm water—
Differences in Factor Endowments Canada is a major exporter of forest products—

Forestland, like labor and capital, is a factor of production: an input used to produce goods and services. (Recall from Chapter 2 that the factors of production are land, labor, physical capital, and human capital.) Due to history and geography, the mix of available factors of production differs among countries, providing an important source of comparative advantage. The relationship between comparative advantage and factor availability is found in an influential model of international trade, the Heckscher-
The factor intensity of production of a good is a measure of which factor is used in relatively greater quantities than other factors in production.
Two key concepts in the model are factor abundance and factor intensity. Factor abundance refers to how large a country’s supply of a factor is relative to its supply of other factors. Factor intensity refers to the fact that producers use different ratios of factors of production in the production of different goods. For example, oil refineries use much more capital per worker than clothing factories. Economists use the term factor intensity to describe this difference among goods: oil refining is capital-
According to the Heckscher-
According to the Heckscher-
The basic intuition behind this result is simple and based on opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of a given factor—
The most dramatic example of the validity of the Heckscher-
The fact that international trade is the result of differences in factor endowments helps explain another fact: international specialization of production is often incomplete. That is, a country often maintains some domestic production of a good that it imports. A good example of this is the United States and oil. Saudi Arabia exports oil to the United States because Saudi Arabia has an abundant supply of oil relative to its other factors of production; the United States exports medical devices to Saudi Arabia because it has an abundant supply of expertise in medical technology relative to its other factors of production. But the United States also produces some oil domestically because the size of its domestic oil reserves in Texas and Alaska (and now, increasingly, its oil shale reserves elsewhere) makes it economical to do so.
In our supply and demand analysis in the next section, we’ll consider incomplete specialization by a country to be the norm. We should emphasize, however, that the fact that countries often incompletely specialize does not in any way change the conclusion that there are gains from trade.
Differences in Technology In the 1970s and 1980s, Japan became by far the world’s largest exporter of automobiles, selling large numbers to the United States and the rest of the world. Japan’s comparative advantage in automobiles wasn’t the result of climate. Nor can it easily be attributed to differences in factor endowments: aside from a scarcity of land, Japan’s mix of available factors is quite similar to that in other advanced countries. Instead, Japan’s comparative advantage in automobiles was based on the superior production techniques developed by its manufacturers, which allowed them to produce more cars with a given amount of labor and capital than their American or European counterparts.
Increasing Returns to Scale and International Trade
Most analyses of international trade focuses on how differences between countries—
Production of a good is characterized by increasing returns to scale if the productivity of labor and other resources used in production rise with the quantity of output. For example, in an industry characterized by increasing returns to scale, increasing output by 10% might require only 8% more labor and 9% more raw materials. Examples of industries with increasing returns to scale include auto manufacturing, oil refining, and the production of jumbo jets, all of which require large outlays of capital. Increasing returns to scale (sometimes also called economies of scale) can give rise to monopoly, a situation in which an industry is composed of only one producer, because it gives large firms a cost advantage over small ones.
But increasing returns to scale can also give rise to international trade. The logic runs as follows: if production of a good is characterized by increasing returns to scale, it makes sense to concentrate production in only a few locations, so each location has a high level of output. But that also means production occurs in only a few countries that export the good to other countries. A commonly cited example is the North American auto industry: although both the United States and Canada produce automobiles and their components, each particular model or component tends to be produced in only one of the two countries and exported to the other. Increasing returns to scale probably play a large role in the trade in manufactured goods between advanced countries, which is about 25% of the total value of world trade.

Japan’s comparative advantage in automobiles was a case of comparative advantage caused by differences in technology—
The causes of differences in technology are somewhat mysterious. Sometimes they seem to be based on knowledge accumulated through experience—
!worldview! ECONOMICS in Action: How Hong Kong Lost Its Shirts
How Hong Kong Lost Its Shirts
The rise of Hong Kong was one of the most improbable-
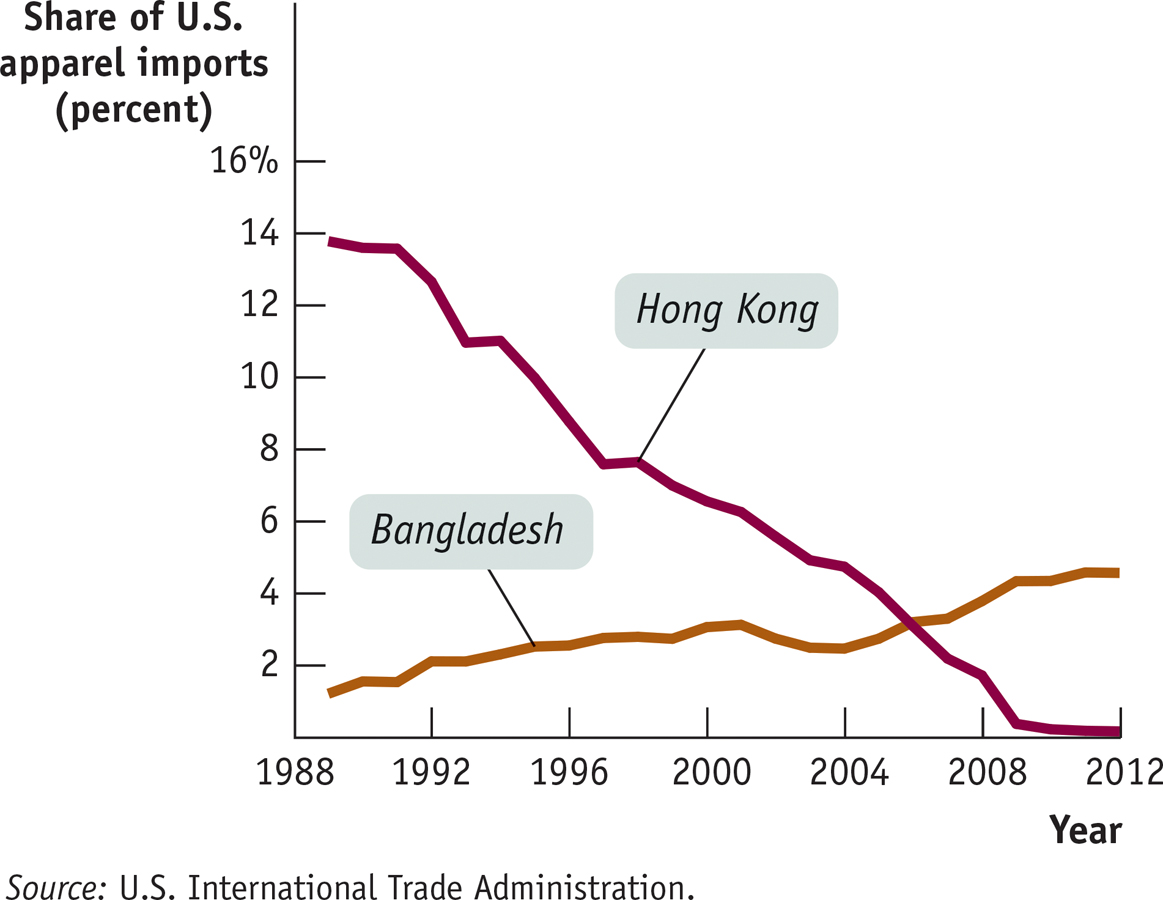
During much of its ascent, Hong Kong’s rise rested, above all, on its clothing industry. In 1980 Hong Kong’s garment and textile sectors employed almost 450,000 workers, close to 20% of total employment. These workers overwhelmingly made apparel—
Since then, however, the Hong Kong clothing industry has fallen sharply in size—
8-4
Education, Skill Intensity, and Trade
Why did Hong Kong lose its comparative advantage in making shirts, pants, and so on? It wasn’t because the city’s garment workers became less productive. Instead, it was because the city got better at other things. Apparel production is a labor-
Quick Review
Imports and exports account for a growing share of the U.S. economy and the economies of many other countries.
The growth of international trade and other international linkages is known as globalization. Extremely high levels of international trade are known as hyperglobalization.
International trade is driven by comparative advantage. The Ricardian model of international trade shows that trade between two countries makes both countries better off than they would be in autarky—that is, there are gains from international trade.
The main sources of comparative advantage are international differences in climate, factor endowments, and technology.
The Heckscher-
Ohlin model shows how comparative advantage can arise from differences in factor endowments: goods differ in their factor intensity, and countries tend to export goods that are intensive in the factors they have in abundance.
8-1
Question 8.1
In the United States, the opportunity cost of 1 ton of corn is 50 bicycles. In China, the opportunity cost of 1 bicycle is 0.01 ton of corn.
Determine the pattern of comparative advantage.
To determine comparative advantage, we must compare the two countries’ opportunity costs for a given good. Take the opportunity cost of 1 ton of corn in terms of bicycles. In China, the opportunity cost of 1 bicycle is 0.01 ton of corn; so the opportunity cost of 1 ton of corn is 1/0.01 bicycles = 100 bicycles. The United States has the comparative advantage in corn since its opportunity cost in terms of bicycles is 50, a smaller number. Similarly, the opportunity cost in the United States of 1 bicycle in terms of corn is 1/50 ton of corn = 0.02 ton of corn. This is greater than 0.01, the Chinese opportunity cost of 1 bicycle in terms of corn, implying that China has a comparative advantage in bicycles.In autarky, the United States can produce 200,000 bicycles if no corn is produced, and China can produce 3,000 tons of corn if no bicycles are produced. Draw each country’s production possibility frontier assuming constant opportunity cost, with tons of corn on the vertical axis and bicycles on the horizontal axis.
Given that the United States can produce 200,000 bicycles if no corn is produced, it can produce 200,000 bicycles × 0.02 ton of corn/bicycle = 4,000 tons of corn when no bicycles are produced. Likewise, if China can produce 3,000 tons of corn if no bicycles are produced, it can produce 3,000 tons of corn × 100 bicycles/ton of corn = 300,000 bicycles if no corn is produced. These points determine the vertical and horizontal intercepts of the U.S. and Chinese production possibility frontiers, as shown in the accompanying diagram.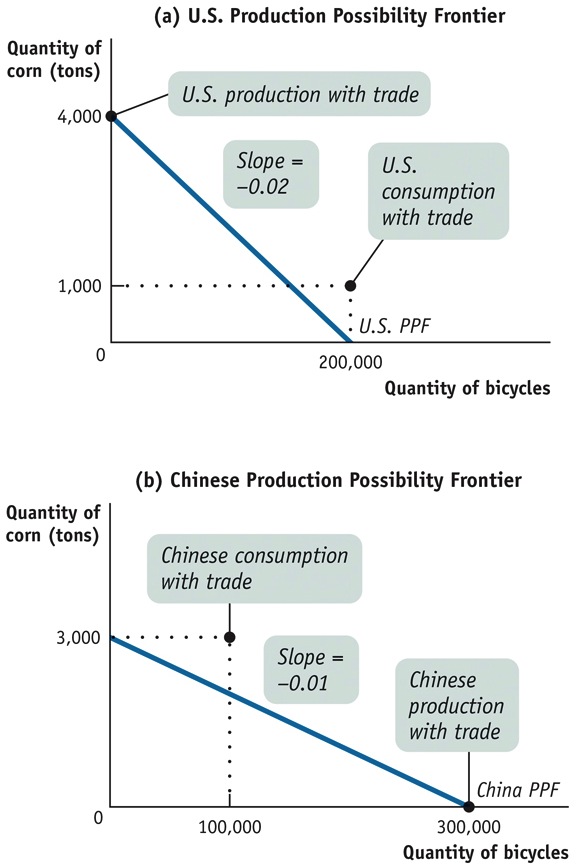
With trade, each country specializes its production. The United States consumes 1,000 tons of corn and 200,000 bicycles; China consumes 3,000 tons of corn and 100,000 bicycles. Indicate the production and consumption points on your diagrams, and use them to explain the gains from trade.
The diagram shows the production and consumption points of the two countries. Each country is clearly better off with international trade because each now consumes a bundle of the two goods that lies outside its own production possibility frontier, indicating that these bundles were unattainable in autarky.
Question 8.2
Explain the following patterns of trade using the Heckscher-
Ohlin model. France exports wine to the United States, and the United States exports movies to France.
According to the Heckscher-Ohlin model, this pattern of trade occurs because the United States has a relatively larger endowment of factors of production, such as human capital and physical capital, that are suited to the production of movies, but France has a relatively larger endowment of factors of production suited to wine-making, such as vineyards and the human capital of vintners.Brazil exports shoes to the United States, and the United States exports shoe-
making machinery to Brazil. According to the Heckscher-Ohlin model, this pattern of trade occurs because the United States has a relatively larger endowment of factors of production, such as human and physical capital, that are suited to making machinery, but Brazil has a relatively larger endowment of factors of production suited to shoe-making, such as unskilled labor and leather.
Solutions appear at back of book.