FIGURE9-2Unit-Elastic Demand, Inelastic Demand, and Elastic Demand
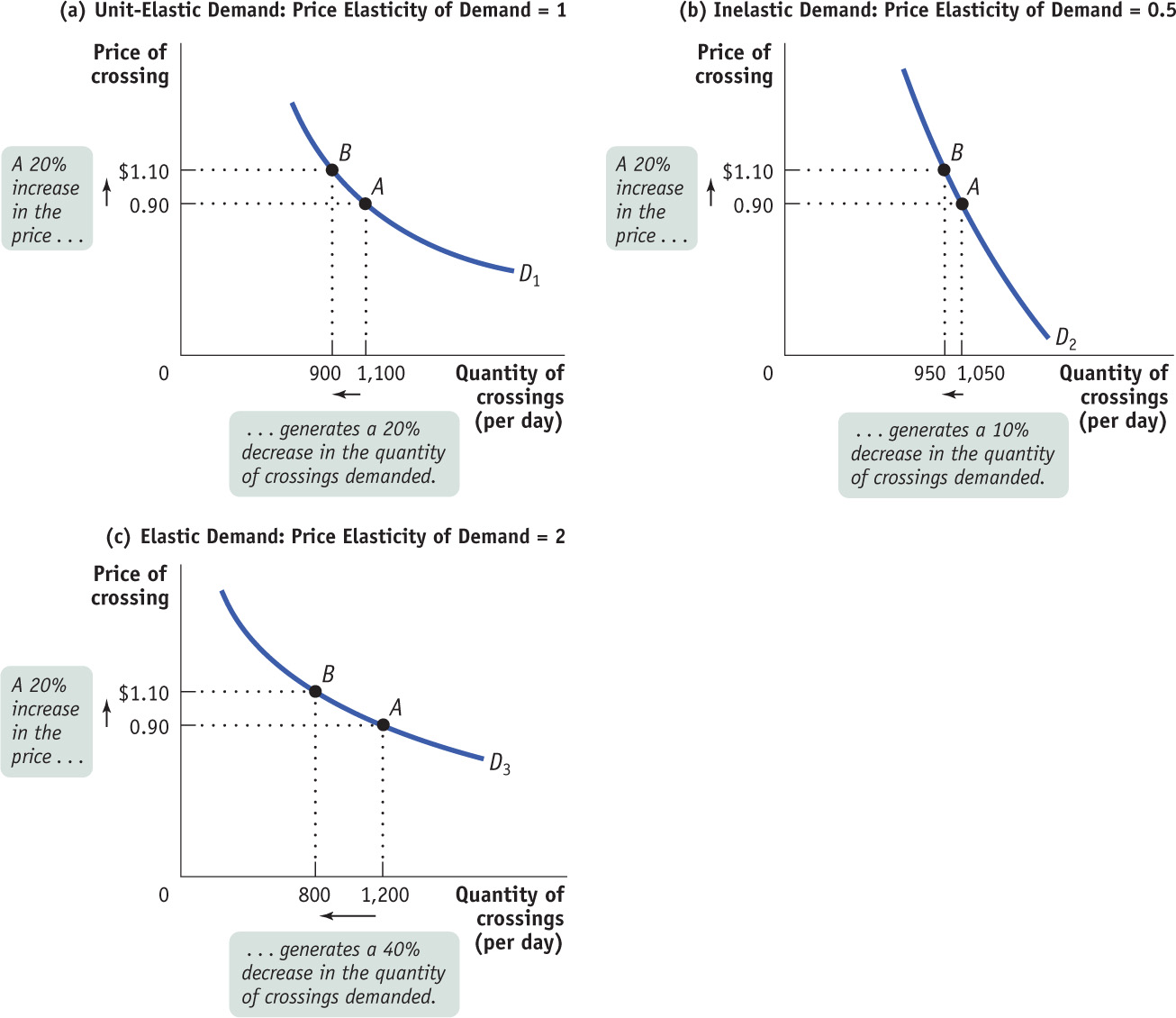
Panel (a) shows a case of unit-elastic demand: a 20% increase in price generates a 20% decline in quantity demanded, representing a price elasticity of demand of 1. Panel (b) shows a case of inelastic demand: a 20% increase in price generates a 10% decline in quantity demanded, representing a price elasticity of demand of 0.5. A case of elastic demand is shown in Panel (c): a 20% increase in price causes a 40% decline in quantity demanded, representing a price elasticity of demand of 2. All percentages are calculated using the midpoint method.