FIGURE28-1Comparing the Demand Curves of a Perfectly Competitive Producer and a Monopolist
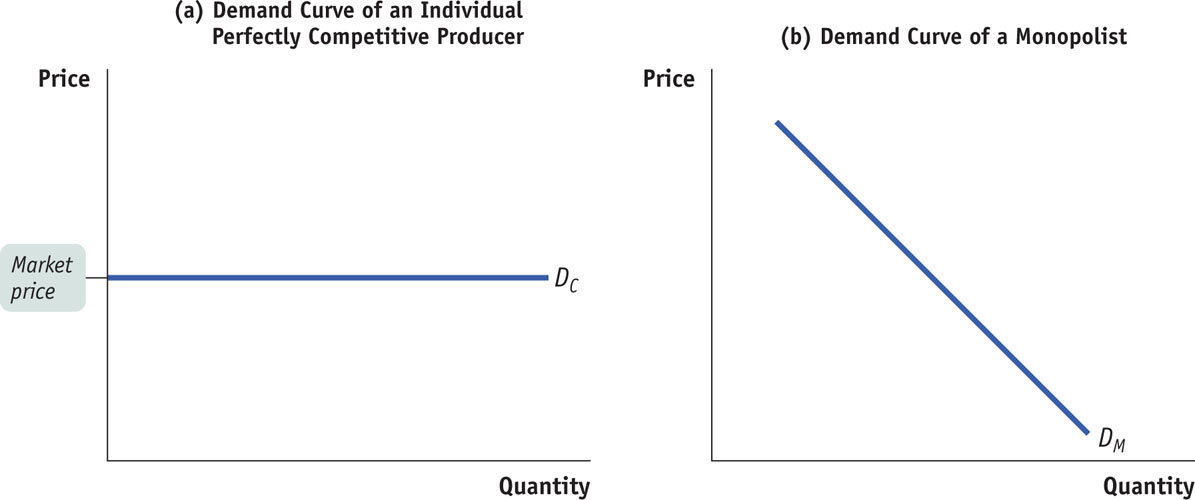
Because an individual perfectly competitive producer cannot affect the market price of the good, it faces a horizontal demand curve DC, as shown in panel (a). A monopolist, on the other hand, can affect the price. Because it is the sole supplier in the industry, its demand curve is the market demand curve DM, as shown in panel (b). To sell more output, it must lower the price; by reducing output, it can raise the price.