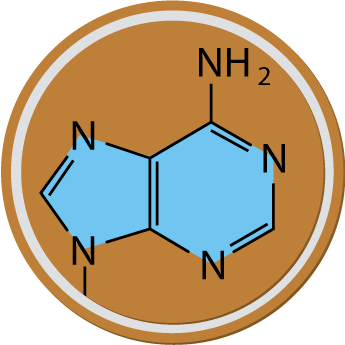
Objective
Build nucleosides and nucleotides from their respective components, and understand the chemical differences between DNA and RNA nucleotides.
Reward
Collect the Nucleotide Structure token and unlock the DNA/RNA Structure simulation marker.

Build nucleosides and nucleotides from their respective components, and understand the chemical differences between DNA and RNA nucleotides.
Collect the Nucleotide Structure token and unlock the DNA/RNA Structure simulation marker.