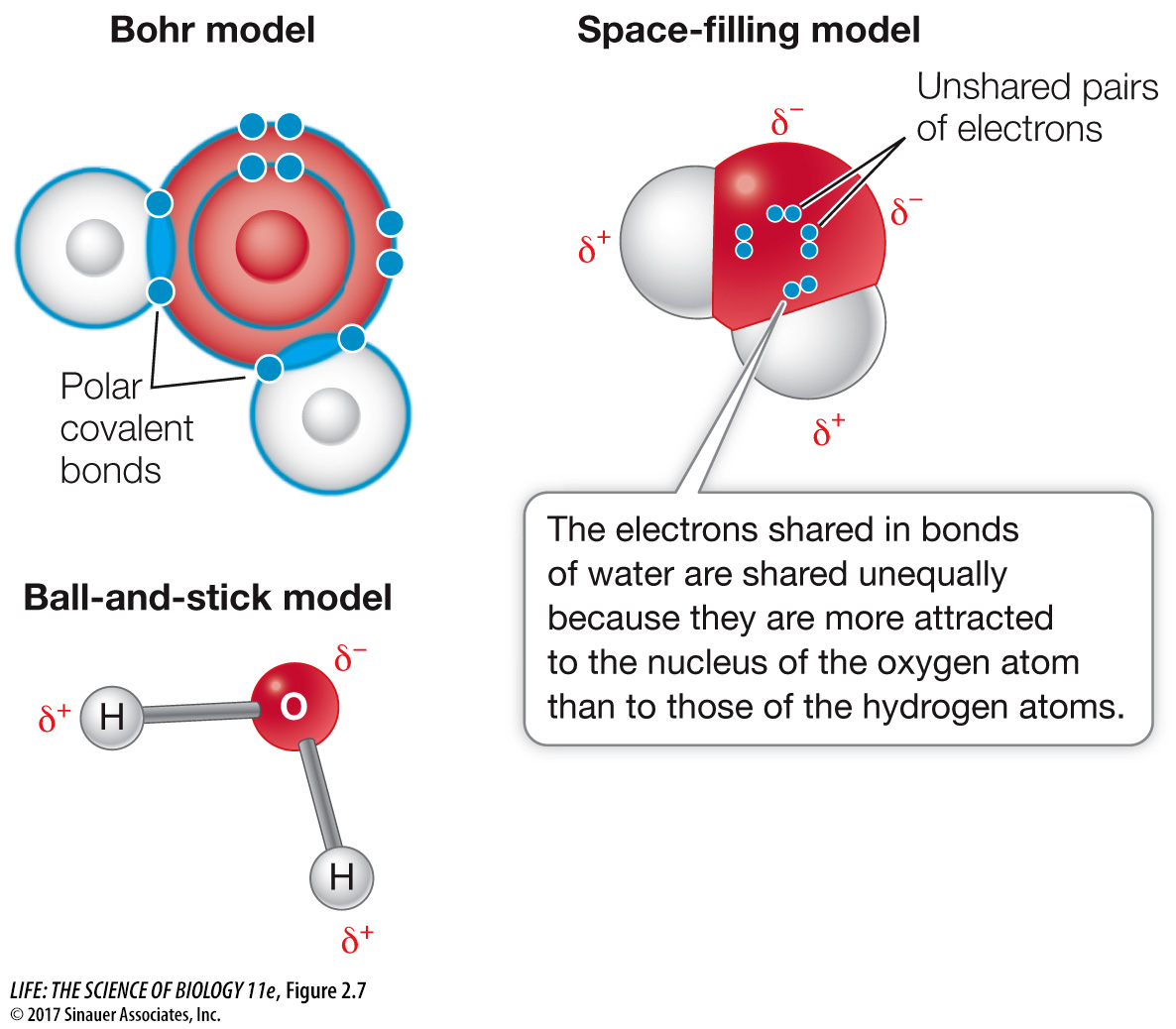
Figure 2.7 Water’s Covalent Bonds Are Polar These three representations all illustrate polar covalent bonding in water (H2O). When atoms with different electronegativities, such as oxygen and hydrogen, form a covalent bond, the electrons are drawn to one nucleus more than to the other. A molecule held together by such a polar covalent bond has partial (δ+ and δ–) charges at different surfaces. In water, the shared electrons are displaced toward the oxygen atom’s nucleus.