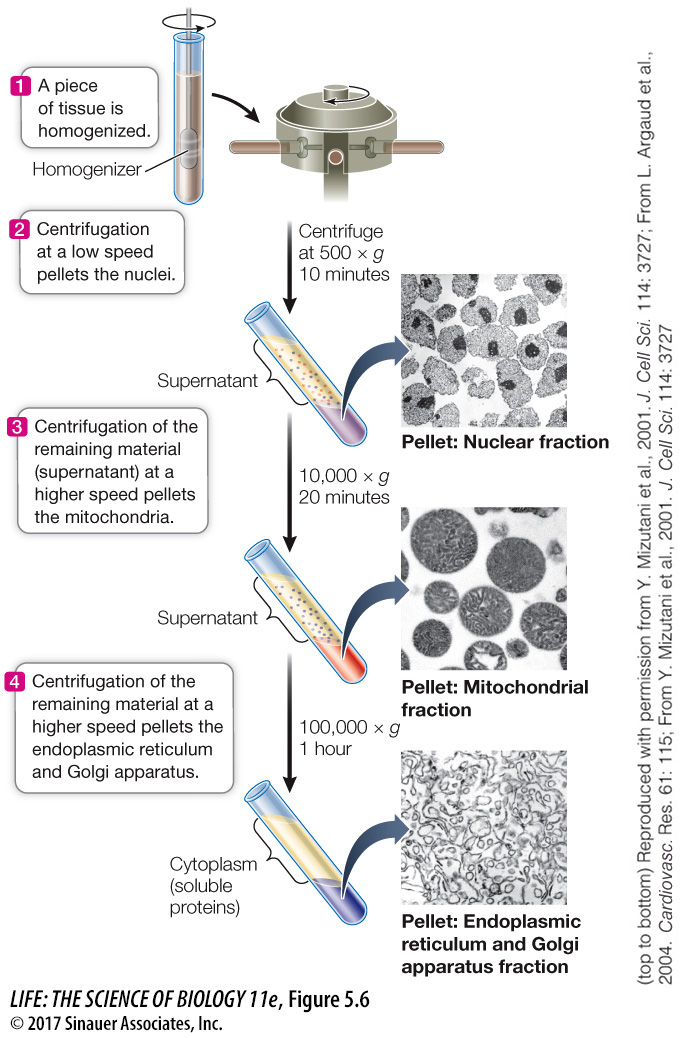
Figure 5.6 Cell Fractionation Organelles can be separated from one another after cells are broken open and their contents suspended in an aqueous medium. The medium is placed in a tube and spun in a centrifuge, which rotates about an axis at high speed. Centrifugal forces (measured in multiples of gravity, × g) cause particles to sediment (form a pellet) at the bottom of the tube, which may be collected for biochemical study. Heavier particles sediment at lower speeds (lower centrifugal forces) than lighter particles. By adjusting the speed of centrifugation, researchers can separate and partially purify cellular organelles and large particles such as ribosomes.