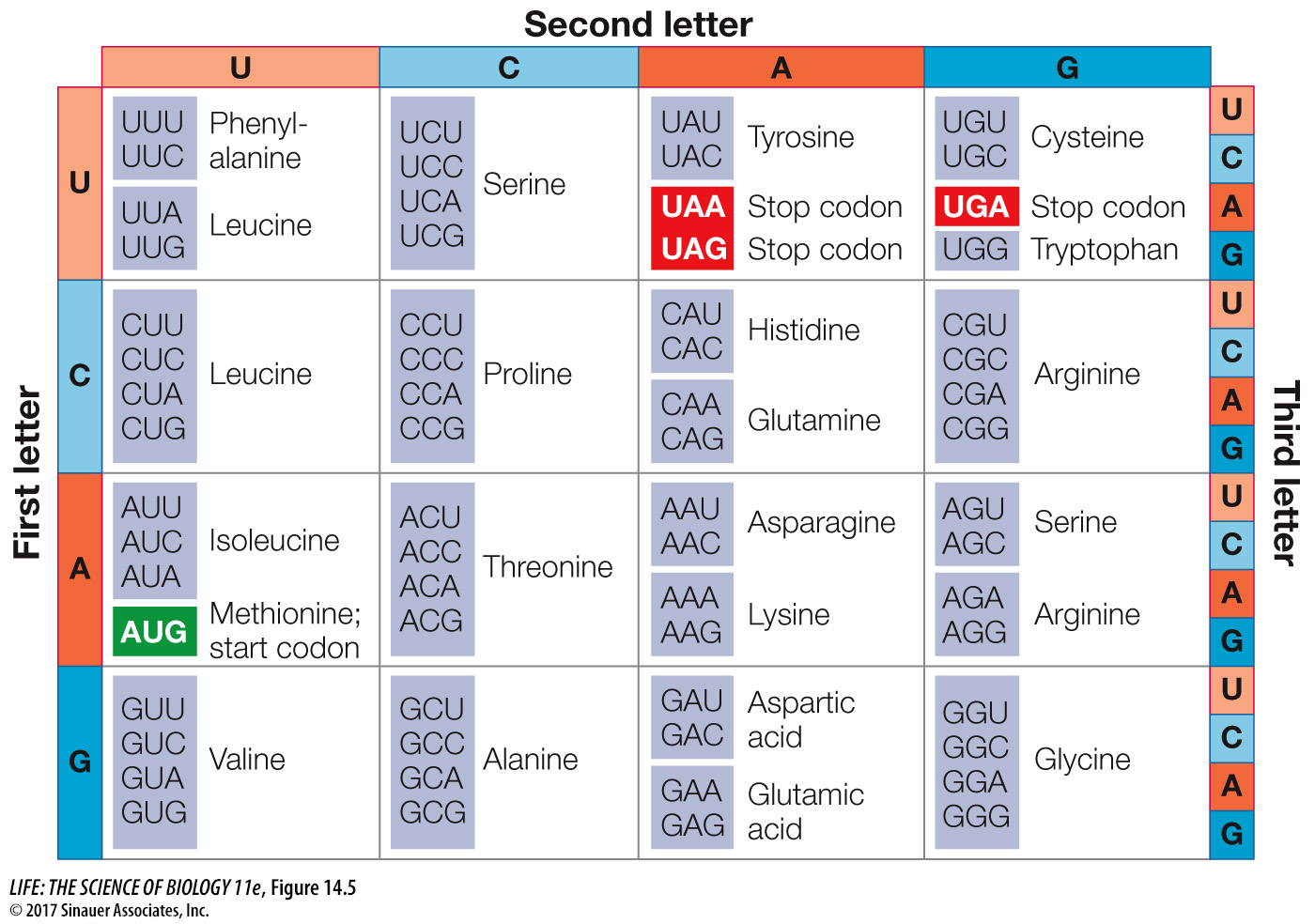
Figure 14.5 The Genetic Code Genetic information is encoded in mRNA in three- letter units— codons— made up of nucleoside monophosphates with the bases uracil (U), cytosine (C), adenine (A), and guanine (G) and is read in a 5′-to- 3′ direction on mRNA. To decode a codon, find its first letter in the left column, then read across the top to its second letter, then read down the right column to its third letter. The amino acid the codon specifies is given in the corresponding row. For example, AUG codes for methionine, and GUA codes for valine.