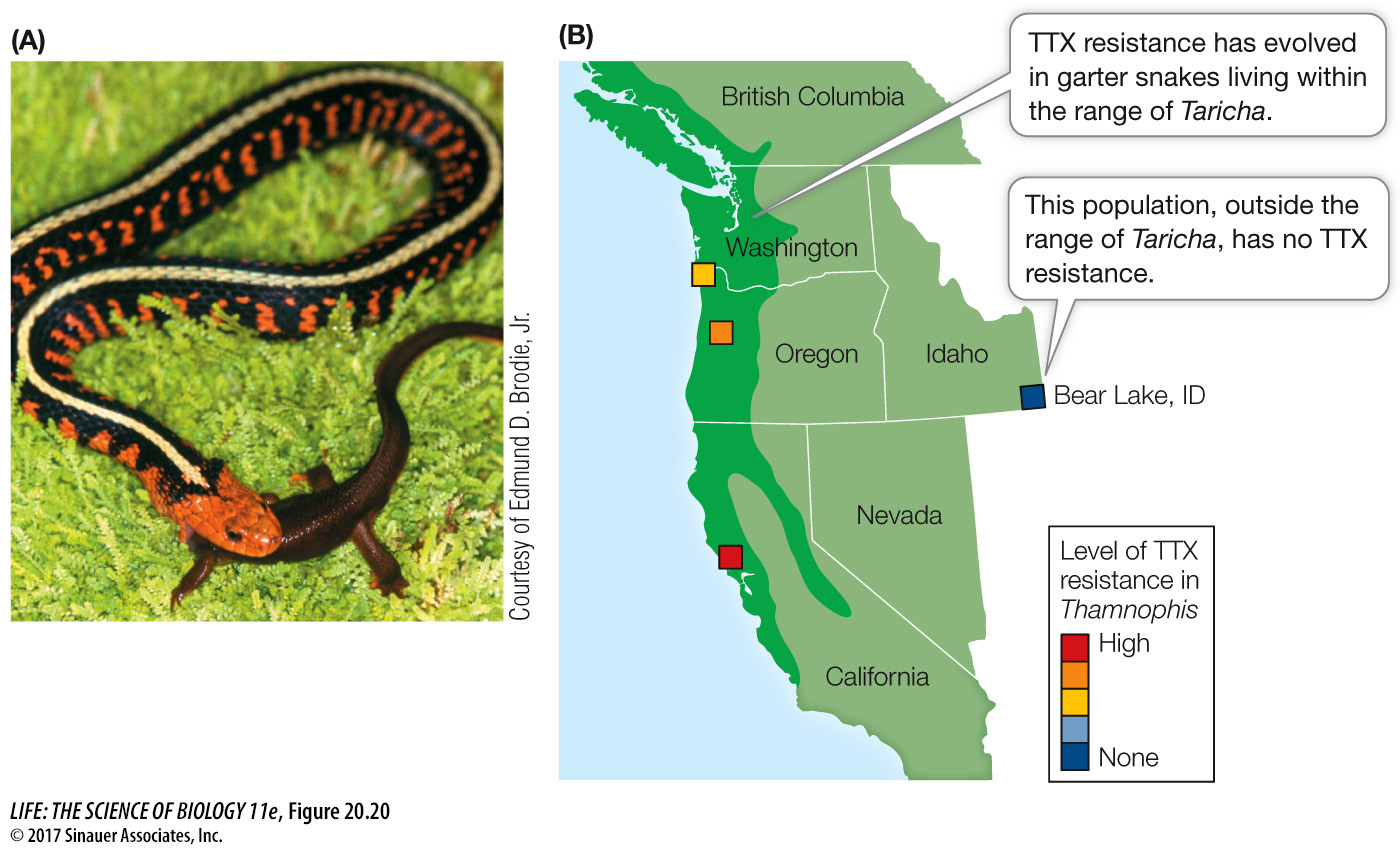
Figure 20.20 Resistance to a Toxin Comes at a Cost (A) Garter snakes (Thamnophis sirtalis) prey on rough- h- X-