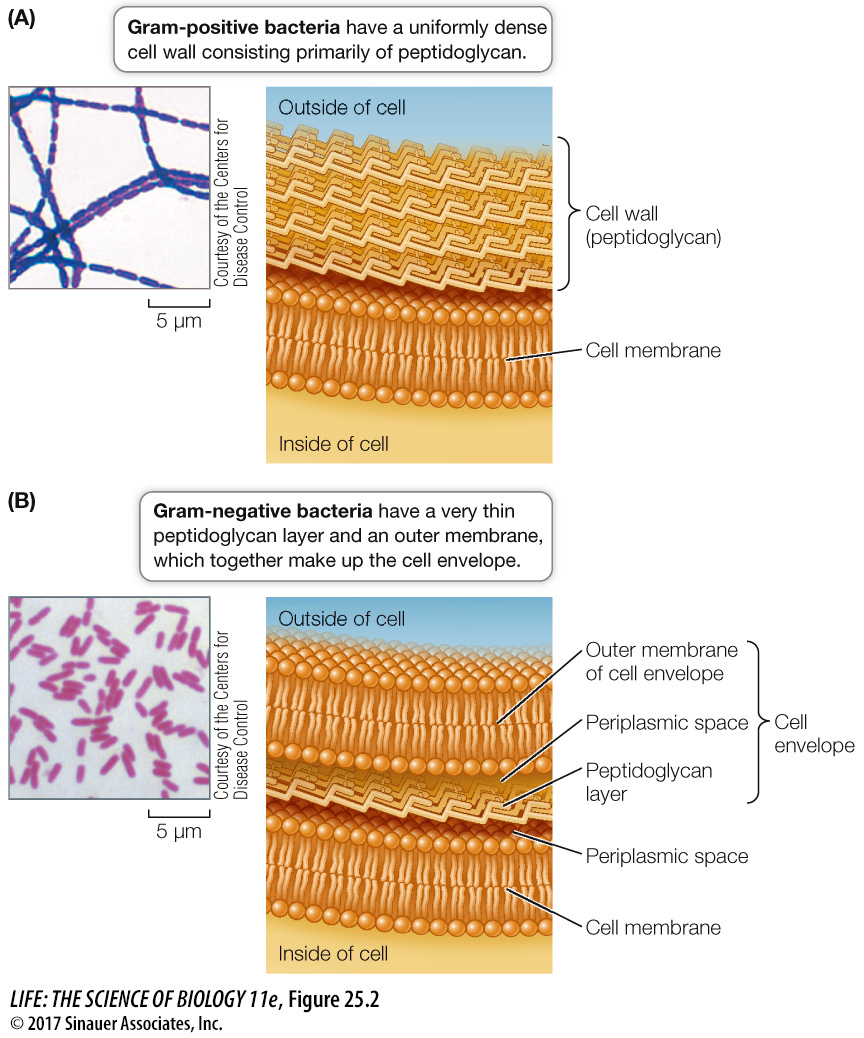
Figure 25.2 The Gram Stain and the Bacterial Cell Wall When treated with Gram- m- m-