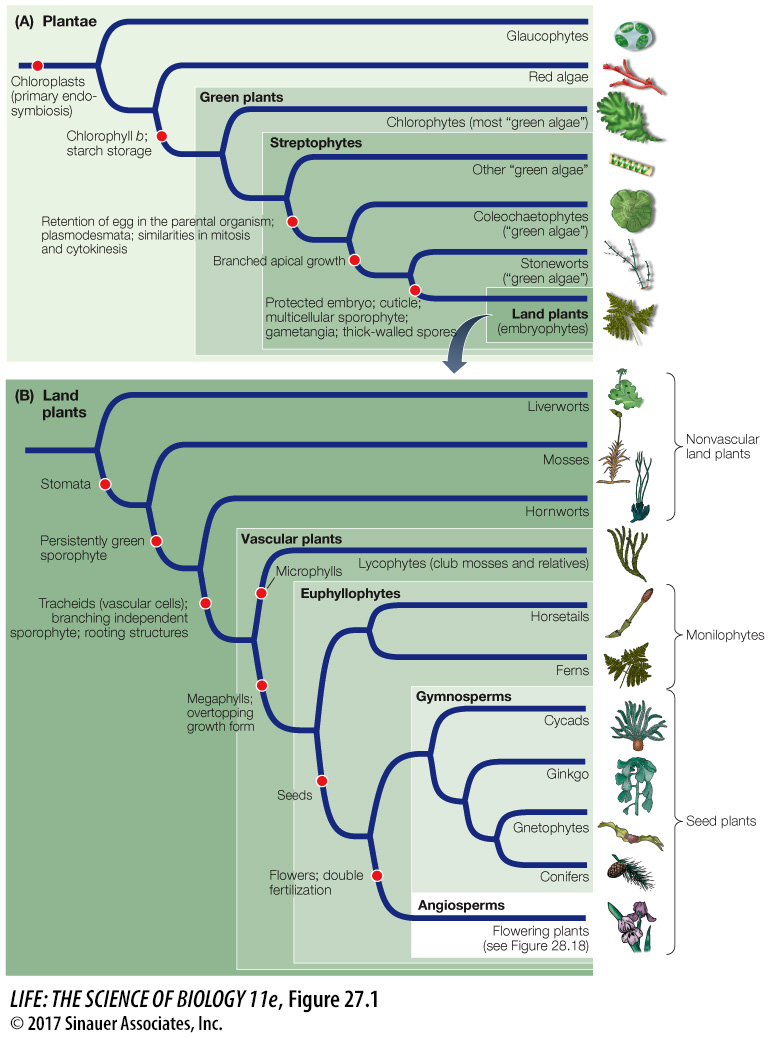
Figure 27.1 The Evolution of Plants In its broadest definition, the term “plant” includes the glaucophytes, red algae, and green plants— s— s—