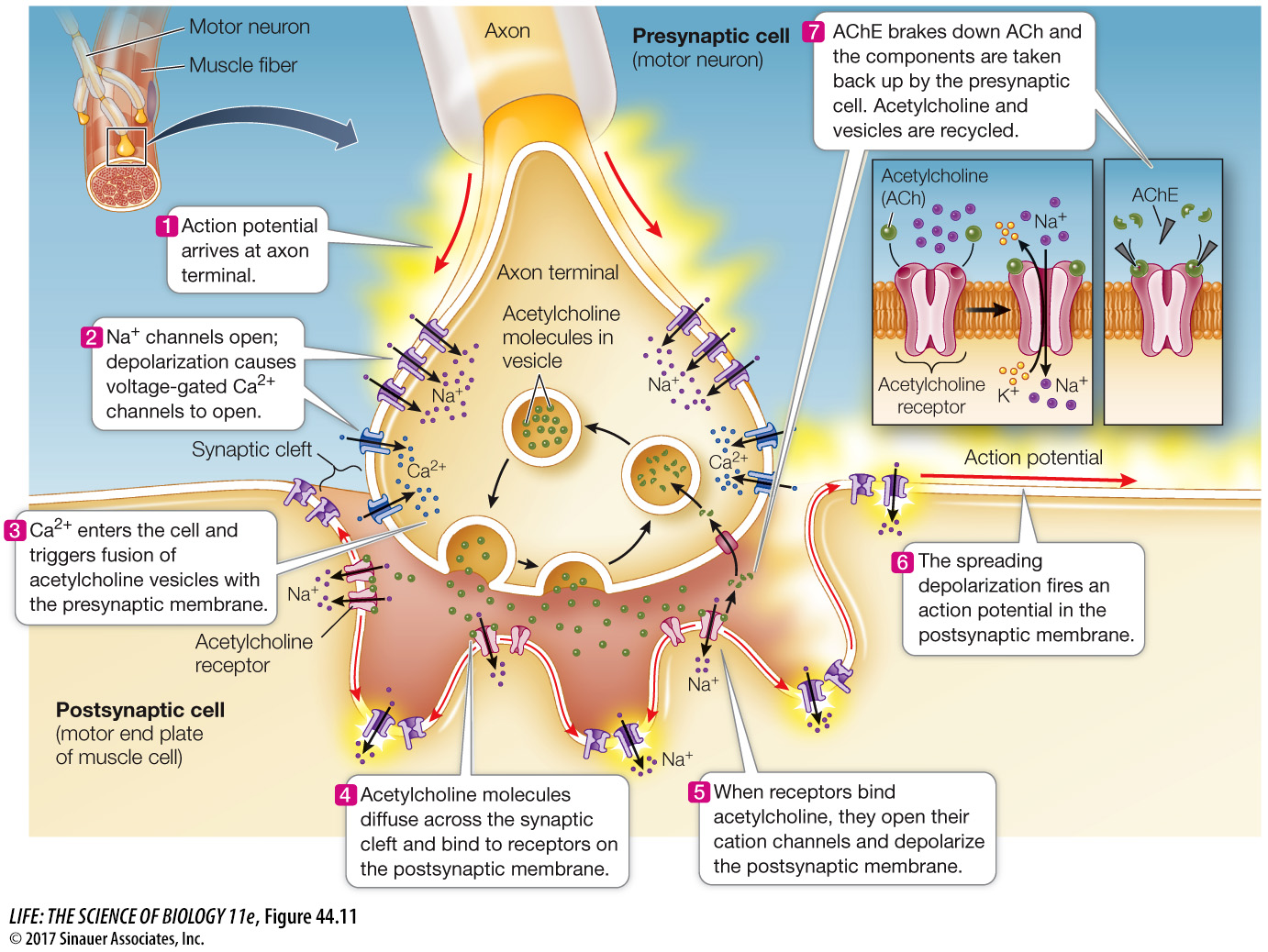
Figure 44.11 Chemical Synaptic Transmission Begins with the Arrival of an Action Potential The neuromuscular junction is a typical chemical synapse. Events shown here are similar for other neurotransmitters at other synapses. Both chemically gated and voltage gated ACh receptors are found in the motor end plate. These are non- selective cation channels, but are more permeable to Na+ than to K+ (inset). When one of the chemically gated receptors binds ACh, its channel pore opens and the net increase in Na+ permeability of the postsynaptic membrane depolarizes it. The depolarization spreads beyond the motor endplate activating voltage gated Na+ channels in the muscle cell membrane, depolarizing it and initiating an action potential. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) breaks down ACh in the synapse, closing the chemically gated channels. The breakdown products (acetate and choline) are taken up by the presynaptic membrane and resynthesized into more ACh.