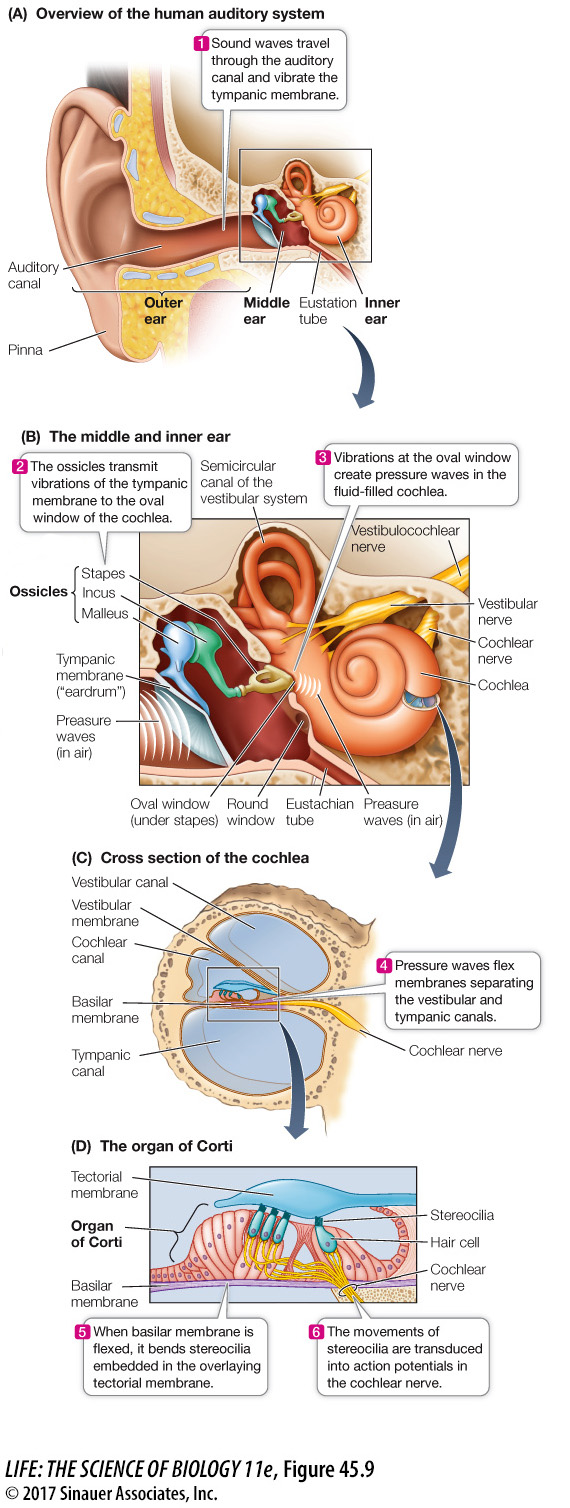
Figure 45.9 Structures of the Human Ear (A) The pinnae direct sound waves down the auditory canal to impinge on the tympanic membrane. The tympanic membrane mechanically transmits these pressure waves into movements of the ossicles in the middle ear. (B) The ossicles transmit their movement into pressure waves in the fluid of the cochlea at the oval window. (C) The cochlea is divided into fluid-