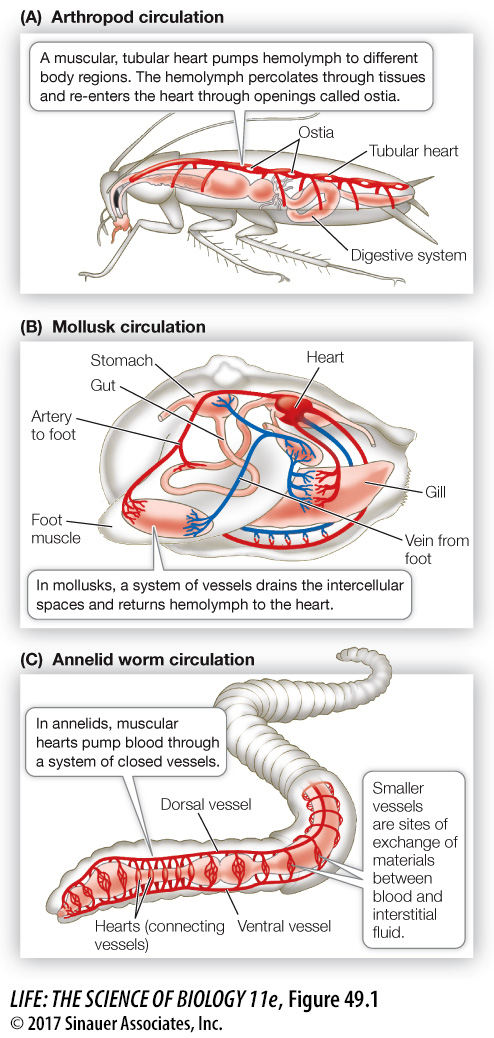
Figure 49.1 Circulatory Systems Arthropods, illustrated here by an insect (A), and mollusks such as clams (B) have an open circulatory system. Hemolymph is pumped by a tubular heart and directed to different regions of the body through vessels that open into intercellular spaces. (C) Annelids such as earthworms have a closed circulatory system, in which the cellular and macromolecular elements of the blood are confined in a system of vessels, and the blood is pumped through those vessels by one or more muscular hearts. Earthworms exchange respiratory gases across their skin. The circulation distributes those gases between the skin and the deeper tissues.