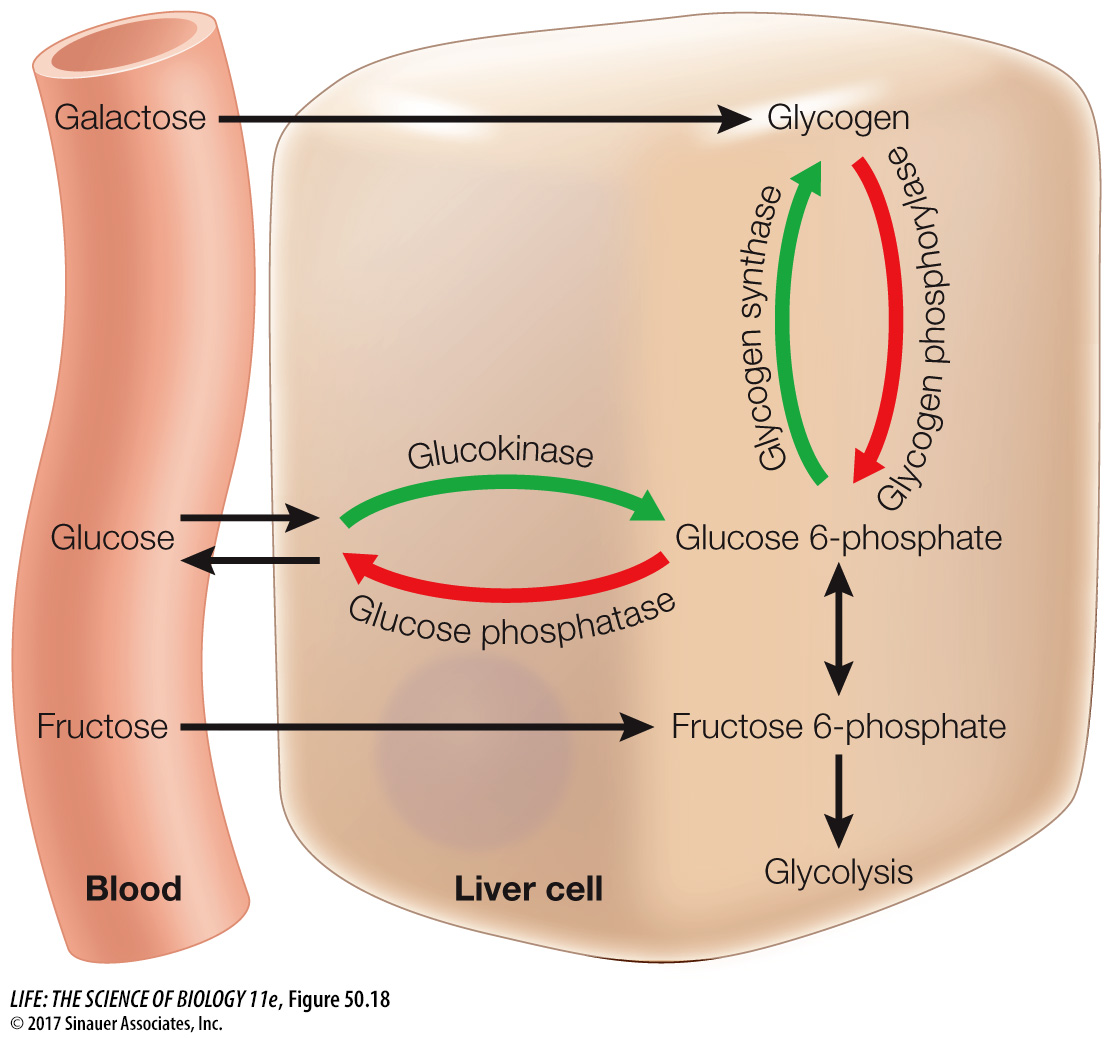
Figure 50.18 Insulin Controls Glucose Traffic in the Liver Glucose freely enters and leaves liver cells by diffusion. But, when insulin is present (green arrows), glucose is phosphorylated and cannot leave the cell. The glucose 6- s— e—