Molecular chaperones help shape proteins
Within a living cell, a polypeptide chain is sometimes in danger of binding the wrong substance. There are two major situations when this can occur:
Just after a protein is made. When a protein has not yet folded completely, it can present a surface that binds the wrong molecule.
Following denaturation. Certain conditions, such as moderate heat, can cause some proteins in a living cell to denature without killing the organism. Before the protein can refold, it may present a surface that binds the wrong molecule. In these cases, the inappropriate binding may be irreversible.
Many cells have a special class of proteins, called chaperones, that protect the three-
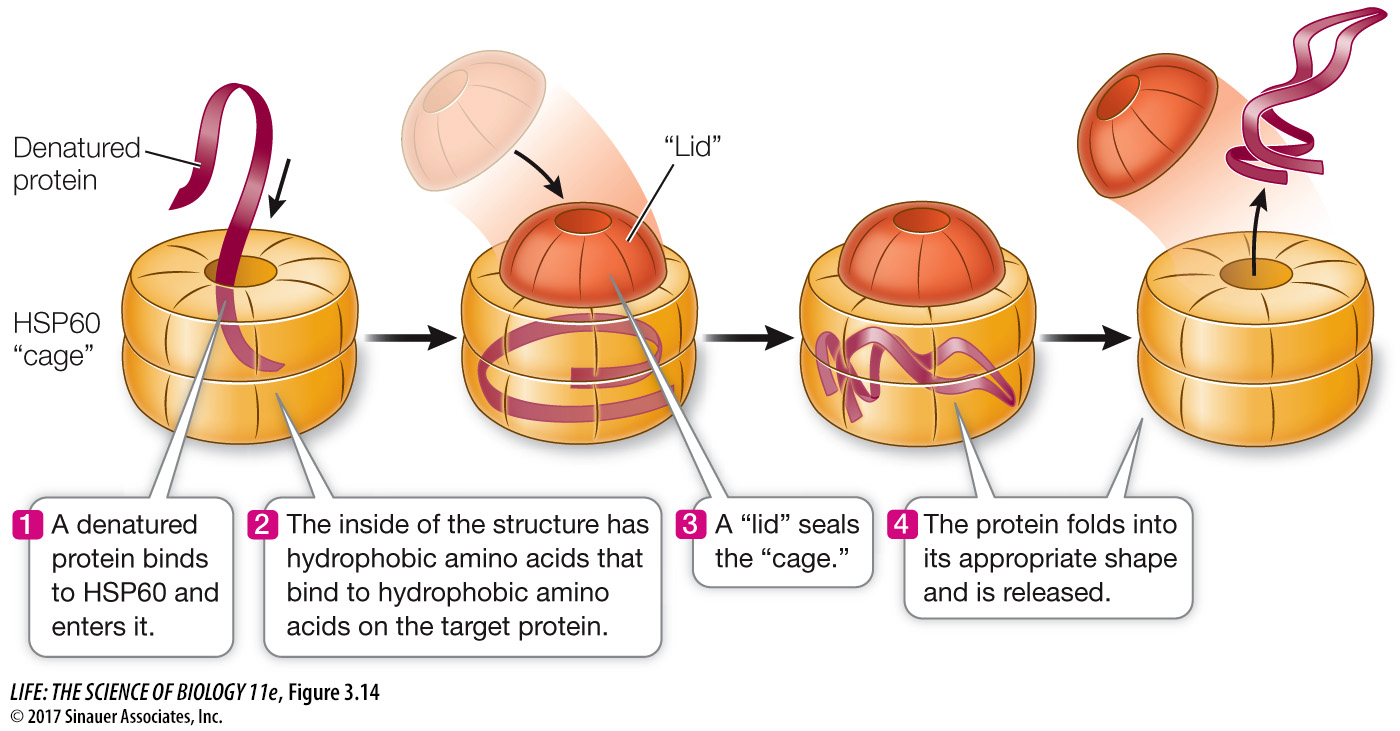
Q: Why are heat shock proteins important for a cell?
Heat shock proteins protect cellular proteins from being denatured and possibly broken down. This can occur not only when proteins are exposed to heat, but in any chemical situation where their structure is altered (e.g., a change in pH).