key concept
8.1
Physical Principles Underlie Biological Energy Transformations
key concept
8.1
Physical Principles Underlie Biological Energy Transformations
A chemical reaction occurs when atoms have sufficient energy to combine or change their bonding partners. Consider the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose to its component monomers, glucose and fructose (see p. 56 for the chemical structures of these sugars). We can express this reaction by a chemical equation:
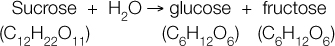
In this equation, sucrose and water are the reactants, and glucose and fructose are the products. During the reaction, some of the bonds in sucrose and water are broken and new bonds are formed, resulting in products with chemical properties that are very different from those of the reactants. The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a biological system at a given time is called metabolism. Metabolic reactions involve energy changes; for example, the energy contained in the chemical bonds of sucrose (reactants) is greater than the energy in the bonds of the two products, glucose and fructose.
focus your learning
The second law of thermodynamics states that disorder is constantly increasing in the universe.
Chemical reactions in biological systems are either exergonic or endergonic.
Physicists define energy as the capacity to do work, which occurs when a force operates on an object over a distance. In biochemistry, it is more useful to think of energy as the capacity for change. In biochemical reactions, energy changes are usually associated with changes in the chemical compositions and properties of molecules.